4.61
Date Code 20170927 Instruction Manual SEL-751 Relay
Protection and Logic Functions
Group Settings (SET Command)
50GFP—Forward Directional Residual Ground Current Pickup
50GRP—Reverse Directional Residual Ground Current Pickup
If setting ORDER does not contain V or I (no zero-sequence voltage-polarized
or channel IN current-polarized directional elements are enabled), then set-
tings 50GFP and 50GRP are not made or displayed.
The 50GFP setting (3I0 current value) is the pickup for the forward fault
detector 50GF of the zero-sequence voltage-polarized and channel IN current-
polarized directional elements (see Figure 4.24). Ideally, this setting is above
normal load unbalance and below the lowest expected zero-sequence current
magnitude for unbalanced forward faults.
The 50GRP setting (3I0 current value) is the pickup for the reverse fault detec-
tor 50GR of the zero-sequence voltage-polarized and channel IN current-
polarized directional elements (see Figure 4.24). Ideally, this setting is above
normal load unbalance and below the lowest expected zero-sequence current
magnitude for unbalanced reverse faults.
See Petersen Coil Considerations for Setting ORDER on page 4.58 for more
information on setting 50GFP and 50GRP for a Petersen coil-grounded sys-
tem.
50GFP and 50GRP Set Automatically. If enable setting EDIR := AUTO,
settings 50GFP and 50GRP are set automatically at:
50GFP = 0.50 A secondary (5 A nominal phase current inputs, IA, IB, IC)
50GRP = 0.25 A secondary (5 A nominal phase current inputs, IA, IB, IC)
50GFP = 0.10 A secondary (1 A nominal phase current inputs, IA, IB, IC)
50GRP = 0.05 A secondary (1 A nominal phase current inputs, IA, IB, IC)
Operation of the Channel IN Current-Polarized Directional Element
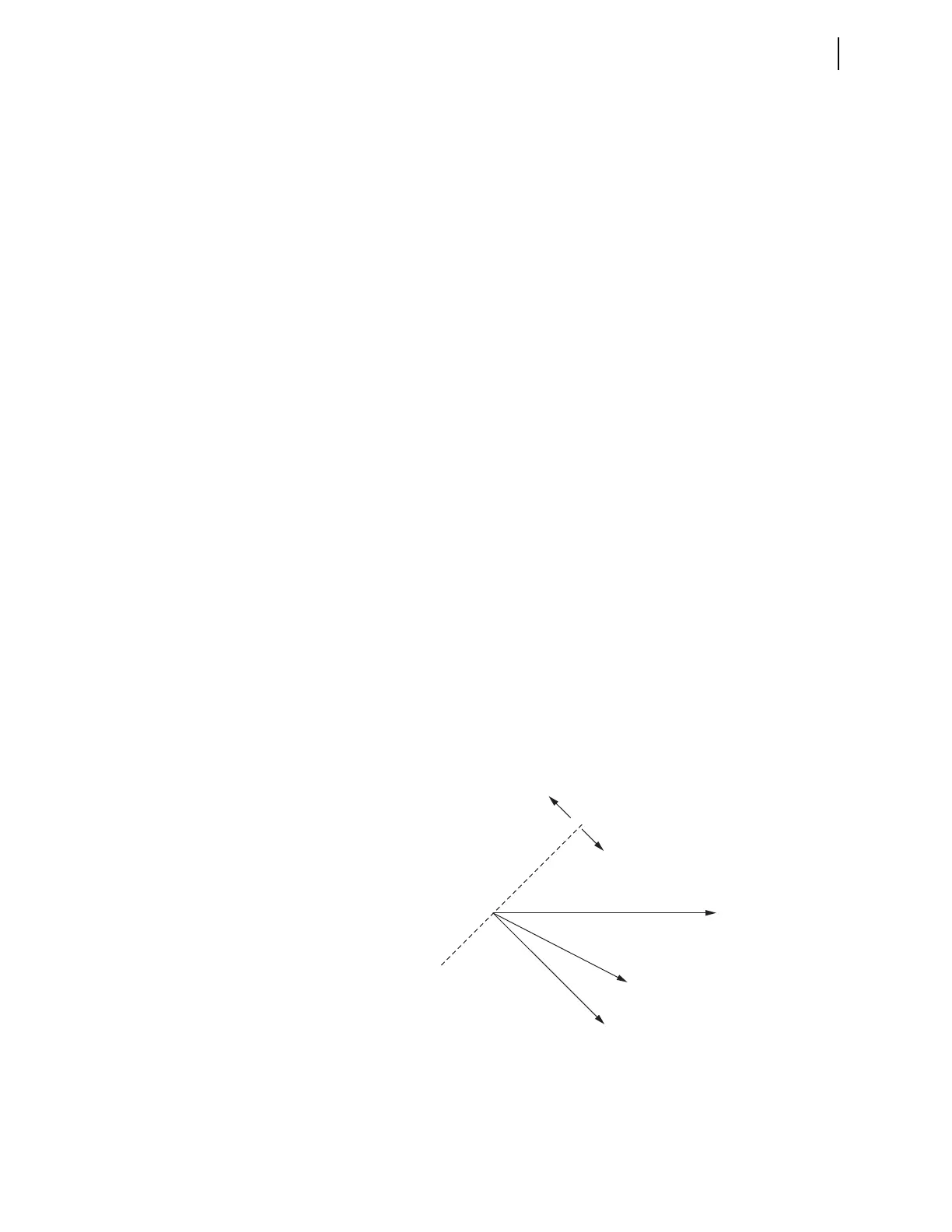
Figure 4.28 shows the logic for the current polarized directional element for
ground faults. Traditional elements of this type use the directional characteris-
tics shown in Figure 4.42, where the maximum torque line of the element is in
phase with the polarizing current, I
N
. This is adequate for solidly-grounded
and most low-impedance grounded systems.
Figure 4.42 Traditional Channel IN Current-Polarized Directional Element
V
A
I
N
Reverse
Forward
I
G
Maximum
Torque
Line

 Loading...
Loading...