MIPS R4000 Microprocessor User's Manual 251
Cache Organization, Operation, and Coherency
In all R4000 processors, the W (write-back) bit, not the cache state,
indicates whether or not the primary cache contains modified data that
must be written back to memory or to the secondary cache.
Accessing the Primary Caches
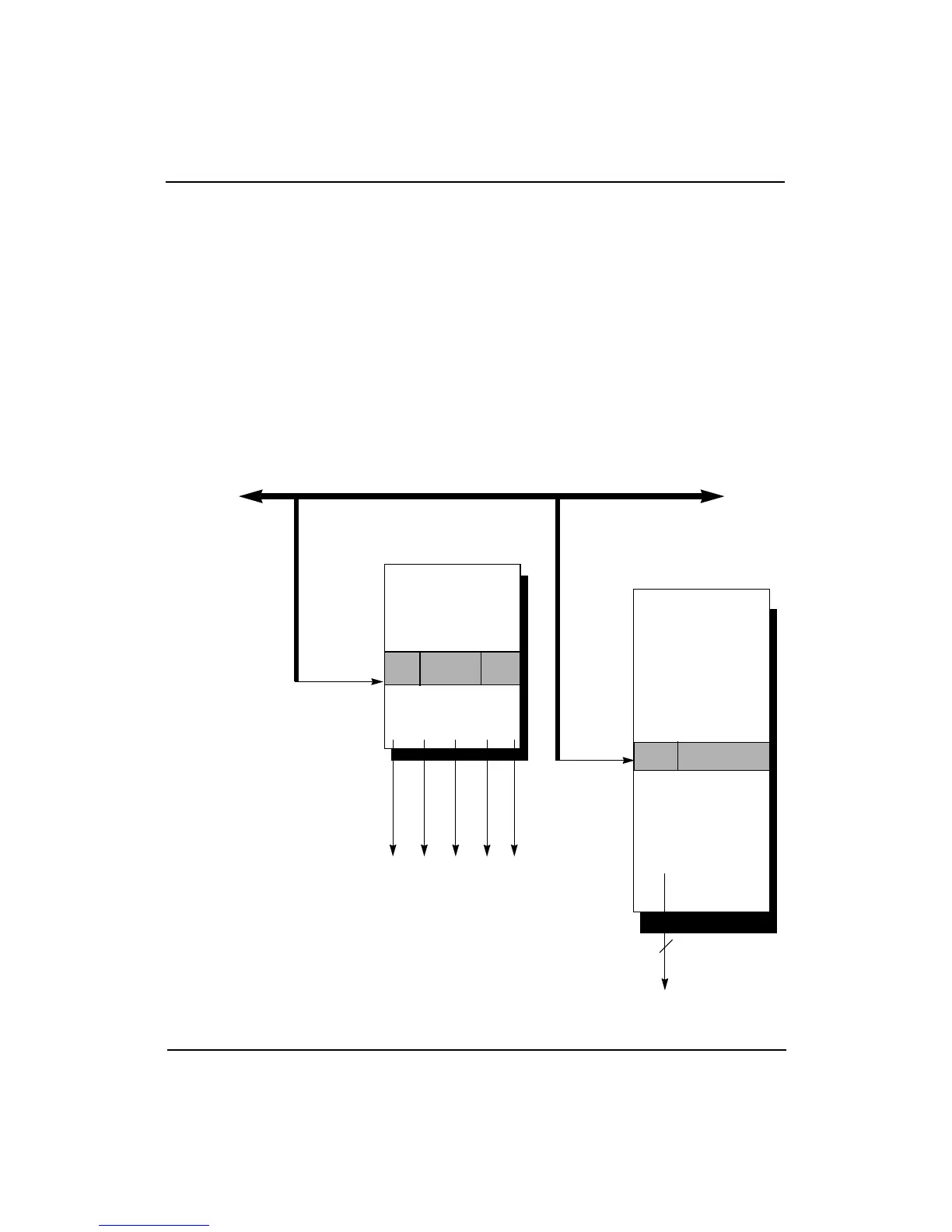
Figure 11-5 shows the virtual address (VA) index into the primary caches.
Each instruction and data cache range in size from 8 Kbytes to 32 Kbytes;
therefore, the number of virtual address bits used to index the cache
depends on the cache size. For example, VA(12:4) accesses a 8-Kbyte page
tag in a cache with a 4-word line (VA(12) addresses 8 Kbytes and VA(4)
provides quadword resolution); similarly, VA(14:5) accesses an 8-word
tag: VA(5) provides octalword access in a 32-Kbyte cache (VA(14)
addresses 32 Kbytes).
Figure 11-5 Primary Cache Data and Tag Organization
Tags
VA(12:n*) for 8 Kbyte
to
VA(14:n*) for 32 Kbyte
VA(12:n*)
to
VA(14:n*)
Data
W W’ State P
Data
64
Tag line
Data line
Tag
*n = 4 for 4-word lines
n = 5 for 8-word lines
 Loading...
Loading...