13: LPT library function reference Model 4200A-SCS Parameter Analyzer
13-122 4200A-901-01 Rev. C / February 2017
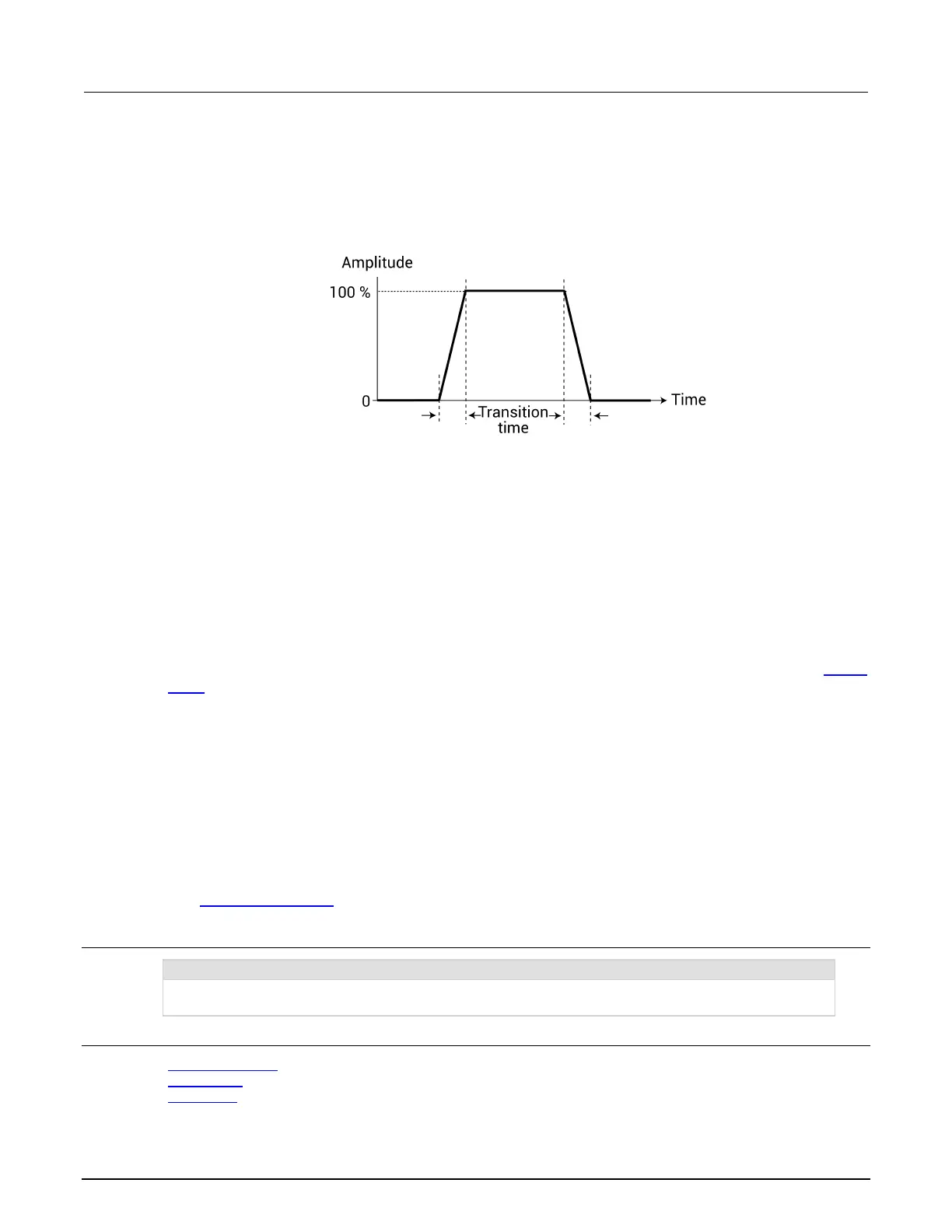
Pulse rise time and fall time:
Pulse rise time is the transition time (in seconds) from pulse low to pulse high. Pulse fall time is the
transition time from pulse high to pulse low. The transition time is the interval between corresponding
0% and 100% amplitude points on the rising and falling edge of the pulse, as shown in this figure.
Figure 507: Transition time
SweepType examples:
PULSE_RISE_SP (stepping or sweeping): Start = 0.001 s, stop = 0.005 s,
step = 0.001 s
Rise times for pulse output sequence: 0.001 s, 0.002 s, 0.003 s, 0.004 s, and 0.005 s.
PULSE_FALL_SP (stepping or sweeping): Start = 0.001 s, stop = 0.005 s,
step = 0.001 s
Fall times for pulse output sequence: 0.001 s, 0.002 s, 0.003 s, 0.004 s, and 0.005 s.
Pulse width:
The width of a pulse (in seconds) is measured at full-width half-maximum (FWHM) as shown in
Pulse
width (on page 6-102). SweepType example:
PULSE_WIDTH_SP (stepping or sweeping): Start = 0.01 s, stop = 0.05 s,
step = 0.01 s
Pulse widths for pulse output sequence: 0.01 s, 0.02 s, 0.03 s, 0.04 s, and 0.05 s.
Dual Sweep:
The dual sweep allows for a voltage level sweep that goes up and down based on the voltage start
stop and step. For example, a voltage amplitude sweep from 0 V to 4 V in 1 V steps. A single sweep
(PULSE_AMPLITUDE_SP) would output 5 points: 0 V, 1 V, 2 V, 3 V, 4 V. A dual sweep version
(PULSE_DUAL_AMPLITUDE_SP) outputs 10 points: 0 V, 1 V, 2 V, 3 V, 4 V, 4 V, 3 V, 2 V, 1 V, 0 V.
See Dual Sweep Option (on page 6-71
) for a diagram of this example.
Example
pulse_sweep_linear(PMU1, 1, PULSE_AMPLITUDE_SP, 1, 5, 1);
This example configures channel 1 of the PMU to perform an amplitude sweep from 1 V to 5 V in 1 V
steps.
Also see
pulse_step_linear (on page 13-118)
pulse_vhigh (on page 13-157)
pulse_vlow (on page 13-159)

 Loading...
Loading...