12: Maintenance Model 4200A-SCS Parameter Analyzer
12-12 4200A-901-01 Rev. C / February 2017
Generated currents
Any extraneous generated currents in the test system add to the expected current, which can cause
errors. Currents can be internally generated, as in the case of preamplifier input offset current, or they
can come from external sources such as insulators and cables. The following paragraphs discuss the
various types of generated currents. The next table summarizes the typical ranges of a number of
generated currents.
Typical generated currents
Effect Generated current range
Mechanical stress (Teflon)
Mechanical stress (ceramics)
Clean epoxy circuit board
Dirty epoxy circuit board
Offset currents
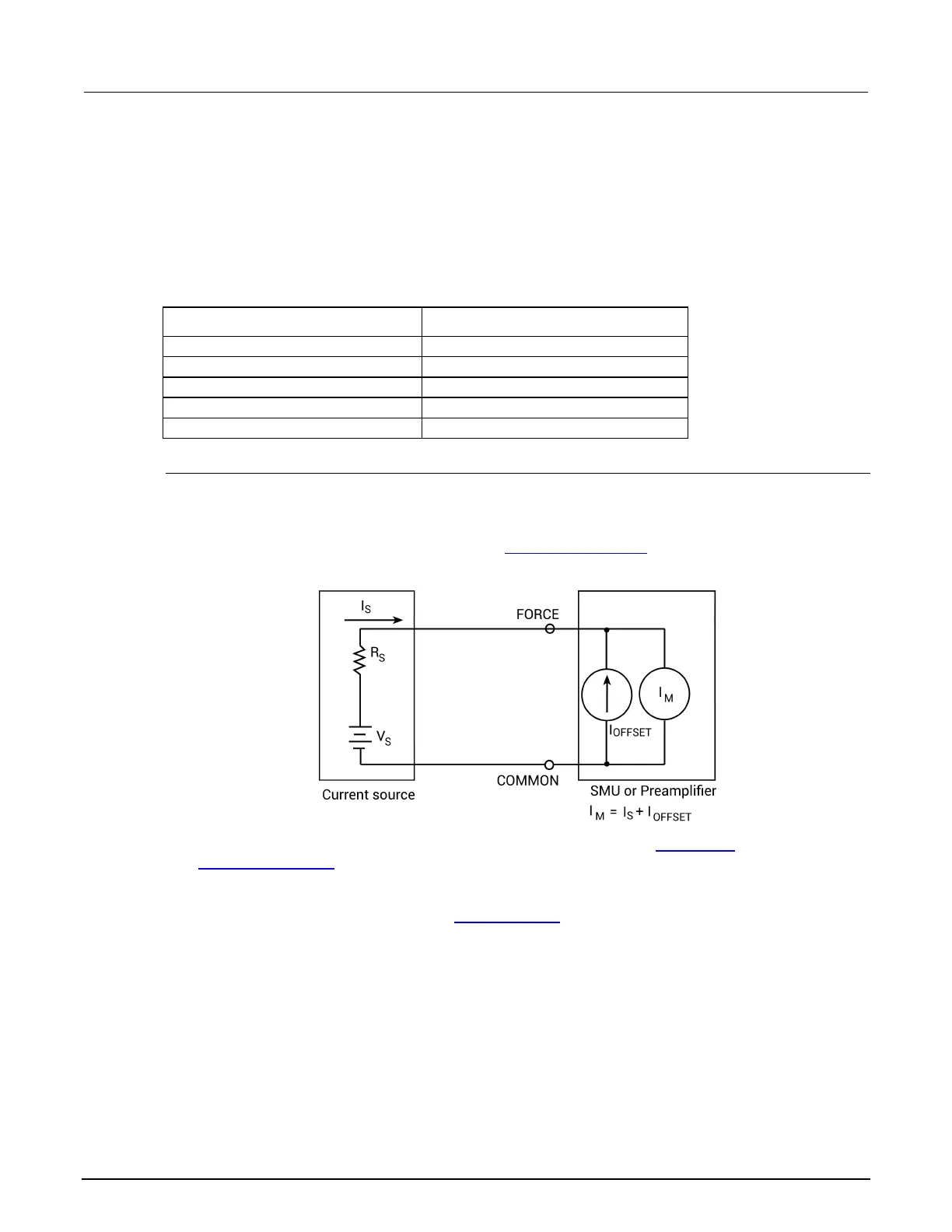
The preamplifier has a small current, known as the input offset current, that flows at all times. As
shown in the figure below, the input offset current adds to the measured current so that the SMU
measures the sum of the two currents. Note that input offset current can be brought to within
specifications by calibrating the system. Refer to Calibrate the system (on page 12-5
).
Figure 495: Input offset currents
Offset currents can also be generated externally from such sources as triboelectric (on page 12-13)
and piezoelectric effects (on page 12-13). As shown in the next figure, the external offset current also
adds to the source current, and the SMU again measures the sum of the two. These external offset
currents can be suppressed manually by subtracting them using the Formulator or the Calc
worksheet. For more information, refer to
The Formulator (on page 6-222) and Analyze data using the
Run tab.

 Loading...
Loading...