Measurement modes 201
imc CANSAS Users Manual - Doc. Version 1.9 - 05.12.2014© 2014 imc Meßsysteme GmbH
5.1.3.2.2 Distance
Distance (differential)
Path traveled within one sampling interval. For this purpose, the number of pulses per meter must be
entered.
Distance (absolute)
Absolute distance. The differential distance measurement is converted to the absolute distance. By
taking the zero impulse (the counter with no zero impulse should not be selected) into account, the
absolute distance position is determined and indicated. Otherwise, the distance value is assumed to
be 0° when the measurement begins.
5.1.3.2.3 Angle
Angle (differential)
Angle traveled within one sampling interval. For this purpose, the number of pulses per revolution
must be entered. The absolute angle can be calculated in imc Online FAMOS or determined by the
mode Angle(abs).
Angle (absolute)
Absolute angle. The differential angle measurement is converted to the absolute angle. By taking the
zero impulse (the counter with no zero impulse should not be selected) into account, the absolute
angle position is determined and indicated. Otherwise, the angle value is assumed to be 0° when the
measurement begins.
5.1.3.3 Mode (Time measurement)
5.1.3.3.1 Time measurement
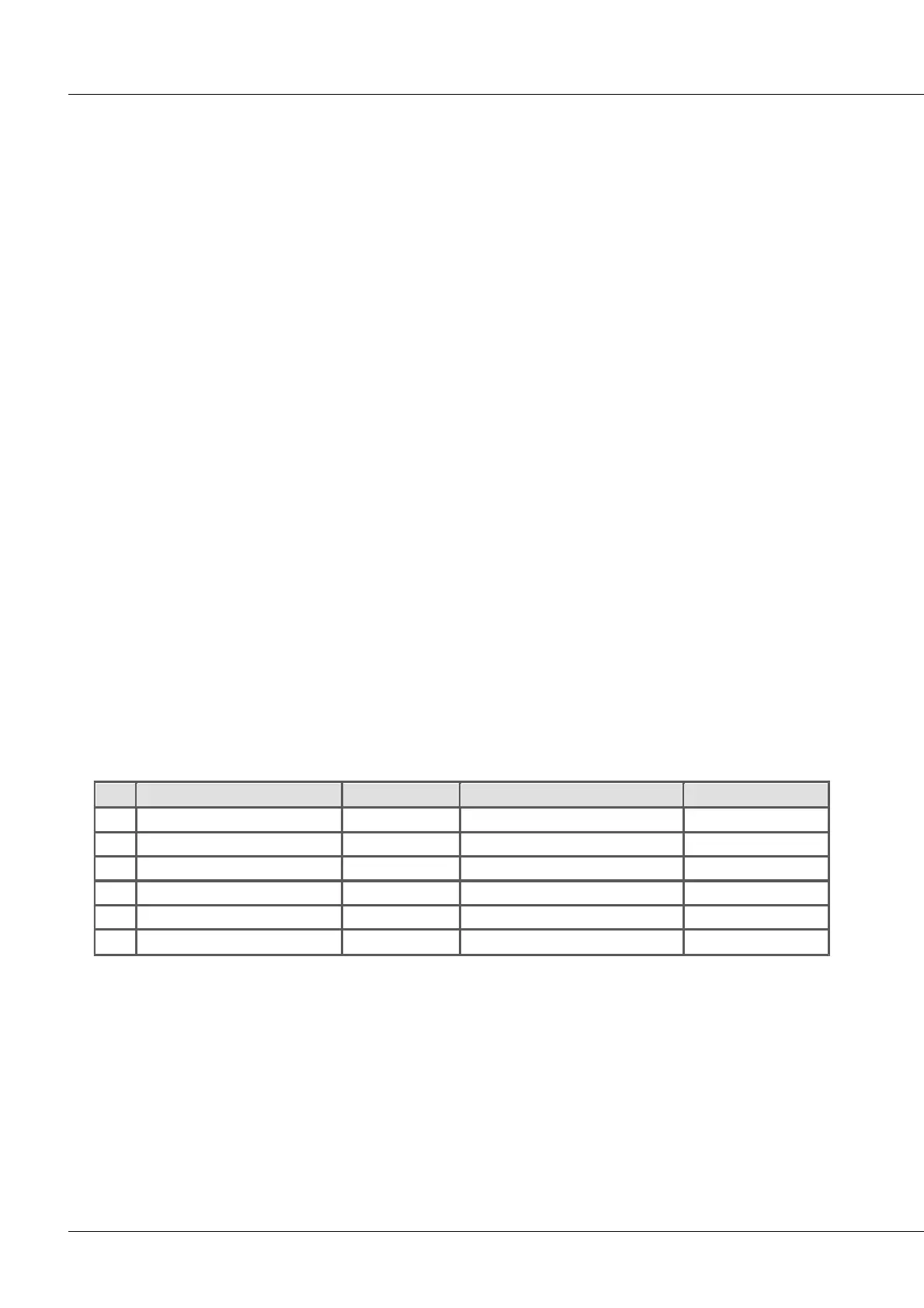
The time measurement mode allows the definition of edge conditions between which the time interval is
to be measured.
The following combinations are possible:
To ensure a high time resolution for the measurement results, suitable scaling must be set for the
measurement. An input range specifies the maximum time interval which can be measured between the
selected starting and stopping edge. The time between the signal edges may not be greater than the
selected input range. If the maximum time interval is exceeded during measurement, the system returns
the input value range end instead of the true measured value.
 Loading...
Loading...