-SCS Parameter Analyzer Reference Manual Section 13:
LPT library function reference
4200A-901-01 Rev. C / February 2017 13-173
The frequency points to sweep are set using the startf and stopf parameters. If an entered value
is not a supported frequency, the closest supported frequency is selected (for example, 15 kHz input
selects 20 kHz). If a specified frequency is equidistant from two adjacent frequencies, it is rounded up
to the higher frequency. The sweep can step forward (low frequency to high frequency) or it can step
in reverse (high frequency to low frequency).
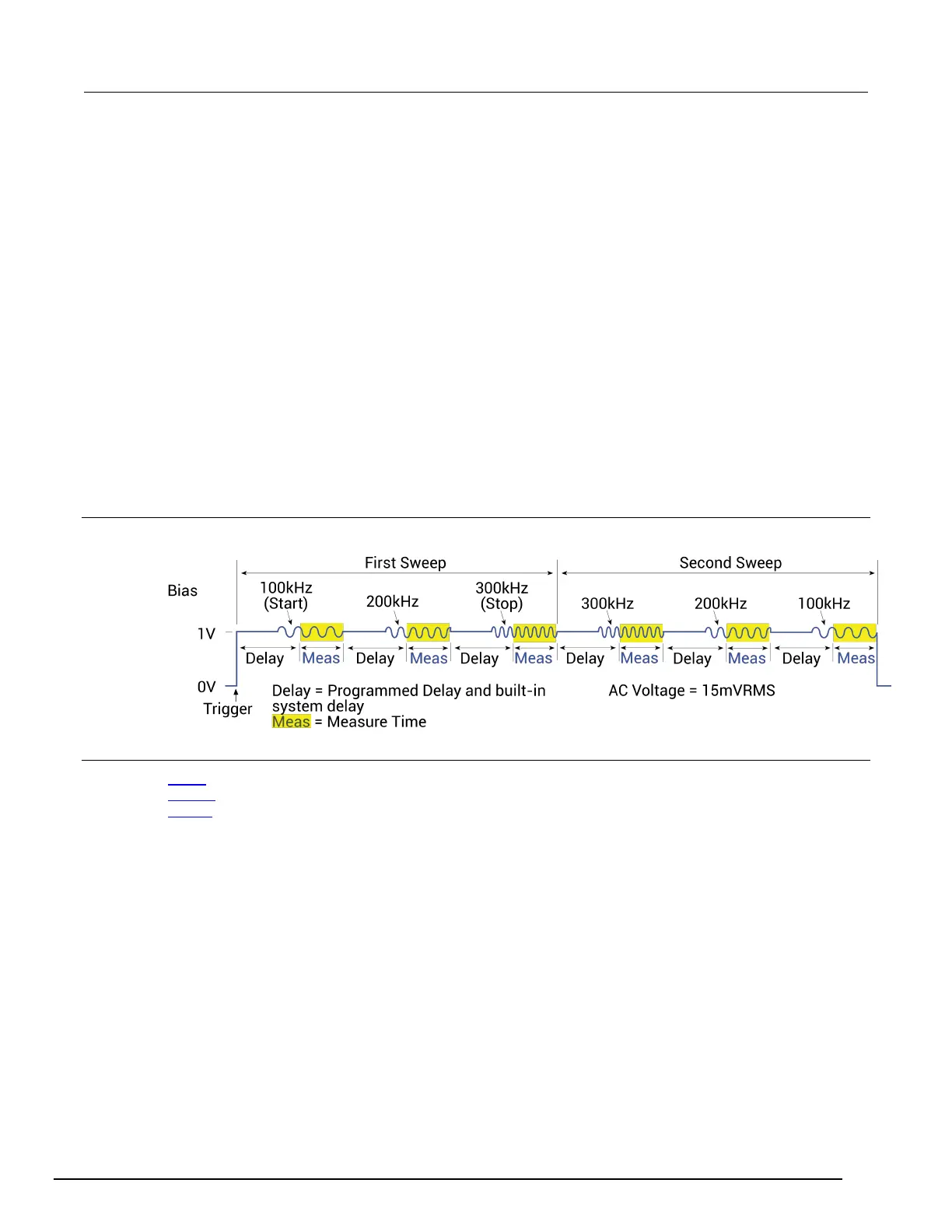
When the sweep is started, the CVU will step through all the supported frequency points from start to
stop for the first sweep, and then repeat (in the reverse direction) from stop to start for the second
sweep. For example, if the start frequency is 800 kHz and the stop frequency is 3 MHz, the CVU will
step through the following frequency points:
• 800 kHz, 900 kHz, 1 MHz, 2 MHz, 3 MHz, 3 MHz, 2 MHz, 1 MHz, 900 kHz, 800 kHz
The total number of sweep points is returned in the NumPts parameter. For the above example,
NumPts is assigned a value of 10.
The delayTime parameter sets the delay that occurs before each measurement. Note that there is
an inherent system overhead delay on each frequency step of the sweep.
Use the forcev command to set the DC bias level and setlevel command to set the AC drive
voltage.
Example
Figure 515: Dual frequency sweep example
Also see
forcev (on page 13-175)
setlevel (on page 13-182)
sweepf (on page 13-192)
 Loading...
Loading...