The CMOD[1:0] bits may be read or written at any time. Disabling the TPM counter by
writing zero to the CMOD[1:0] bits does not affect the TPM counter value or other
registers, but must be acknowledged by the TPM counter clock domain before they read
as zero.
The external clock input passes through a synchronizer clocked by the TPM counter
clock to assure that counter transitions are properly aligned to counter clock transitions.
Therefore, to meet Nyquist criteria considering also jitter, the frequency of the external
clock source must be less than half of the counter clock frequency.
31.4.2 Prescaler
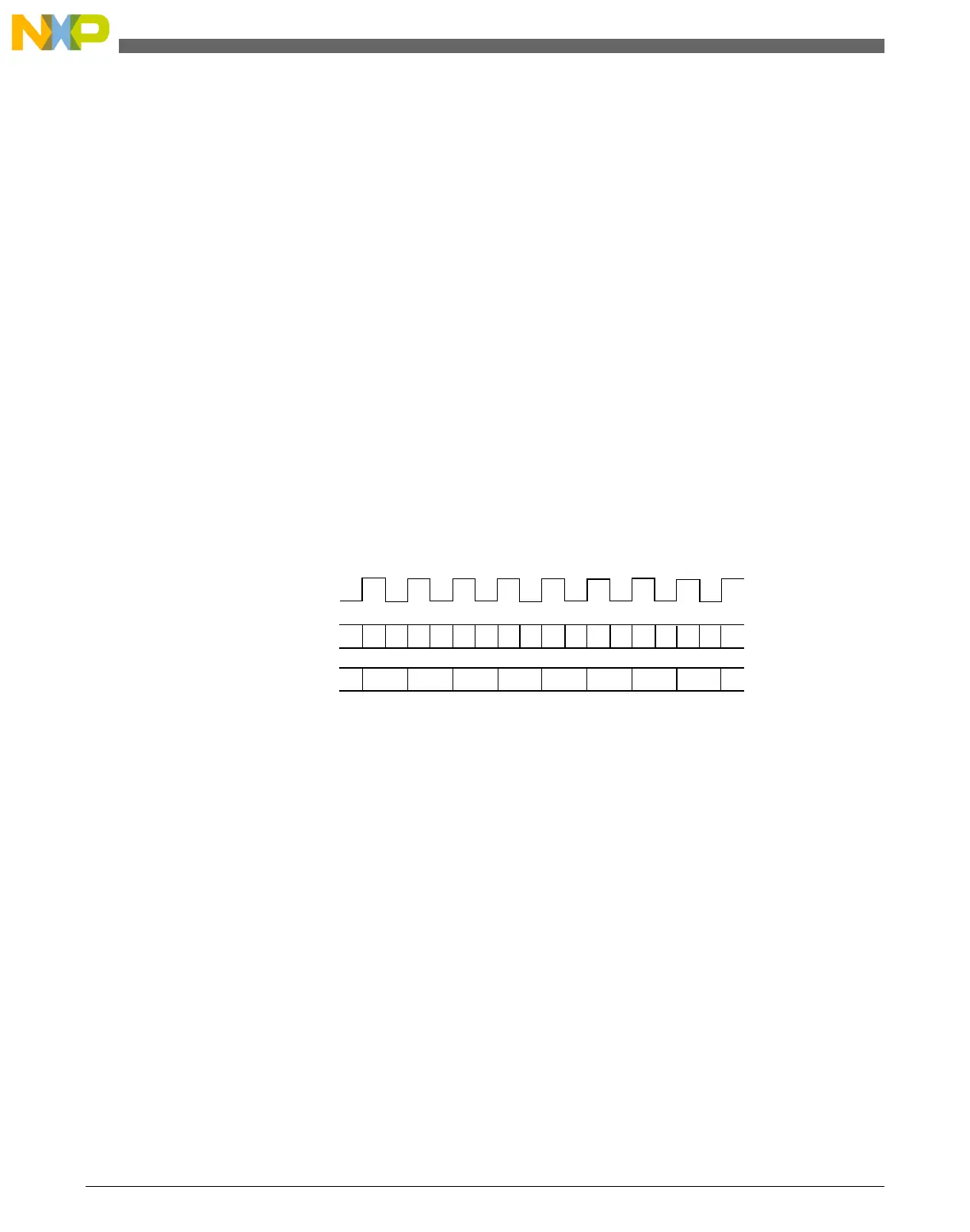
The selected counter clock source passes through a prescaler that is a 7-bit counter. The
value of the prescaler is selected by the PS[2:0] bits. The following figure shows an
example of the prescaler counter and TPM counter.
0
0
0
0
0
0 0
0 00 0 0
1
1 1
2 2
3 3
1
1
1 1 11 1 1
1
selected input clock
prescaler counter
timer module counting is up.
PS[2:0] = 001
CNTIN = 0x0000
timer module counter
Figure 31-78. Example of the Prescaler Counter
31.4.3 Counter
The TPM has a 16-bit counter that is used by the channels either for input or output
modes. The counter updates from the selected clock divided by the prescaler.
The TPM counter has these modes of operation:
• up counting (see Up Counting)
• up-down counting (see Up-Down Counting)
31.4.3.1 Up Counting
Up counting is selected when (CPWMS = 0)
Functional Description
KL25 Sub-Family Reference Manual, Rev. 3, September 2012
562 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...