Raisecom
ISCOM2600G-HI (A) Series Configuration Guide
Raisecom Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd.
Traffic statistics is not a QoS control measure, but can be used in combination with other QoS
actions to improve network supervision.
7.1.5 Priority mapping
Priority mapping refers to sending packets to different queues with different local priorities
according to pre-configured mapping from external priority to local priority. Therefore,
packets in different queues can be scheduled on the egress interface.
The ISCOM2600G-HI series switch supports performing priority mapping based on DSCP of
IP packets or CoS of VLAN packets. The Traffic-Class field of IPv6 packets corresponds to
DSCP of IPv4 packets. The mapping from DSCP to local priority is applicable to IPv6 packets.
Take the first 6 bits of the Traffic-Class field for use.
By default, the mapping from the DSCP or CoS to local priority of the ISCOM2600G-HI
series switch is listed in Table 7-1 and Table 7-2.
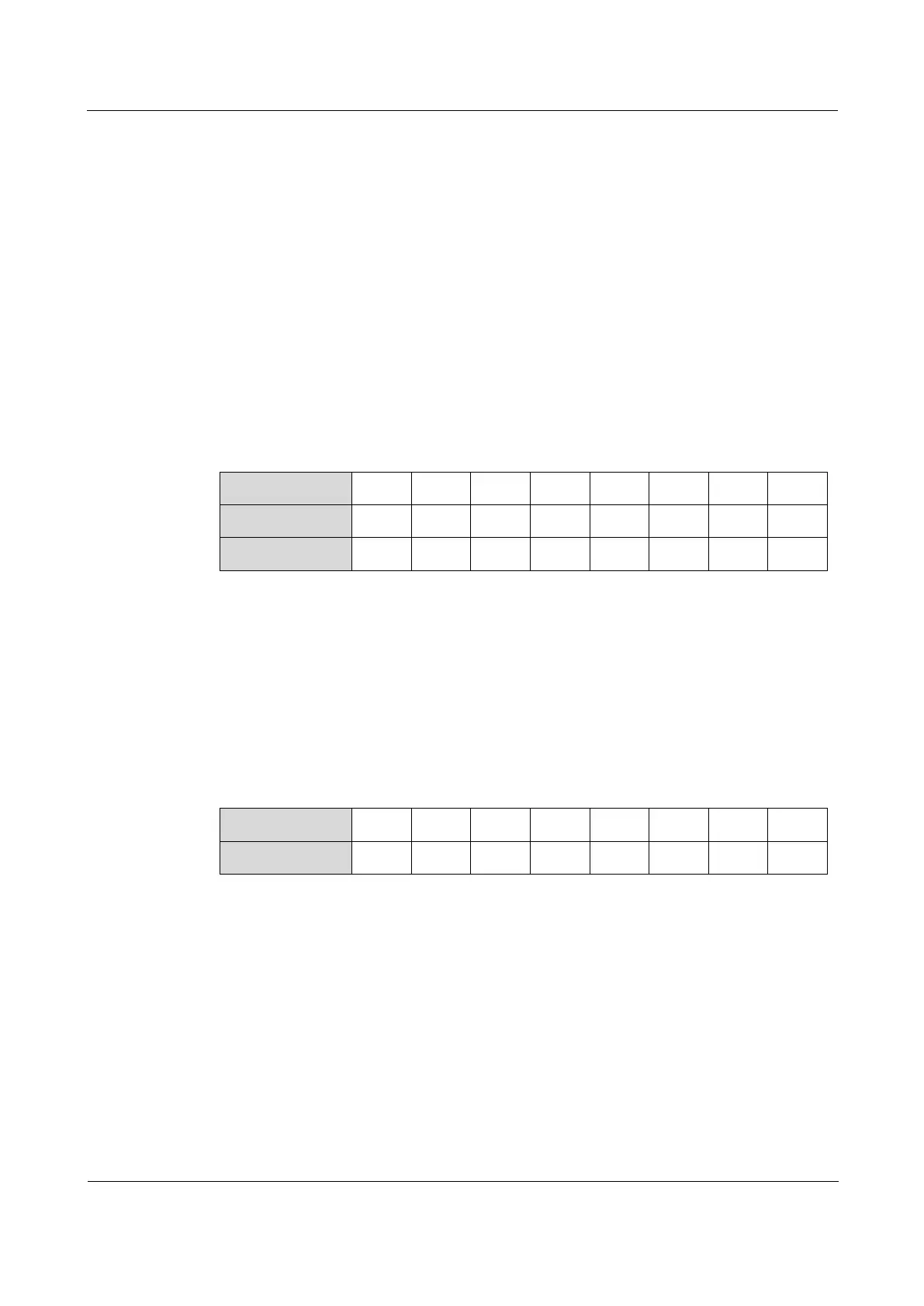
Table 7-1 Mapping from DSCP or CoS to local priority
Local priority refers to a kind of packet priority with internal meaning assigned by the
ISCOM2600G-HI series switch and is the priority corresponding to queue in QoS queue
scheduling.
Local priority ranges from 0 to 7. Each interface of the ISCOM2600G-HI series switch
supports 8 queues. Local priority and interface queue are in one-to-one mapping. The packet
can be sent to the assigned queue according to the mapping between local priority and queue,
as shown in Table 7-2.
Table 7-2 Mapping between local priority and queue
7.1.6 Queue scheduling
The ISCOM2600G-HI series switch needs to perform queue scheduling when delay-sensitive
services need better QoS services than non-delay-sensitive services and when the network is
congested once in a while.
Queue scheduling adopts different scheduling algorithms to send packets in a queue.
Scheduling algorithms supported by the ISCOM2600G-HI series switch include Strict-
Priority (SP), Weight Round Robin (WRR), Deficit Round Robin (DRR), SP+WRR, and
SP+DRR. All scheduling algorithms are designed for addressing specified traffic problems.
And they have different effects on bandwidth distribution, delay, and jitter.

 Loading...
Loading...










