Chapter 11
250 MIPS R4000 Microprocessor User's Manual
Organization of the Primary Data Cache (D-Cache)
Each line of primary D-cache data has an associated 29-bit tag that
contains a 24-bit physical address, 2-bit cache line state, a write-back bit, a
parity bit for the physical address and cache state fields, and a parity bit
for the write-back bit. Byte parity is used on D-cache data.
The R4000 processor primary D-cache has the following characteristics:
• write-back
• direct-mapped
• indexed with a virtual address
• checked with a physical tag
• organized with either a 4-word (16-byte) or 8-word (32-byte)
cache line.
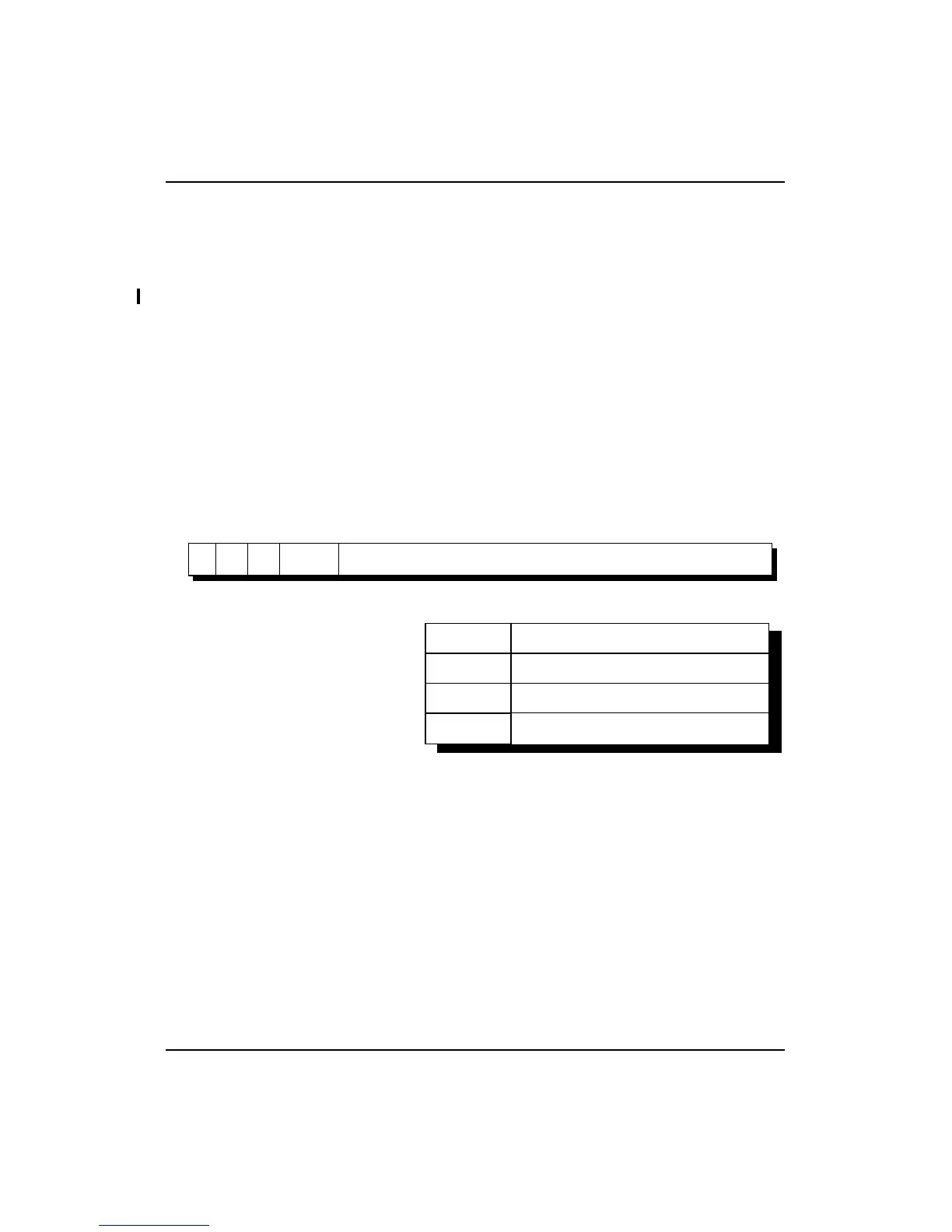
Figure 11-4 shows the format of a 8-word (32-byte) primary D-cache line.
Figure 11-4 R4000 8-Word Primary Data Cache Line Format
W’ Even parity for the write-back bit
W Write-back bit (set if cache line has been written)
P Even parity for the PTag and CS fields
CS Primary cache state:
0 = Invalid in all R4000 configurations
1 = Shared (either Clean or Dirty) in R4000MC configuration only
2 = Clean Exclusive in R4000SC and MC configurations only
3 = Dirty Exclusive in all R4000 configurations
PTag Physical tag (bits 35:12 of the physical address)
DataP Even parity for the data
Data Cache data
24
28 0
1
W’
2627
W PTag
1
P CS
12
25 24 23
8
71 06364
64
DataP Data
Data
DataP Data
DataP Data
DataP Data
DataP Data
DataP Data
 Loading...
Loading...