334 www.xilinx.com Virtex-5 FPGA User Guide
UG190 (v5.0) June 19, 2009
Chapter 7: SelectIO Logic Resources
Two cases that use the bidirectional IODELAY functionality are important for a given I/O
pin. The first case uses bidirectional IODELAY when the I/O is an output being switched
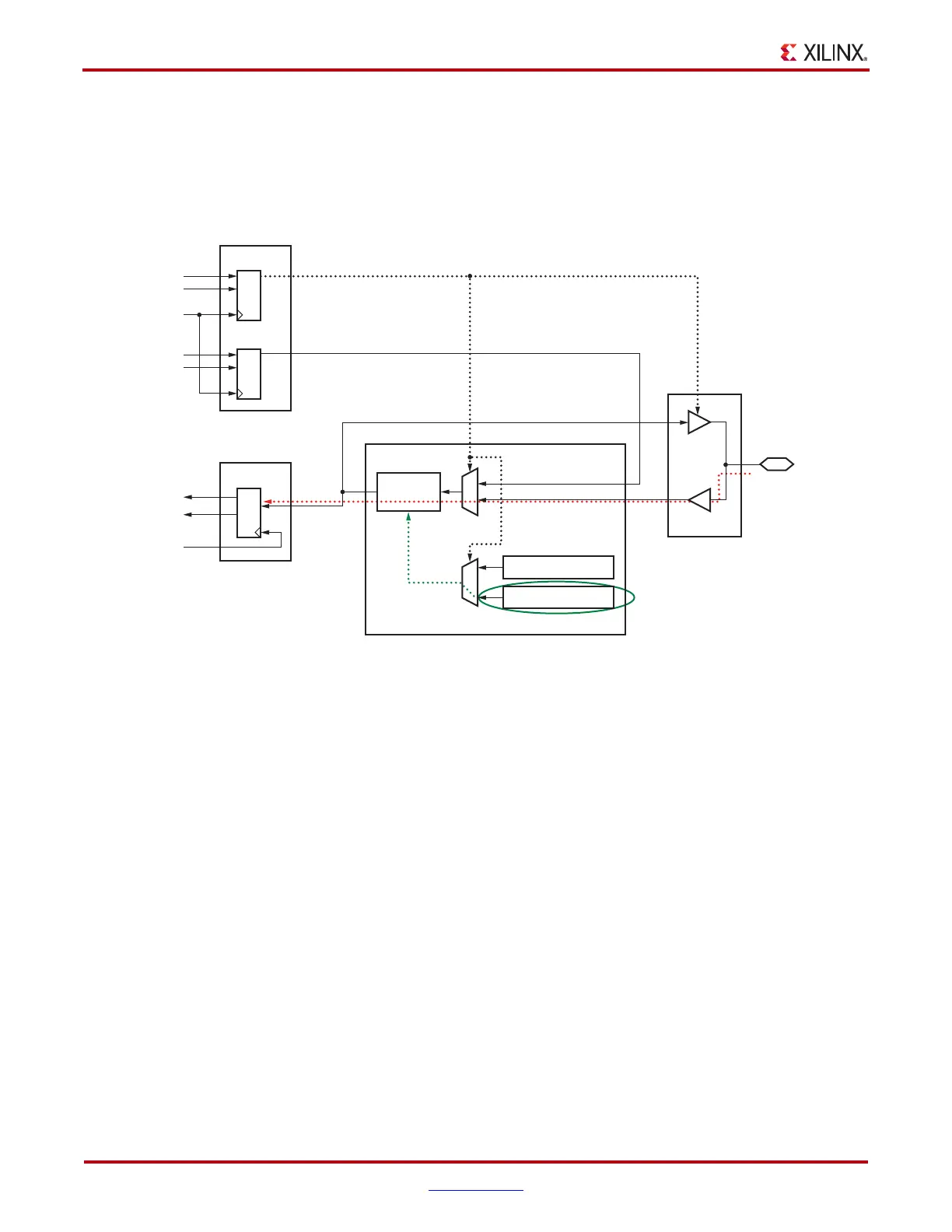
to an input. Figure 7-11 shows the IOB and IODELAY moving toward the input mode as
set by the TSCONTROL net coming from the ODDR flip-flop. This controls the selection of
MUXes E and F for the IOB input path and IDELAY_VALUE, respectively. Additionally,
the OBUF is 3-stated.
X-Ref Target - Figure 7-11
Figure 7-11: IODELAY and IOB in Input Mode when 3-state is Disabled
IODELAY_02_082107
IOB
IODELAY
T
Q1
Q2
T2
CLK
CLK
MUX E
Delay
Chain
ODATAIN
IDATAIN
MUX F
OBUF
PA D
IBUF
D1
T1
D2
ODELAY_VALUE
IDELAY_VALUE
ODDR
TSCONTROL
O DATAI N
DATAOUT
ODDR
IDDR

 Loading...
Loading...











