The three primary modes of operation are run, wait and stop. The WFI instruction
invokes both wait and stop modes for the chip. The primary modes are augmented in a
number of ways to provide lower power based on application needs.
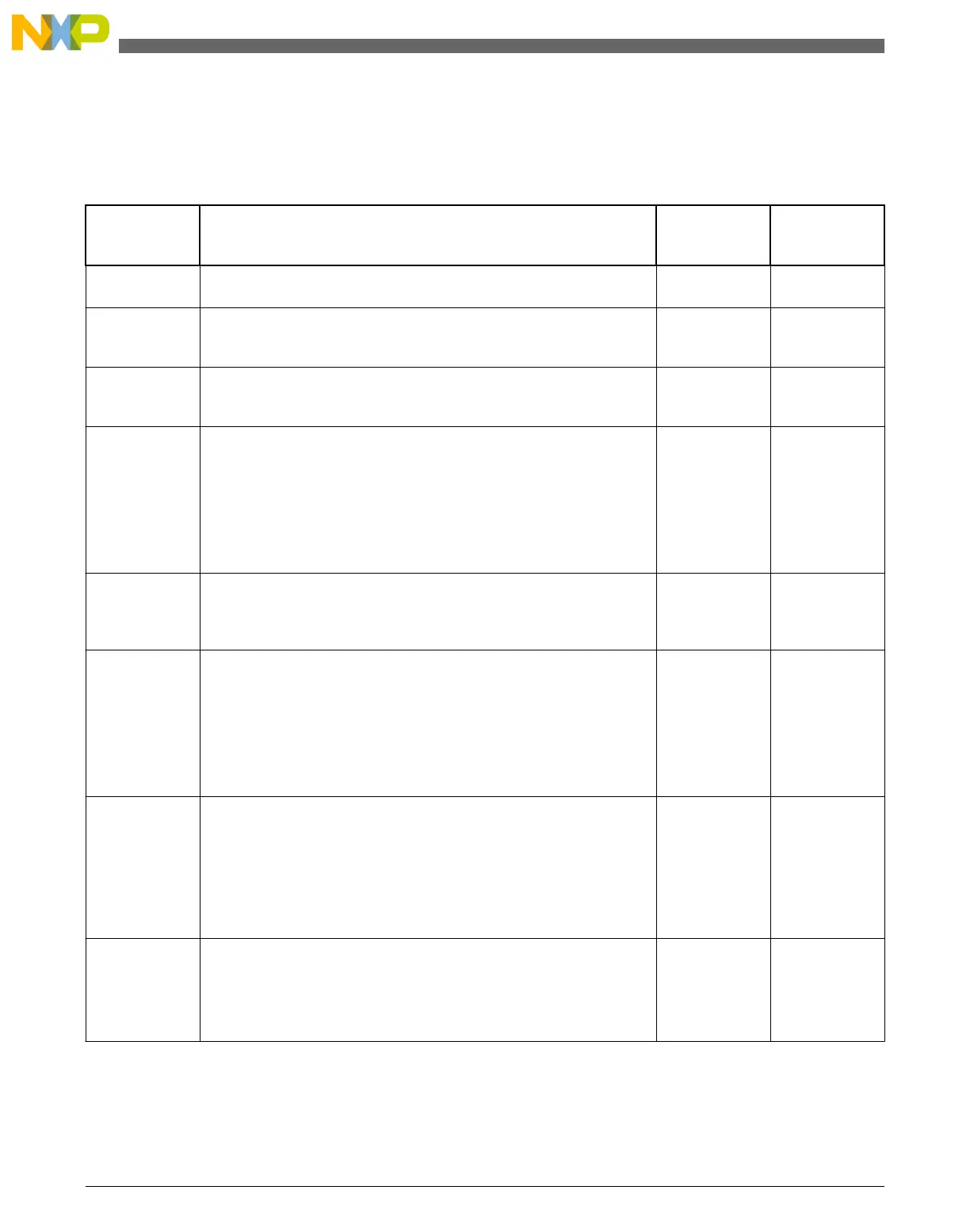
Table 7-1. Chip power modes
Chip mode Description Core mode Normal
recovery
method
Normal run Allows maximum performance of chip. Default mode out of reset; on-
chip voltage regulator is on.
Run —
Normal Wait -
via WFI
Allows peripherals to function while the core is in sleep mode, reducing
power. NVIC remains sensitive to interrupts; peripherals continue to be
clocked.
Sleep Interrupt
Normal Stop -
via WFI
Places chip in static state. Lowest power mode that retains all registers
while maintaining LVD protection. NVIC is disabled; AWIC is used to
wake up from interrupt; peripheral clocks are stopped.
Sleep Deep Interrupt
VLPR (Very Low
Power Run)
On-chip voltage regulator is in a low power mode that supplies only
enough power to run the chip at a reduced frequency. Reduced
frequency Flash access mode (1 MHz); LVD off; in BLPI clock mode,
the fast internal reference oscillator is available to provide a low power
nominal 4MHz source for the core with the nominal bus and flash clock
required to be <800kHz; alternatively, BLPE clock mode can be used
with an external clock or the crystal oscillator providing the clock
source.
Run —
VLPW (Very
Low Power
Wait) -via WFI
Same as VLPR but with the core in sleep mode to further reduce
power; NVIC remains sensitive to interrupts (FCLK = ON). On-chip
voltage regulator is in a low power mode that supplies only enough
power to run the chip at a reduced frequency.
Sleep Interrupt
VLPS (Very Low
Power Stop)-via
WFI
Places chip in static state with LVD operation off. Lowest power mode
with ADC and pin interrupts functional. Peripheral clocks are stopped,
but OSC, LPTMR, RTC, CMP, TSI can be used. TPM and UART can
optionally be enabled if their clock source is enabled. NVIC is disabled
(FCLK = OFF); AWIC is used to wake up from interrupt. On-chip
voltage regulator is in a low power mode that supplies only enough
power to run the chip at a reduced frequency. All SRAM is operating
(content retained and I/O states held).
Sleep Deep Interrupt
LLS (Low
Leakage Stop)
State retention power mode. Most peripherals are in state retention
mode (with clocks stopped), but OSC, LLWU, LPTMR, RTC, CMP,,
TSI can be used. NVIC is disabled; LLWU is used to wake up.
NOTE: The LLWU interrupt must not be masked by the interrupt
controller to avoid a scenario where the system does not fully
exit stop mode on an LLS recovery.
All SRAM is operating (content retained and I/O states held).
Sleep Deep Wakeup
Interrupt
1
VLLS3 (Very
Low Leakage
Stop3)
Most peripherals are disabled (with clocks stopped), but OSC, LLWU,
LPTMR, RTC, CMP, TSI can be used. NVIC is disabled; LLWU is used
to wake up.
SRAM_U and SRAM_L remain powered on (content retained and I/O
states held).
Sleep Deep Wakeup Reset
2
Table continues on the next page...
Power modes
KL25 Sub-Family Reference Manual, Rev. 3, September 2012
142 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...