Power Management
7-4 Copyright © 2005-2008 ARM Limited. All rights reserved. ARM DDI 0337G
Non-Confidential
Unrestricted Access
power savings. SLEEPDEEP is never asserted without SLEEPING also
being asserted. SLEEPDEEP on page 7-5 shows an example of
SLEEPDEEP usage.
7.2.1 SLEEPING
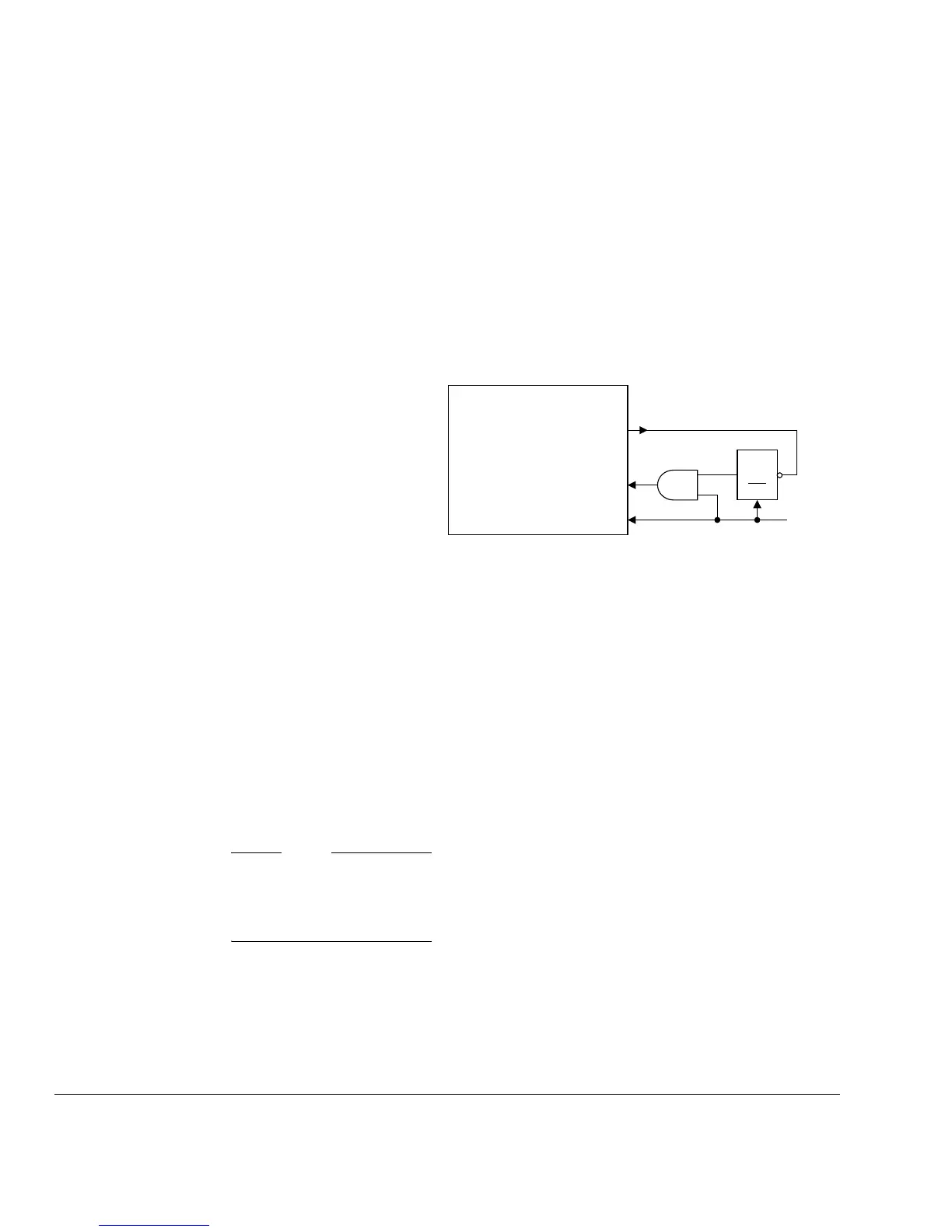
Figure 7-1 shows an example of how to reduce power consumption by gating the
HCLK clock to the processor with SLEEPING in the low-power state. If necessary,
you can also use SLEEPING to gate other system components. You can use the output
signal GATEHCLK instead of creating your own clock gate enable term.
Figure 7-1 SLEEPING power control example
To detect interrupts, the processor must receive the free-running FCLK at all times,
unless the WIC is in use. FCLK clocks:
• A small amount of logic in the NVIC that detects interrupts.
•The Data Watchpoint and Trace (DWT) and Instrumentation Trace Macrocell
(ITM) blocks. These blocks can generate trace packets during sleep when so
enabled. If the TRCENA bit of the Debug Exception and Monitor Control
Register is enabled then the power consumption of those blocks is minimized. See
Debug Exception and Monitor Control Register on page 10-8.
FCLK frequency can be reduced during SLEEPING assertion.
Note
Suppressing HCLK using the clock-gating scheme in Figure 7-1 prevents debug
accesses. The CoreSight Debug Ports (DPs) provide a power up signal that enables the
system to bypass the clock-gating logic in Figure 7-1.
Cortex-M3 processor
SLEEPING
HCLK
FCLK
FCLK
EN
 Loading...
Loading...