Virtex-5 FPGA User Guide www.xilinx.com 145
UG190 (v5.0) June 19, 2009
FIFO Operations
Status Flags
Table 4-16 shows the number of clock cycles to assert or deassert each flag of a multirate
FIFO. Synchronous FIFOs do not have a clock cycle latency when asserting or deasserting
flags. Due to the asynchronous nature of the clocks, the simulation model only reflects the
deassertion latency cycles listed.
Empty Flag
The Empty flag is synchronous with RDCLK, and is asserted when the last entry in the
FIFO is read. When there are no more valid entries in the FIFO queue, the read pointer will
be frozen. The Empty flag is deasserted after three (in standard mode) or four (in FWFT
mode) read clocks after new data is written into the FIFO.
The empty flag is used in the read clock domain. The rising edge of EMPTY is inherently
synchronous with RDCLK. The empty condition can only be terminated by WRCLK,
usually asynchronous to RDCLK. The falling edge of EMPTY must, therefore, artificially
be moved onto the RDCLK time domain. Since the two clocks have an unknown phase
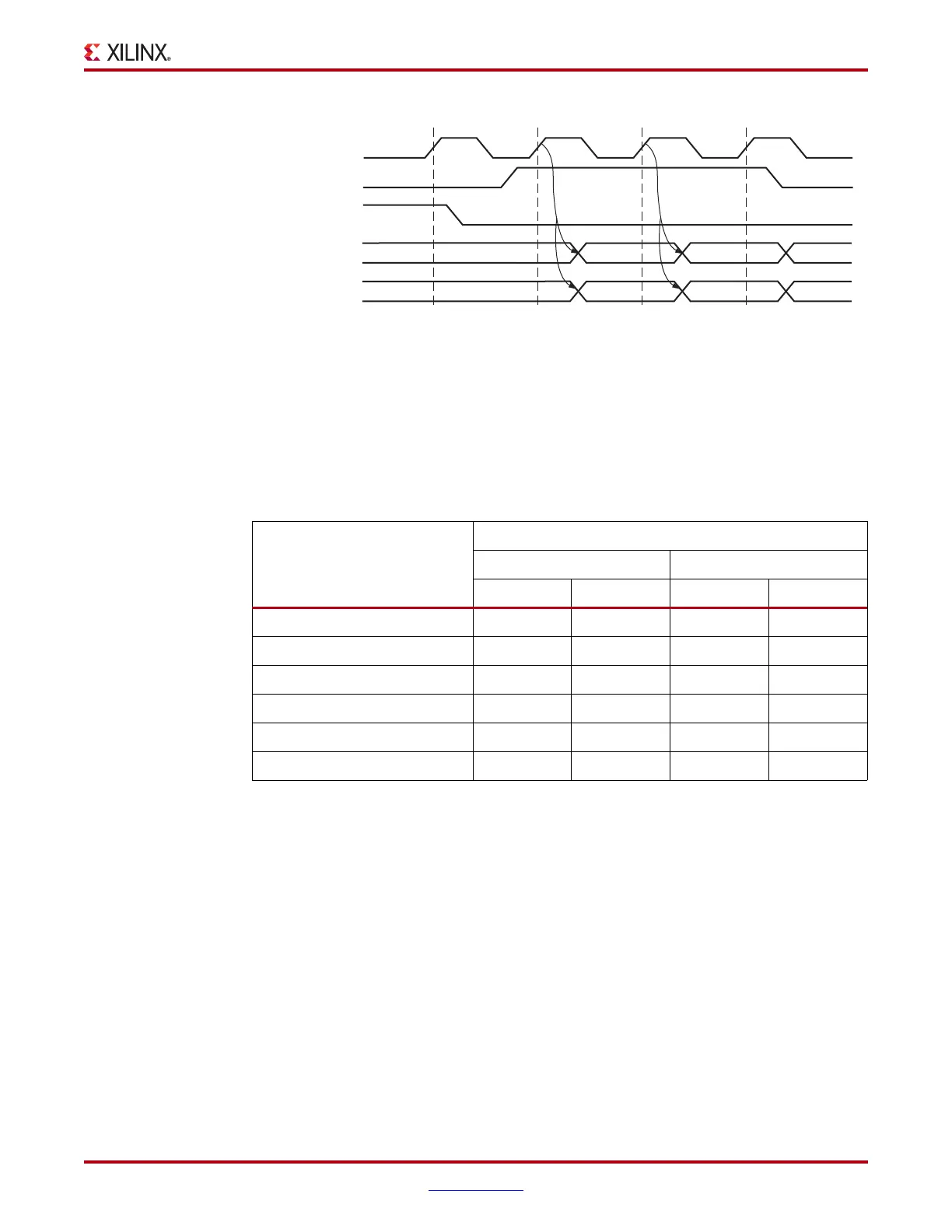
X-Ref Target - Figure 4-20
Figure 4-20: Read Cycle Timing (Standard and FWFT Modes)
RDCLK
RDEN
EMPTY
DO (Standard)
DO (FWFT)
Previous Data
W1
W2 W3
W1
W2 W3
ug190_4_17_032506
Table 4-16: Multirate FIFO Flag Assertion and Deassertion Latency
Status Flag
Write/Read Cycle Latency
(1)
Assertion Deassertion
Standard FWFT Standard FWFT
EMPTY
(2)
0034
FULL
(2)
0033
ALMOST EMPTY
(3)
1133
ALMOST FULL
(3)
1133
READ ERROR 0 0 0 0
WRITE ERROR 0 0 0 0
Notes:
1. Latency is with respect to RDCLK and WRCLK.
2. Depending on the offset between read and write clock edges, the Empty and Full flags can deassert
one cycle later.
3. Depending on the offset between read and write clock edges, the Almost Empty and Almost Full flags
can deassert one cycle later.

 Loading...
Loading...











