RM0402 Rev 6 667/1163
RM0402 Fast-mode Plus Inter-integrated circuit (FMPI2C) interface
722
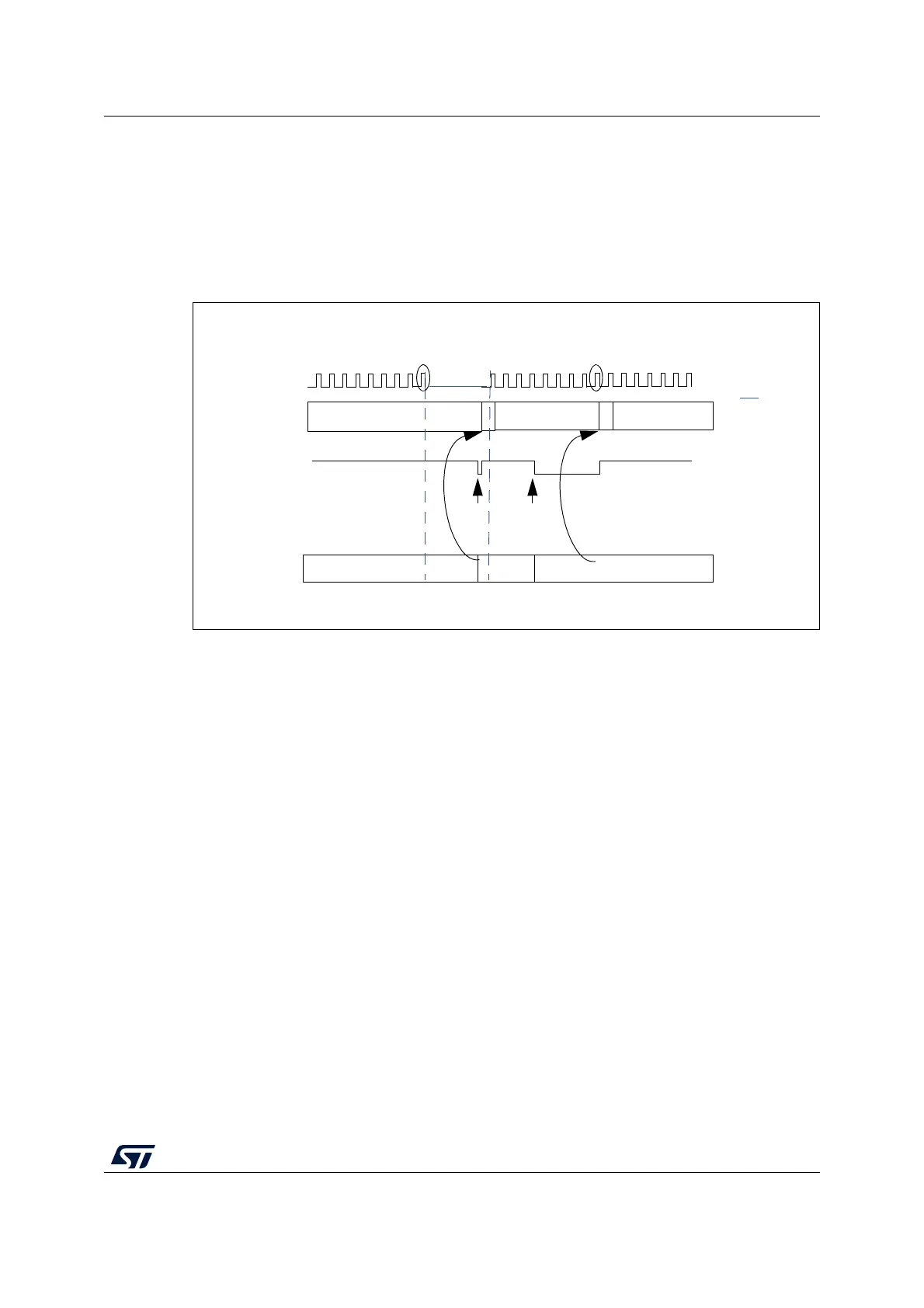
Transmission
If the FMPI2C_TXDR register is not empty (TXE=0), its content is copied into the shift
register after the 9th SCL pulse (the Acknowledge pulse). Then the shift register content is
shifted out on SDA line. If TXE=1, meaning that no data is written yet in FMPI2C_TXDR,
SCL line is stretched low until FMPI2C_TXDR is written. The stretch is done after the 9th
SCL pulse.
Figure 213. Data transmission
Hardware transfer management
The FMPI2C has a byte counter embedded in hardware in order to manage byte transfer
and to close the communication in various modes such as:
– NACK, STOP and ReSTART generation in master mode
– ACK control in slave receiver mode
– PEC generation/checking when SMBus feature is supported
The byte counter is always used in master mode. By default it is disabled in slave mode, but
it can be enabled by software by setting the SBC (Slave Byte Control) bit in the
FMPI2C_CR2 register.
The number of bytes to be transferred is programmed in the NBYTES[7:0] bit field in the
FMPI2C_CR2 register. If the number of bytes to be transferred (NBYTES) is greater than
255, or if a receiver wants to control the acknowledge value of a received data byte, the
reload mode must be selected by setting the RELOAD bit in the FMPI2C_CR2 register. In
this mode, the TCR flag is set when the number of bytes programmed in NBYTES is
transferred, and an interrupt is generated if TCIE is set. SCL is stretched as long as TCR
flag is set. TCR is cleared by software when NBYTES is written to a non-zero value.
When the NBYTES counter is reloaded with the last number of bytes, RELOAD bit must be
cleared.
MSv35977V1
xx
Shift register
data1
data1
xx
data2
TXE
ACK pulse
data0 data2
ACK pulse
xx
FMPI2C_TXDR
wr data1
wr data2
SCL
legend:
SCL
stretch
 Loading...
Loading...











