144 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA User Guide
UG190 (v5.0) June 19, 2009
Chapter 4: Block RAM
FIFO Operations
Reset
Reset is an asynchronous signal for both multirate and synchronous FIFO. Reset must be
asserted for three cycles to reset all read and write address counters and initialize flags
after power up. Reset does not clear the memory, nor does it clear the output register.
When reset is asserted High, EMPTY and ALMOST_EMPTY will be set to 1, FULL and
ALMOST_FULL will be reset to 0. The reset signal must be High for at least three read
clock and write clock cycles to ensure all internal states are reset to the correct values.
During RESET, RDEN and WREN must be held Low.
Operating Mode
There are two operating modes in FIFO functions. They differ only in output behavior
immediately after the first word is written to a previously empty FIFO.
Standard Mode
After the first word is written into an empty FIFO, the Empty flag deasserts synchronously
with RDCLK. After Empty is deasserted Low and RDEN is asserted, the first word will
appear at DO on the rising edge of RDCLK.
First Word Fall Through (FWFT) Mode
After the first word is written into an empty FIFO, this word automatically appears at DO
before RDEN is asserted. Subsequent Read operations require Empty to be Low and RDEN
to be High. Figure 4-20 illustrates the difference between standard mode and FWFT mode.
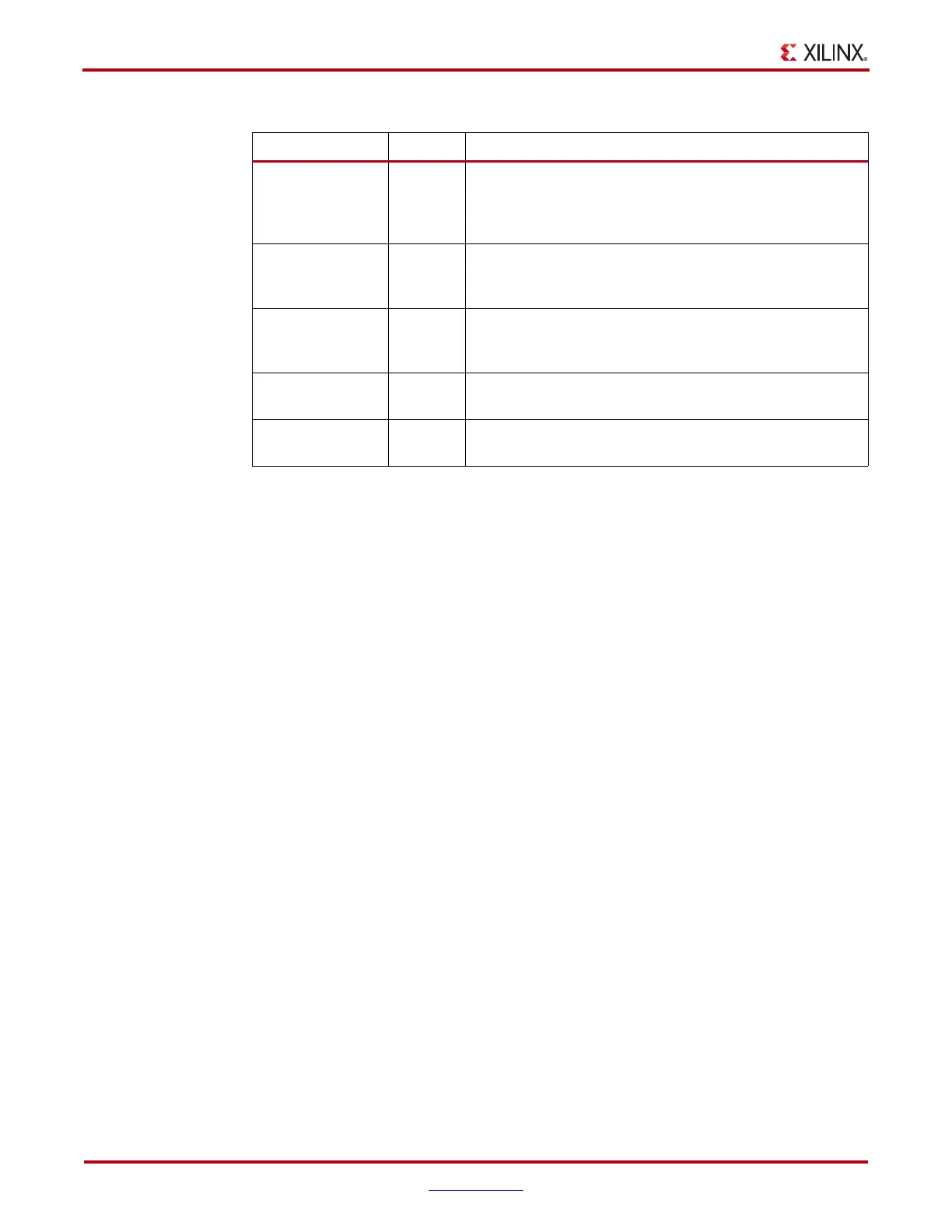
ALMOSTEMPTY Output Almost all valid entries in FIFO have been read.
Synchronous with RDCLK. The offset for this flag is user
configurable. See Table 4-16 for the clock latency for flag
deassertion.
RDCOUNT Output The FIFO data read pointer. It is synchronous with RDCLK.
The value will wrap around if the maximum read pointer
value has been reached.
WRCOUNT Output The FIFO data write pointer. It is synchronous with WRCLK.
The value will wrap around if the maximum write pointer
value has been reached.
WRERR Output When the FIFO is full, any additional write operation
generates an error flag. Synchronous with WRCLK.
RDERR Output When the FIFO is empty, any additional read operation
generates an error flag. Synchronous with RDCLK.
Table 4-15: FIFO I/O Port Names and Descriptions (Continued)
Port Name Direction Description

 Loading...
Loading...











