2.6.3 IPv4 / IPv6
What are the essential differences?
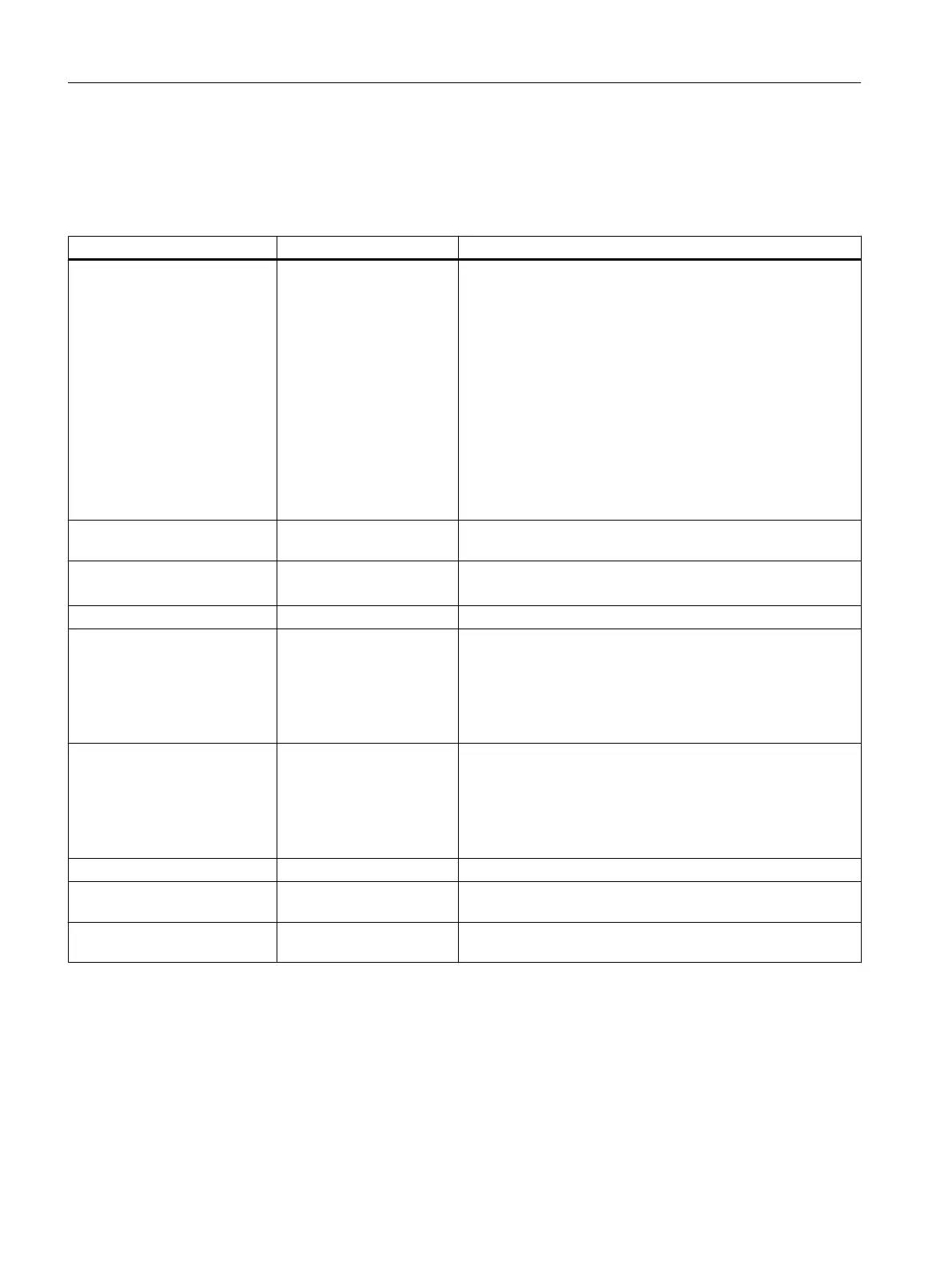
IPv4 IPv6
IP configuration
● DHCP server
● Manual
● Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC): Stateless
autoconfiguration using NDP (Neighbor Discovery
Protocol)
– Creates a link local address for every interface that
does not require a router on the link.
– Checks the uniqueness of the address on the link that
requires no router on the link.
– Specifies whether the global addresses are obtained
via a status-free mechanism, a mechanism with status
or via both mechanisms. (Requires a router on the link.)
● Manual
● DHCPv6 (status dependent)
Available IP addresses 32-bit: 4, 29 * 10
9
address‐
es
128-bit: 3, 4 * 10
38
addresses
Address format Decimal: 192.168.1.1
with port: 192.168.1.1:20
Hexadecimal: 2a00:ad80::0123
with port: [2a00:ad80::0123]:20
Loopback 127.0.0.1 ::1
IP addresses of the interface 4 IP addresses Multiple IP addresses
● LLA: A link local address (formed automatically) fe80::/128
per interface
● ULA: Several unique local unicast addresses per interface
● GUA: Several global unicast addresses per interface
Header
● Checksum
● Variable length
● Fragmentation in the
header
● No security
● Checking at a higher layer
● Fixed size
● Fragmentation in the extension header
Fragmentation Host and router Only endpoint of the communication
Quality of service Type of Service (ToS) for
prioritization
The prioritization is specified in the header field "Traffic Class".
Types of frame Broadcast, multicast, uni‐
cast
Multicast, unicast, anycast
Description
2.6 Interface identifiers and addresses
SCALANCE W770/W730 acc. to IEEE 802.11n Command Line Interface
32 Configuration Manual, 09/2017, C79000-G8976-C324-08

 Loading...
Loading...











