Ethernet Overview
Except on the first page, right running head:
Heading1 or Heading1NewPage text (automatic)
165
Alcatel-Lucent
Beta Beta
OmniAccess 5740 Unified Services Gateway CLI Configuration Guide
ETHERNET TERMINOLOGIES
Ethernet follows a simple set of rules that govern its basic operation. The basics of
Ethernet terminology include:
• Medium - Ethernet devices attach to a common medium that provides a path
along which the electronic signals travel. Historically, this medium has been
coaxial copper cable, but today it is more commonly a twisted pair or fiber optic
cabling.
• Segment - A single shared medium as an Ethernet segment.
• Node - Devices that attach to that segment are stations or nodes.
• Frame - The nodes communicate in short messages called frames, which are
variably sized chunks of information. Each frame must include, for example, both
a destination address and a source address, which identify the recipient and the
sender of the message. The address uniquely identifies the node. No two
Ethernet devices should ever have the same address.
• Ethernet addressing - Ethernet addressing implements a broadcast address. A
frame with a destination address equal to the broadcast address, is intended for
every node on the network, and every node will both receive and process this type
of frame.
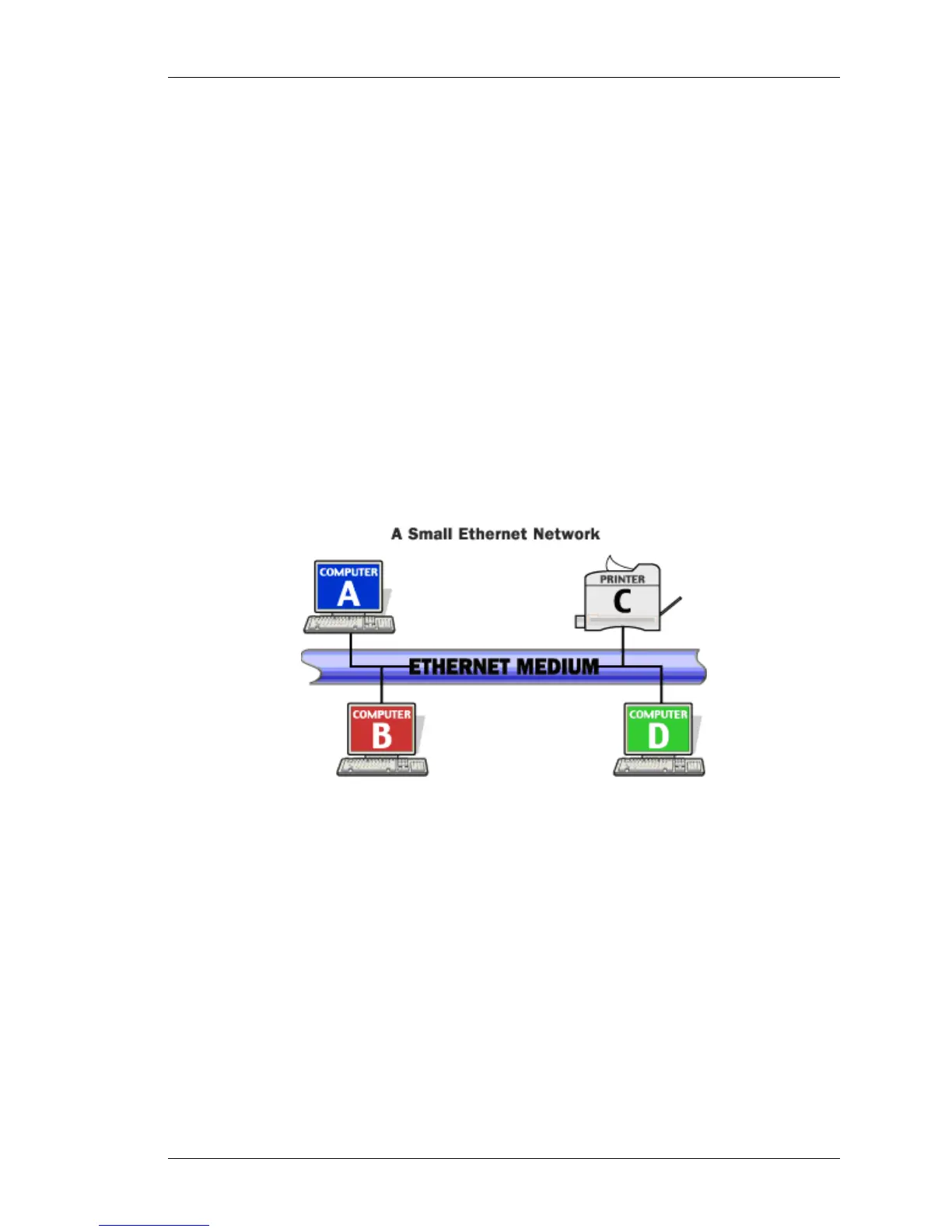
Figure 4: Ethernet Network
For example, in the figure above, when computer B transmits to printer C,
computers A and D will also receive and examine the frame. However, when a
station first receives a frame, it checks the destination address to see if the frame
is intended for itself. If it is not, the station discards the frame without even
examining its contents.

 Loading...
Loading...