4.48
SEL-751 Relay Instruction Manual Date Code 20170927
Protection and Logic Functions
Group Settings (SET Command)
q Figure 4.23; w Figure 4.37; e Figure 4.38; r Figure 4.39; t Figure 4.40; y Figure 4.41; u Figure 4.7;
i Figure 4.2; o Figure 4.6; a Figure 4.2.
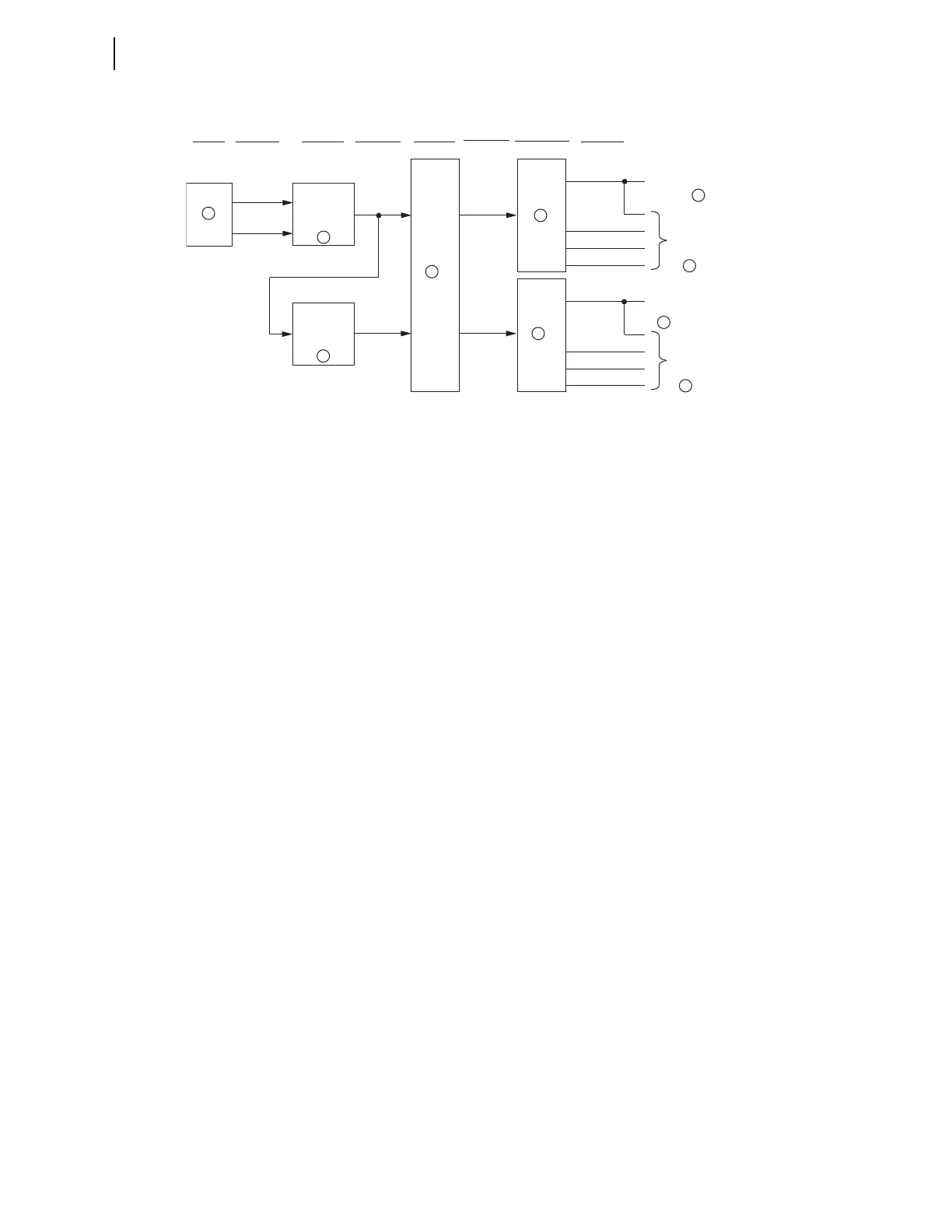
Figure 4.36 General Logic Flow of Directional Control for Negative-Sequence and Phase Overcurrent Elements
The directional control for negative sequence and phase overcurrent elements
is intended to control overcurrent elements with pickup settings above load
current to detect faults. In some applications, it may be necessary to set a sen-
sitive overcurrent element to detect currents in one direction (reverse, for
example) and a less sensitive overcurrent element for the other direction (for-
ward). In such applications, with default relay logic, a reverse overcurrent ele-
ment with pickup setting below forward load may operate for some remote,
unbalanced, reverse faults. If possible, overcurrent element pickup settings
should be set above the current expected for load in either direction. If this is
not possible, refer to the technical paper Use of Directional Elements at the
Utility-Industrial Interface by Dave Costello, Greg Bow, and Martin Moon,
available on the SEL website, or contact SEL for assistance.
Internal Enables
Refer to Figure 4.23 and Figure 4.36.
The internal enable DIRQE corresponds to the negative-sequence voltage-
polarized directional element.
Note that Figure 4.23 has extra internal enable DIRQGE, which is used in the
directional element logic that controls the neutral ground and residual ground
overcurrent elements (see Figure 4.20).
The settings involved with internal enable DIRQE in Figure 4.23 (e.g., set-
tings a2, k2) are explained in Directional Control Settings on page 4.53.
Directional Elements
Refer to Figure 4.36, Figure 4.37, and Figure 4.38.
If a loss-of-potential condition occurs (Relay Word bit LOP asserts), the nega-
tive-sequence voltage-polarized and positive-sequence voltage-polarized
directional elements are disabled (see Figure 4.23 and Figure 4.38).
Refer to Figure 4.73 and accompanying text for more information on loss-of-
potential.
FDIRP/
RDIRP
FDIRQ/
RDIRQ
DIRQE
(Disable)
50QF/
50QR
to Phase
Time-Overcurrent
Elements
to Phase
Instantaneous/Definite
Time Overcurrent
Elements
P1DIR Level 1
DIRPF/
DIRPR
Negative-
Sequence
Voltage-
Polarized
Positive-
Sequence
Voltage-
Polarized
DIRQF/
DIRQR
Q1DIR Level 1
Q2DIR Level 2
Q3DIR Level 3
Q4DIR Level 4
to Negative-Sequence
Instantaneous/Definite
Time Overcurrent
Elements
P2DIR Level 2
P3DIR Level 3
P4DIR Level 4
to Negative-Sequence
Time-Overcurrent
Element
Internal
Enables
Relay Word
Bit Outputs
Directional
Elements
Relay Word
Bit Outputs
Relay Word
Bit Outputs
Direction
Forward/
Reverse Logic
Directional
Control
Directional
Element
Routing
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10

 Loading...
Loading...