VRF-CE Overview
Except on the first page, right running head:
Heading1 or Heading1NewPage text (automatic)
659
Alcatel-Lucent
Beta Beta
OmniAccess 5740 Unified Services Gateway CLI Configuration Guide
VRF-CE OVERVIEW
VRF-CE technology is similar to BGP/MPLS VPNs. The primary difference
between the two is the manner in which the connectivity is established between
the remote sites of a VPN. MPLS VPNs use MPLS tunnels to provide connectivity
between the remote sites. VRF-CE on the other hand, requires dedicated point-to-
point communications channels to provide inter-site connectivity between the
remote sites. These communication channels could be either Layer 2 circuits
(such as frame relay PVCs or ATM PVCs) or Layer 3 tunneling protocols such as
GRE, IP-IP, IPsec, L2TP, etc.
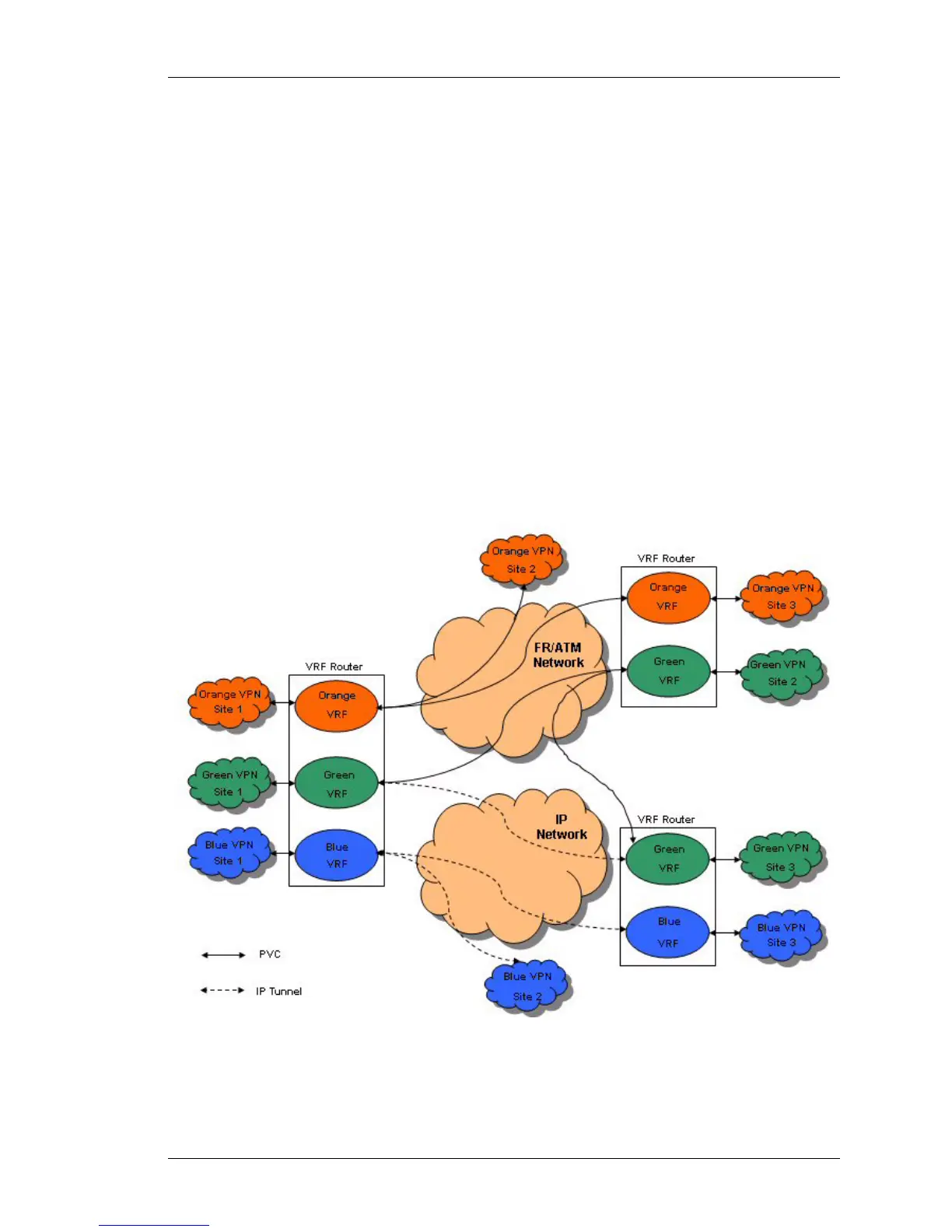
Figure below depicts the possible deployment scenarios using VRF-CE. It shows
three VPN networks; Orange, Green, and Blue. Each VPN has three sites 1, 2
and 3. Orange VPN Site 1 connects to a non-VRF aware router at site 2. Orange
VPN Site 1 connects to a VRF-aware router at site 3 via PVCs. Green VPN site 1
connects to a VRF-aware router at site 2 via PVC. Green VPN site 1 also
connects to a VRF-aware router at site 3 via an IP tunnel. Green VPN site 3
connects to site 2 via PVC. Blue VPN site 1 connects to a non-VRF aware router
at site 2 via an IP tunnel. Similarly, it connects to a VRF-aware router at site 3 via
an IP tunnel.
Figure 14: VRF-CE Deployment Scenario

 Loading...
Loading...