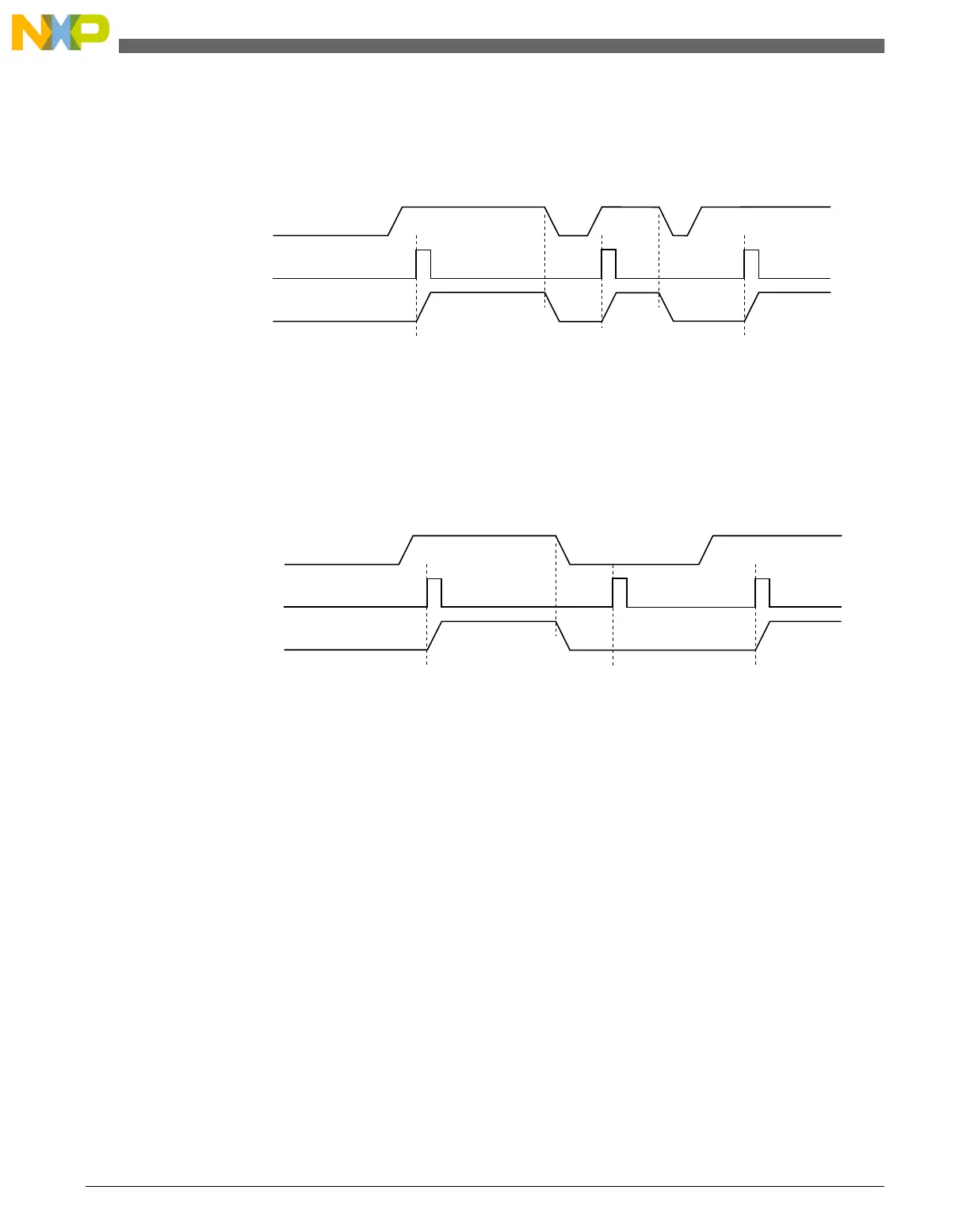
The DMA channel triggering capability allows the system to schedule regular DMA
transfers, usually on the transmit side of certain peripherals, without the intervention of
the processor. This trigger works by gating the request from the peripheral to the DMA
until a trigger event has been seen. This is illustrated in the following figure.
DMA request
Peripheral request
Trigger
Figure 22-13. DMAMUX channel triggering: normal operation
After the DMA request has been serviced, the peripheral will negate its request,
effectively resetting the gating mechanism until the peripheral re-asserts its request AND
the next trigger event is seen. This means that if a trigger is seen, but the peripheral is not
requesting a transfer, then that trigger will be ignored. This situation is illustrated in the
following figure.
DMA request
Peripheral request
Trigger
Figure 22-14. DMAMUX channel triggering: ignored trigger
This triggering capability may be used with any peripheral that supports DMA transfers,
and is most useful for two types of situations:
• Periodically polling external devices on a particular bus
As an example, the transmit side of an SPI is assigned to a DMA channel with a
trigger, as described above. After it has been set up, the SPI will request DMA
transfers, presumably from memory, as long as its transmit buffer is empty. By using
a trigger on this channel, the SPI transfers can be automatically performed every 5μs
(as an example). On the receive side of the SPI, the SPI and DMA can be configured
to transfer receive data into memory, effectively implementing a method to
periodically read data from external devices and transfer the results into memory
without processor intervention.
• Using the GPIO ports to drive or sample waveforms
Functional description
KL25 Sub-Family Reference Manual, Rev. 3, September 2012
342 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...