Chapter 16
418 MIPS R4000 Microprocessor User's Manual
Detecting Data Transmission Errors
The following procedure detects data transmission errors.
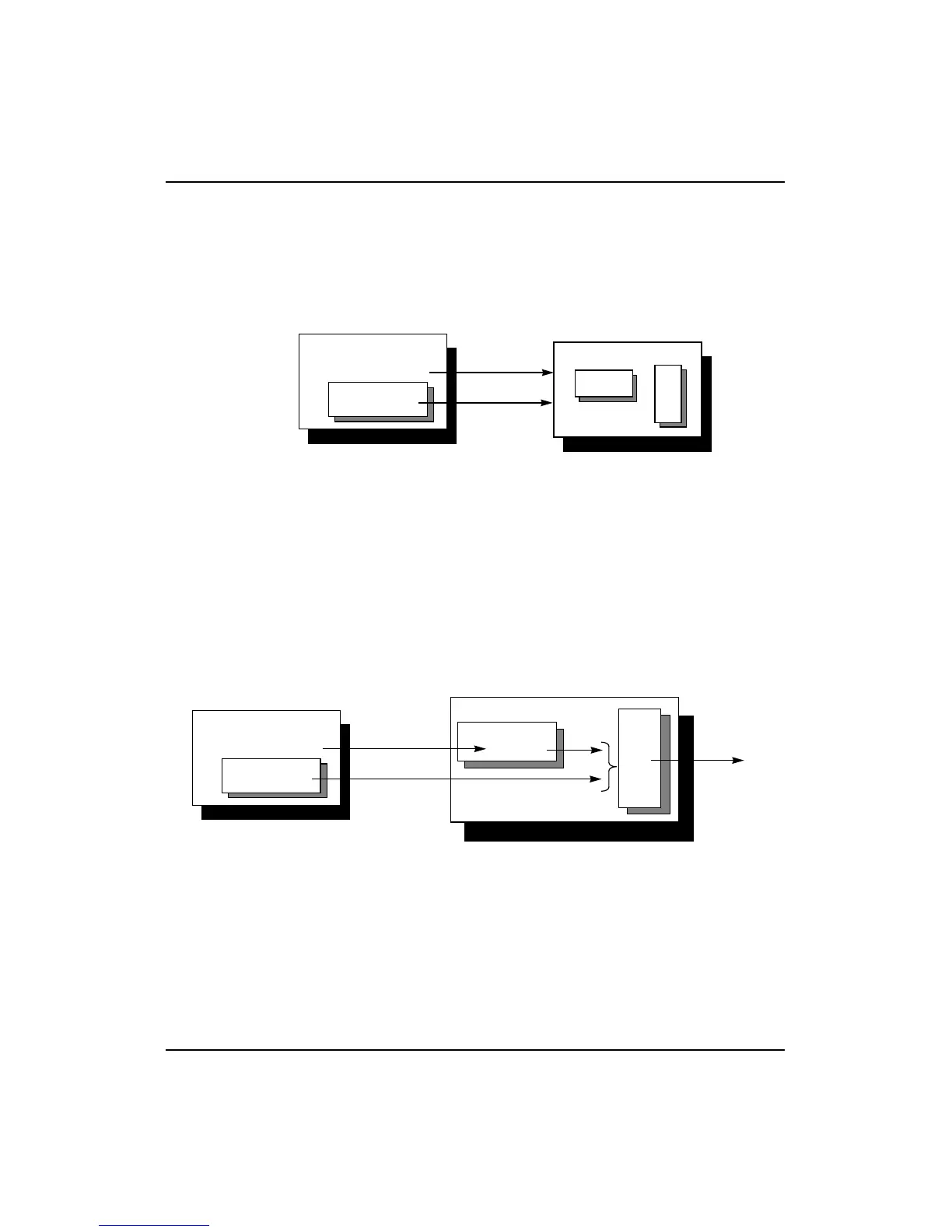
1. System A transmits a 64-bit doubleword together with 8 bits of
SECDED ECC (see Figure 16-2).
Figure 16-2 Detecting ECC Errors: Transmitting Data and ECC
2. System B receives the data doubleword, together with the byte of
ECC check code.
3. To verify proper transmission of the 64-bit doubleword and 8-bit
ECC check code, system B generates its own 8-bit ECC check code
from the 64-bit doubleword of System A, as shown in Figure 16-3.
4. System B executes an Exclusive-OR (XOR) on the check bits of
System A with its own newly-generated ECC check bits, (see
Figure 16-3). The output of this XOR is called the syndrome.
Figure 16-3 Detecting ECC Errors: Deriving the Syndrome
5. If the syndrome is 0000 0000
2
, the data System B received, together
with the newly-generated ECC check bits from System B, are the
same as the data and check bits from System A. If the syndrome
is any other value than 0000 0000
2
, it is assumed either the
received word or the received check bits are in error.
System A
Data(63:0)
ECC(7:0)
System B
ECC Generator
System A
Data(63:0)
ECC(7:0)
System B
ECC Generator
ECC Checker
Exclusive OR
Syndrome
 Loading...
Loading...