General-purpose timers (TIM2 to TIM5) RM0402
540/1163 RM0402 Rev 6
17.4.17 TIMx DMA control register (TIMx_DCR)
Address offset: 0x48
Reset value: 0x0000
17.4.18 TIMx DMA address for full transfer (TIMx_DMAR)
Address offset: 0x4C
Reset value: 0x0000
Example of how to use the DMA burst feature
In this example the timer DMA burst feature is used to update the contents of the CCRx
registers (x = 2, 3, 4) with the DMA transferring half words into the CCRx registers.
This is done in the following steps:
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Res. Res. Res. DBL[4:0] Res. Res. Res. DBA[4:0]
rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw
Bits 15:13 Reserved, must be kept at reset value.
Bits 12:8 DBL[4:0]: DMA burst length
This 5-bit vector defines the number of DMA transfers (the timer recognizes a burst transfer
when a read or a write access is done to the TIMx_DMAR address).
00000: 1 transfer,
00001: 2 transfers,
00010: 3 transfers,
...
10001: 18 transfers.
Bits 7:5 Reserved, must be kept at reset value.
Bits 4:0 DBA[4:0]: DMA base address
This 5-bit vector defines the base-address for DMA transfers (when read/write access are
done through the TIMx_DMAR address). DBA is defined as an offset starting from the
address of the TIMx_CR1 register.
Example:
00000: TIMx_CR1,
00001: TIMx_CR2,
00010: TIMx_SMCR,
...
Example: Let us consider the following transfer: DBL = 7 transfers & DBA = TIMx_CR1. In this
case the transfer is done to/from 7 registers starting from the TIMx_CR1 address.
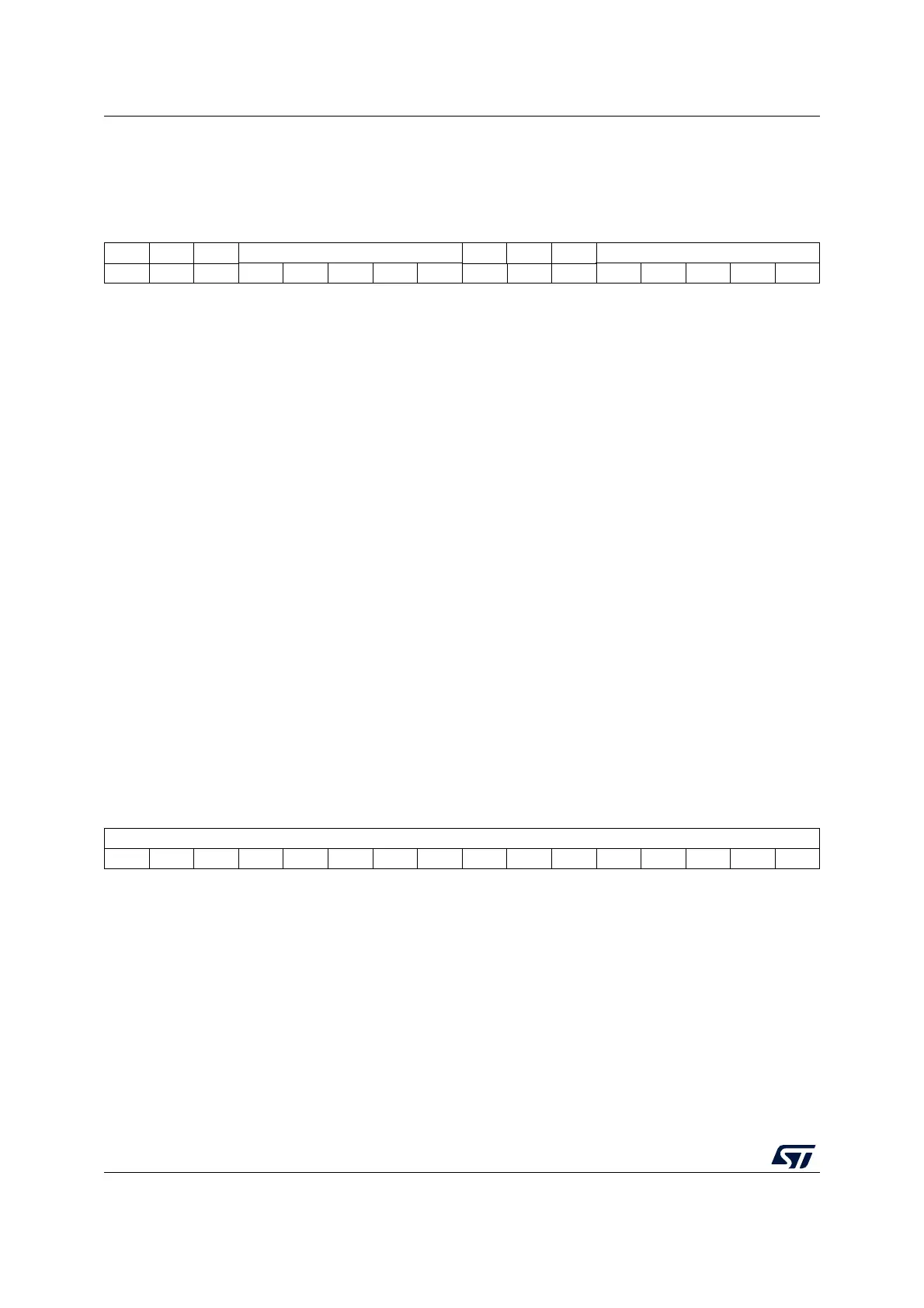
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
DMAB[15:0]
rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw
Bits 15:0 DMAB[15:0]: DMA register for burst accesses
A read or write operation to the DMAR register accesses the register located at the address
(TIMx_CR1 address) + (DBA + DMA index) x 4
where TIMx_CR1 address is the address of the control register 1, DBA is the DMA base
address configured in TIMx_DCR register, DMA index is automatically controlled by the
DMA transfer, and ranges from 0 to DBL (DBL configured in TIMx_DCR).

 Loading...
Loading...











