MIPS R4000 Microprocessor User's Manual 189
Floating-Point Exceptions
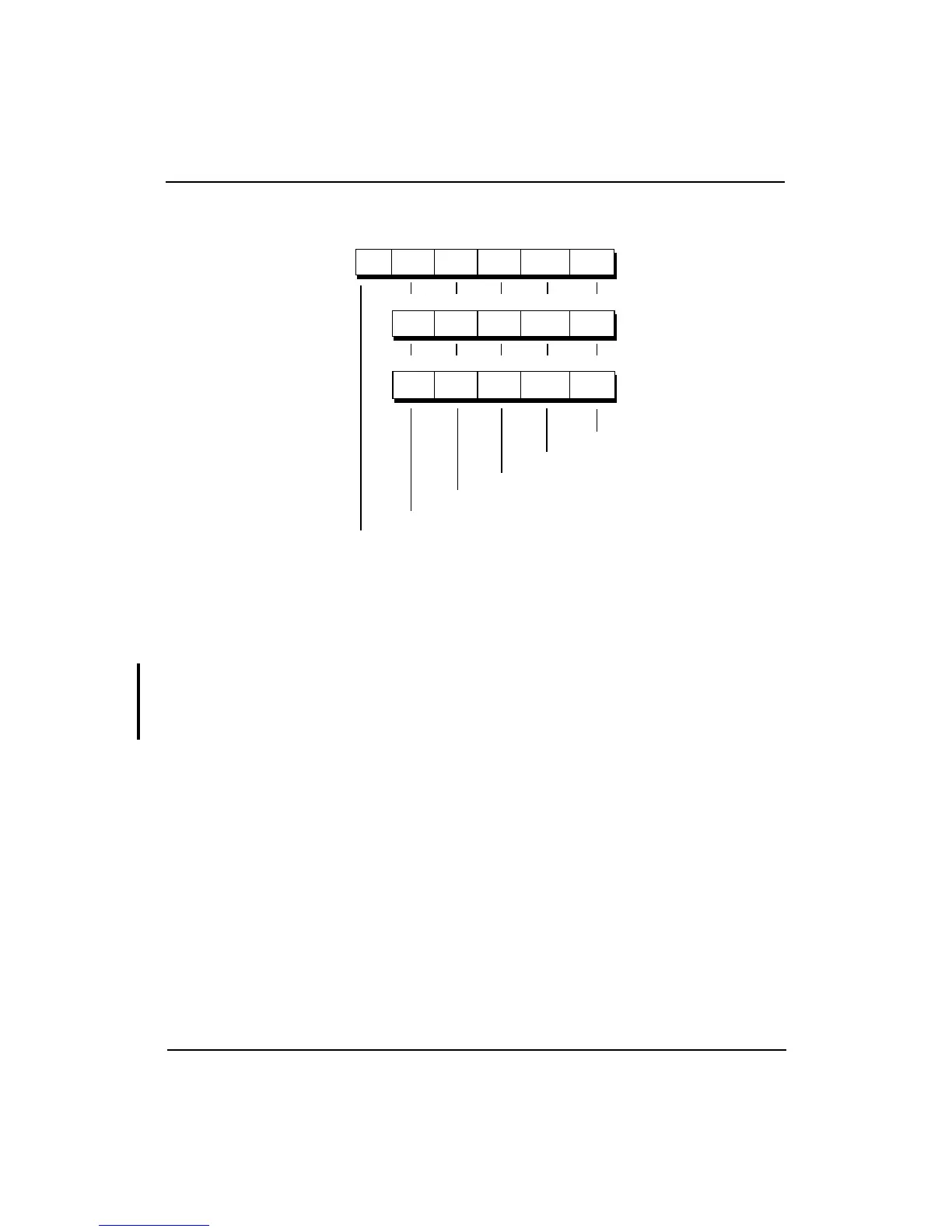
Figure 7-1 Control/Status Register Exception/Flag/Trap/Enable Bits
Each of the five IEEE Standard 754 exceptions (V, Z, O, U, I) is associated
with a trap under user control, and is enabled by setting one of the five
Enable bits. When an exception occurs, the corresponding Cause bit is set.
If the corresponding Enable bit is not set, the Flag bit is also set. If the
correspondingEnable bit is set, the Flag bit is not set and the FPU generates
an interrupt to the CPU. Subsequent exception processing allows a trap to
be taken.
7.2 Exception Trap Processing
When a floating-point exception trap is taken, the Cause register indicates
the floating-point coprocessor is the cause of the exception trap. The
Floating-Point Exception (FPE) code is used, and the Cause bits of the
floating-point Control/Status register indicate the reason for the floating-
point exception. These bits are, in effect, an extension of the system
coprocessor Cause register.
EZOUIV
17 16 15 14 13 12
Unimplemented Operation
Invalid Operation
Division by Zero
Inexact Operation
Overflow
Underflow
Bit #
ZO U IV
11 10 9 8 7
Bit #
ZO U IV
6543 2
Bit #
Cause
Bits
Flag
Bits
Enable
Bits
 Loading...
Loading...