4 E-mail Function
28-38 WindO/I-NV4 User’s Manual
4.1 What Can Be Done with the E-mail Function
The E-mail function enables sending e-mail from the MICRO/I to smartphone, mobile device, computer, etc when a
specified trigger condition is satisfied. The host name of the outgoing mail server (SMTP) can also be specified.
4.2 System Composition
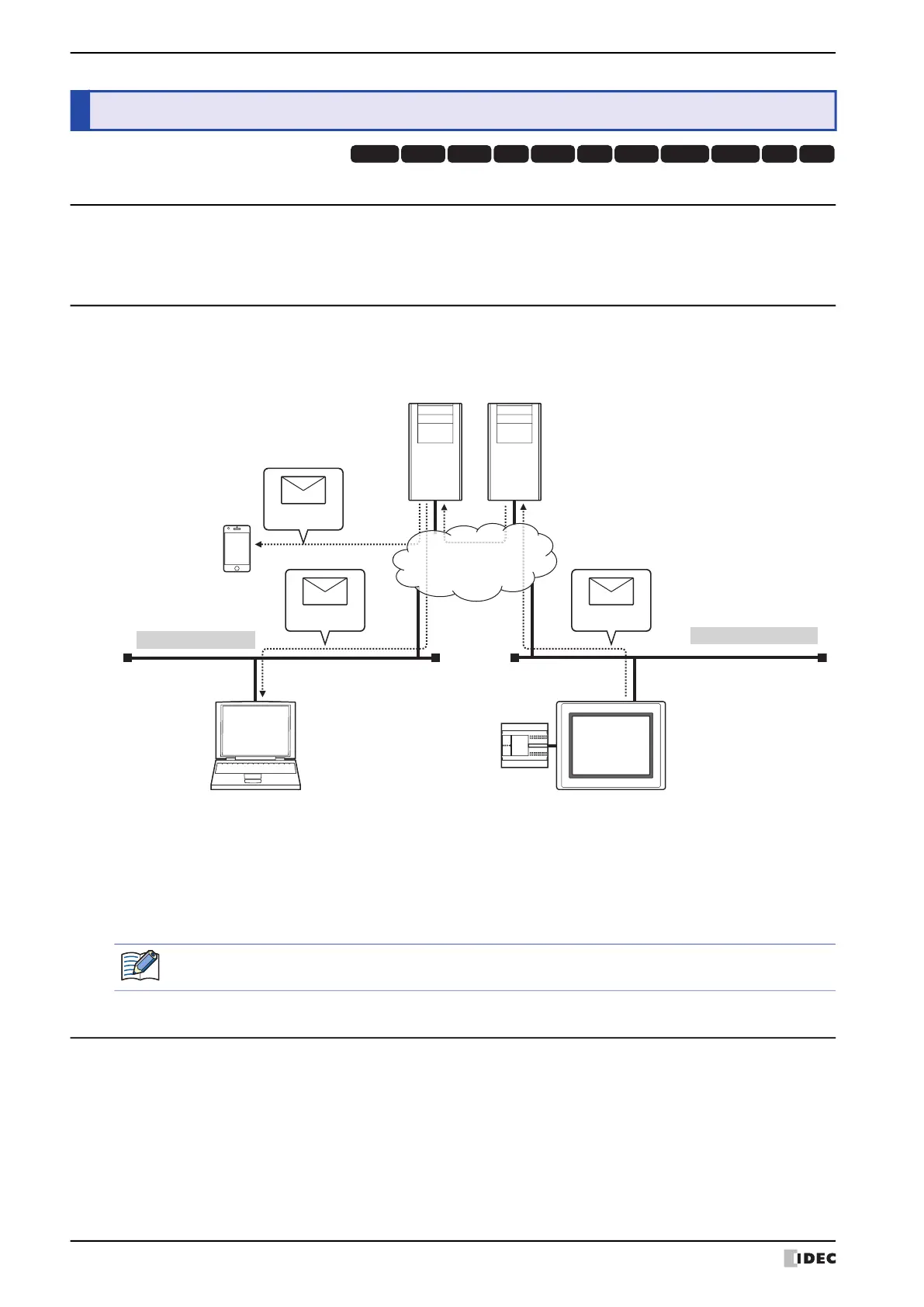
An example system configuration for using the E-mail function is shown below.
Configure the MICRO/I Ethernet settings (IP address, subnet mask, default gateway) and connect to a local network.
Configure the MICRO/I with the outgoing mail server (SMTP).
4.3 Supported Protocols and Authentication methods
• Protocols defined by RFC2821 and RFC2822
• LOGIN for the SMTP Authentication
• SMTPs (SSL communications)
4 E-mail Function
HG3G
HG2G-5FHG5G-V HG4G-V HG3G-V HG2G-V HG2G-5T
HG4G HG1G HG1P
HG2J-7U
(1) When the trigger condition for the E-mail function is satisfied, MICRO/I connected to the local network sends the
e-mail to the outgoing mail server (SMTP).
(2) The outgoing mail server (SMTP) sends the e-mail received from MICRO/I to the incoming mail server of the
destination address.
(3) The e-mail is received by a smartphone, mobile device and computer etc.
Outgoing mail server
(SMTP)
Incoming Mail Server
Local Network
Ethernet Communication (TCP/IP)
Remote Network
(1)
(3) (2)
Computer
Smartphone,
Mobile device
Send
Receive
Receive
External device
MICRO/I
E-mail
E-mail
E-mail
External Network
For the outgoing mail server (SMTP) and the local network settings, contact the administrator of the
network which the MICRO/I is connected to.

 Loading...
Loading...