Chapter 5
102 MIPS R4000 Microprocessor User's Manual
Context Register (4)
The Context register is a read/write register containing the pointer to an
entry in the page table entry (PTE) array; this array is an operating system
data structure that stores virtual-to-physical address translations. When
there is a TLB miss, the CPU loads the TLB with the missing translation
from the PTE array. Normally, the operating system uses the Context
register to address the current page map which resides in the kernel-
mapped segment, kseg3. The Context register duplicates some of the
information provided in the BadVAddr register, but the information is
arranged in a form that is more useful for a software TLB exception
handler. Figure 5-1 shows the format of the Context register; Table 5-2
describes the Context register fields.
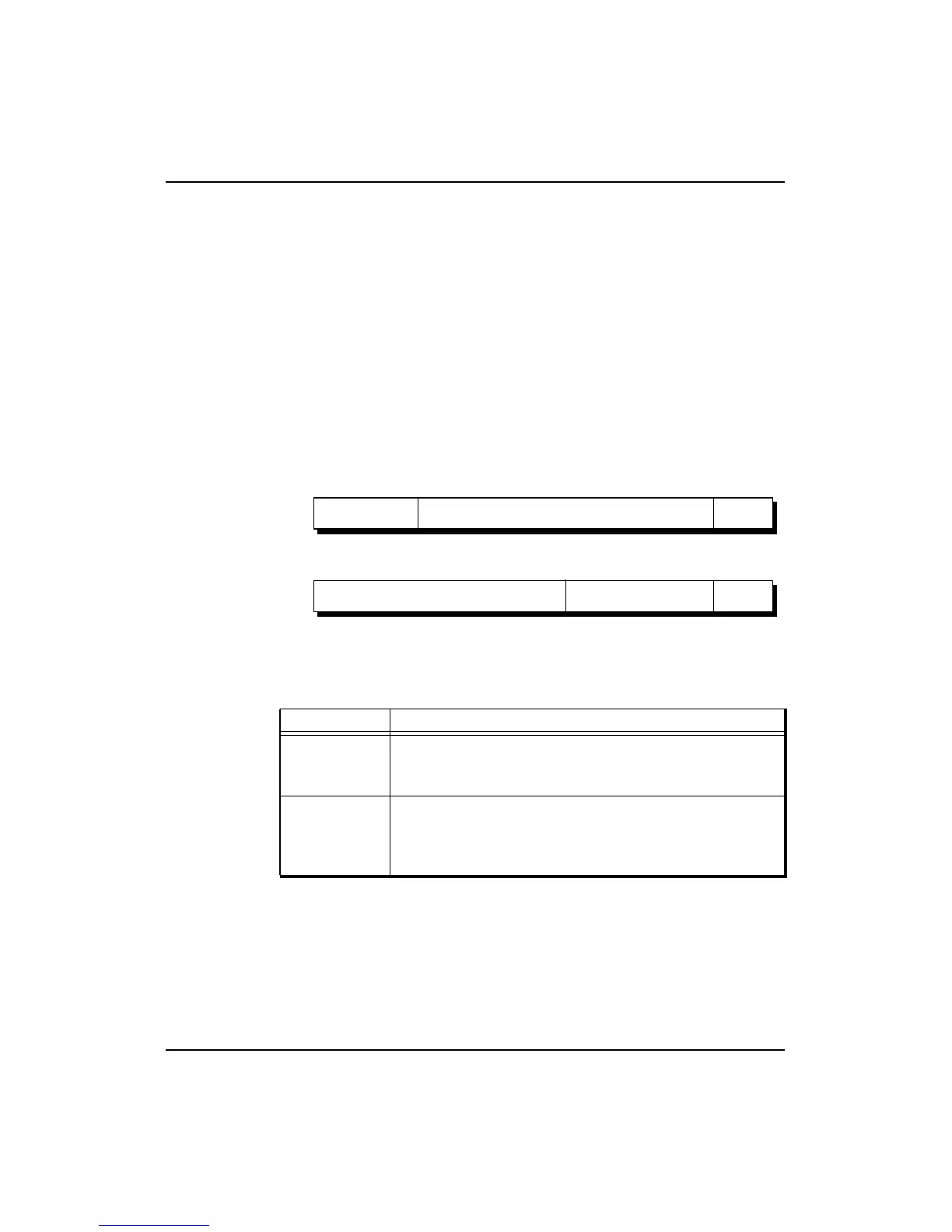
Figure 5-1 Context Register Format
Table 5-2 Context Register Fields
The 19-bit BadVPN2 field contains bits 31:13 of the virtual address that
caused the TLB miss; bit 12 is excluded because a single TLB entry maps
to an even-odd page pair. For a 4-Kbyte page size, this format can directly
address the pair-table of 8-byte PTEs. For other page and PTE sizes,
shifting and masking this value produces the appropriate address.
Field Description
BadVPN2
This field is written by hardware on a miss. It contains
the virtual page number (VPN) of the most recent
virtual address that did not have a valid translation.
PTEBase
This field is a read/write field for use by the operating
system. It is normally written with a value that allows
the operating system to use the Context register as a
pointer into the current PTE array in memory.
23 22 4 331 0
9
PTEBase BadVPN2
19 4
0
Context Register
23 22 4 363 0
41
PTEBase
BadVPN2
19 4
0
32-bit
Mode
64-bit
Mode
 Loading...
Loading...