Chapter 4
70 MIPS R4000 Microprocessor User's Manual
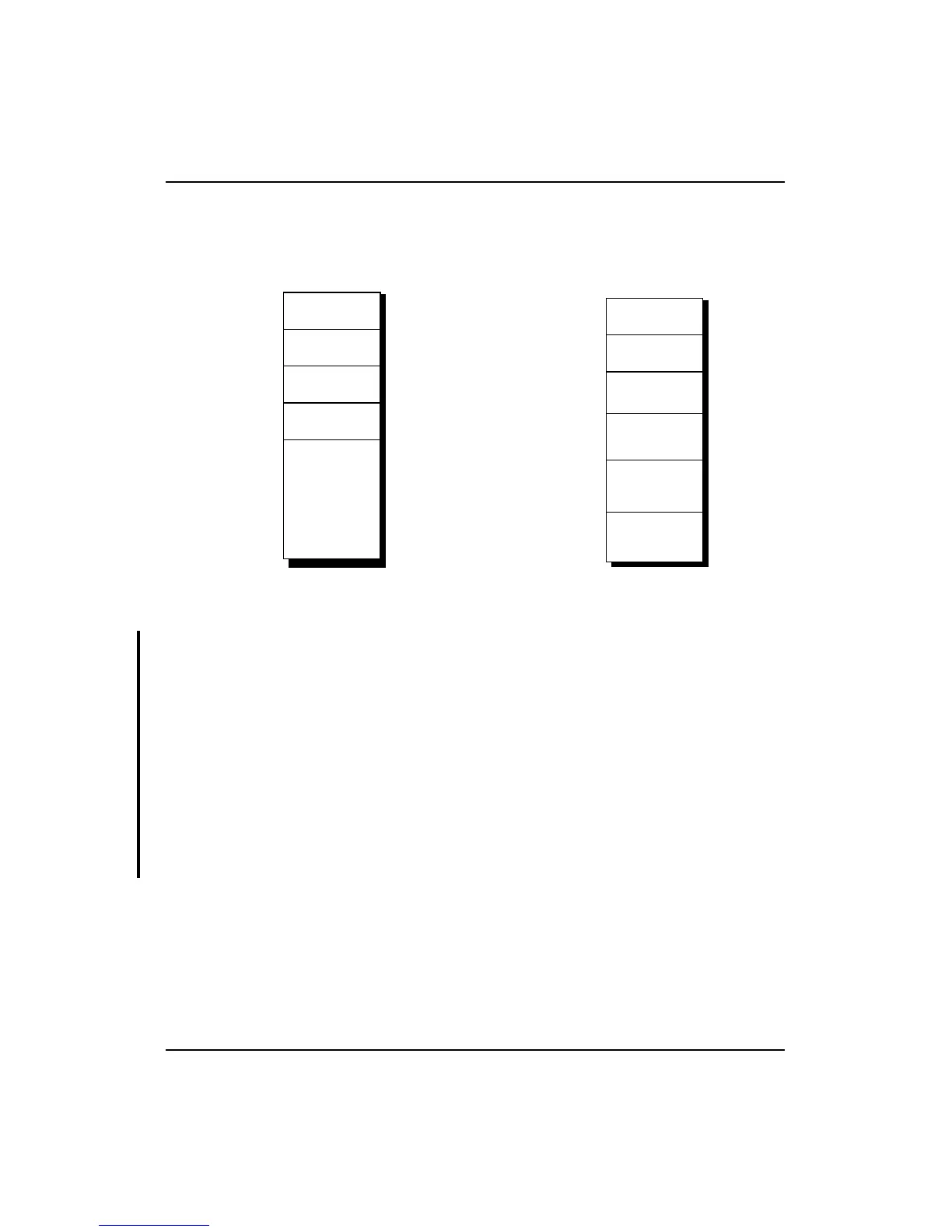
Figure 4-5 shows Supervisor mode address mapping. Table 4-2 lists the
characteristics of the supervisor mode segments; descriptions of the
address spaces follow.
Figure 4-5 Supervisor Mode Address Space
*NOTE: The R4000 uses 64-bit addresses internally. In 32-bit mode,
a valid address must be a 32-bit signed number, where bits 63:32 = bit
31. In normal operation it is not possible for a 32-bit Supervisor-mode
program to create an invalid address through arithmetic operations.
However 32-bit-mode Supervisor programs must not create addresses
using base register+offset calculations that produce a 32-bit 2’s-
complement overflow; in specific, there are two prohibited cases:
• offset with bit 15 = 0 and base register with bit 31 = 0, but (base
register+offset) bit 31 = 1
• offset with bit 15 = 1 and base register with bit 31 = 1, but (base
register+offset) bit 31 = 0
Using this invalid address produces an undefined result.
2 GB
Mapped
Mapped
suseg
Address
0.5 GB
error
sseg
Address
error
Address
error
Mapped
xsuseg
Address
0.5 GB
error
xsseg
1 TB
Mapped
Address
error
32-bit*
64-bit
csseg
0x FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF
0x 4000 0100 0000 0000
0x 0000 0000 0000 0000
0x FFFF FFFF E000 0000
0x FFFF FFFF C000 0000
0x 4000 0000 0000 0000
0x 0000 0100 0000 0000
0x FFFF FFFF
0x 8000 0000
0x 0000 0000
0x E000 0000
0x C000 0000
0x A000 0000
Address
error
1 TB
Mapped
 Loading...
Loading...