Virtex-5 FPGA User Guide www.xilinx.com 181
UG190 (v5.0) June 19, 2009
CLB Overview
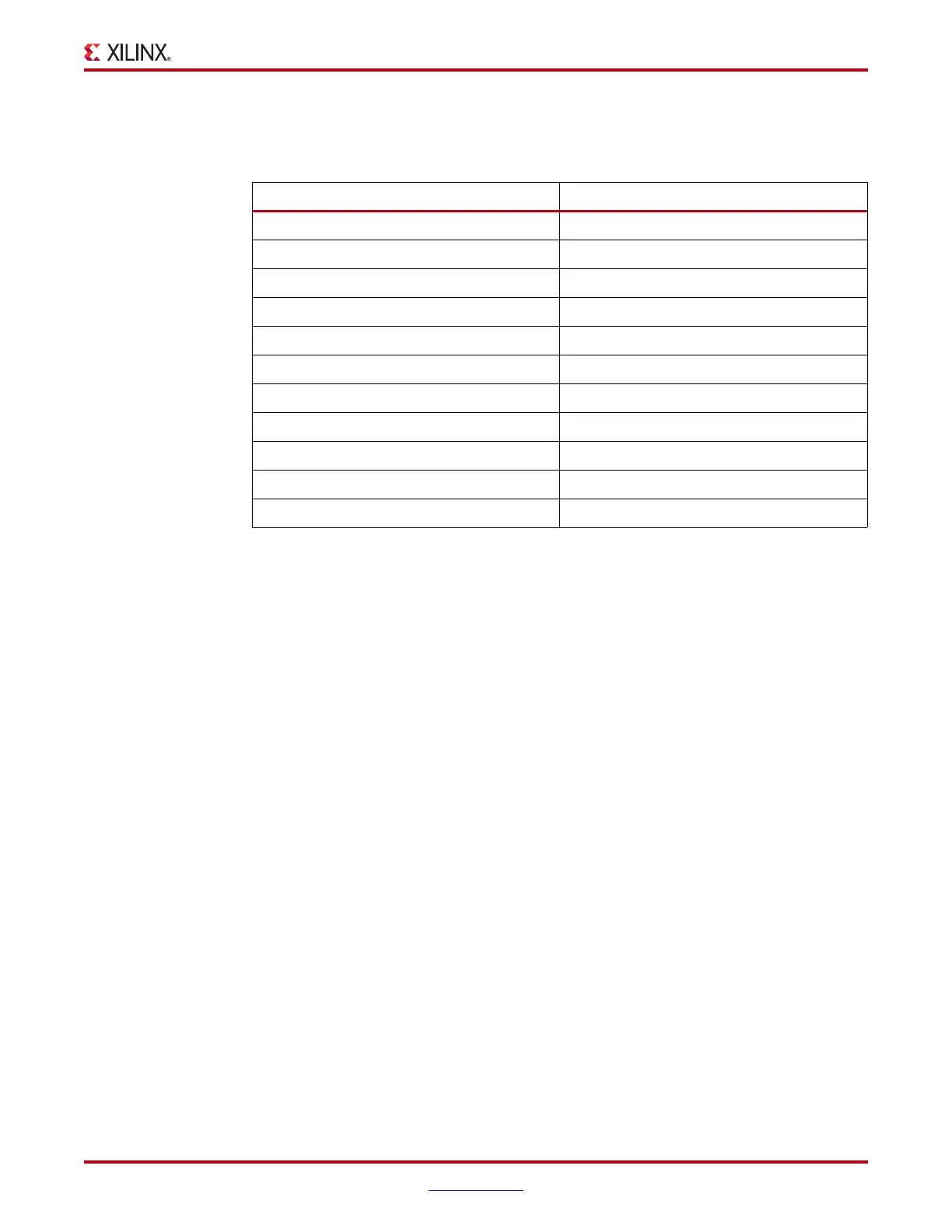
Table 5-5 shows the number of LUTs (four per slice) occupied by each distributed RAM
configuration.
For single-port configurations, distributed RAM has a common address port for
synchronous writes and asynchronous reads. For dual-port configurations, distributed
RAM has one port for synchronous writes and asynchronous reads, and another port for
asynchronous reads. In simple dual-port configuration, there is no data out (read port)
from the write port. For quad-port configurations, distributed RAM has one port for
synchronous writes and asynchronous reads, and three additional ports for asynchronous
reads.
In single-port mode, read and write addresses share the same address bus. In dual-port
mode, one function generator is connected with the shared read and write port address.
The second function generator has the A inputs connected to a second read-only port
address and the WA inputs shared with the first read/write port address.
Figure 5-6 through Figure 5-14 illustrate various example distributed RAM configurations
occupying one SLICEM. When using x2 configuration (RAM32X2Q), A6 and WA6 are
driven High by the software to keep O5 and O6 independent.
Table 5-5: Distributed RAM Configuration
RAM Number of LUTs
32 x 1S 1
32 x 1D 2
32 x 2Q
(2)
4
32 x 6SDP
(2)
4
64 x 1S 1
64 x 1D 2
64 x 1Q
(3)
4
64 x 3SDP
(3)
4
128 x 1S 2
128 x 1D 4
256 x 1S 4
Notes:
1. S = single-port configuration; D = dual-port configuration; Q = quad-port configuration; SDP = simple
dual-port configuration.
2. RAM32M is the associated primitive for this configuration.
3. RAM64M is the associated primitive for this configuration.

 Loading...
Loading...











