MIPS R4000 Microprocessor User's Manual 271
Cache Organization, Operation, and Coherency
Intervention
An intervention request causes the processor to return the secondary
cache state of the specified cache line and, under certain conditions related
to the state of the cache line and the nature of the intervention request, the
contents of the specified secondary cache line.
At the same time, the processor atomically sets the state of the specified
cache line in both the primary and secondary caches according to the value
of the SysCmd(2:0) bits which define cache state change, and are supplied
by an external agent.
11.11 Coherency Conflicts
The R4000MC processor must handle competing coherency conflicts that
arise from the processor and an external source. This section describes
how coherency conflicts arise and how they are handled. A system model
illustrates the implications of coherency conflicts in a multiprocessor
environment; a coherent read request cycle is described at the end of this
section.
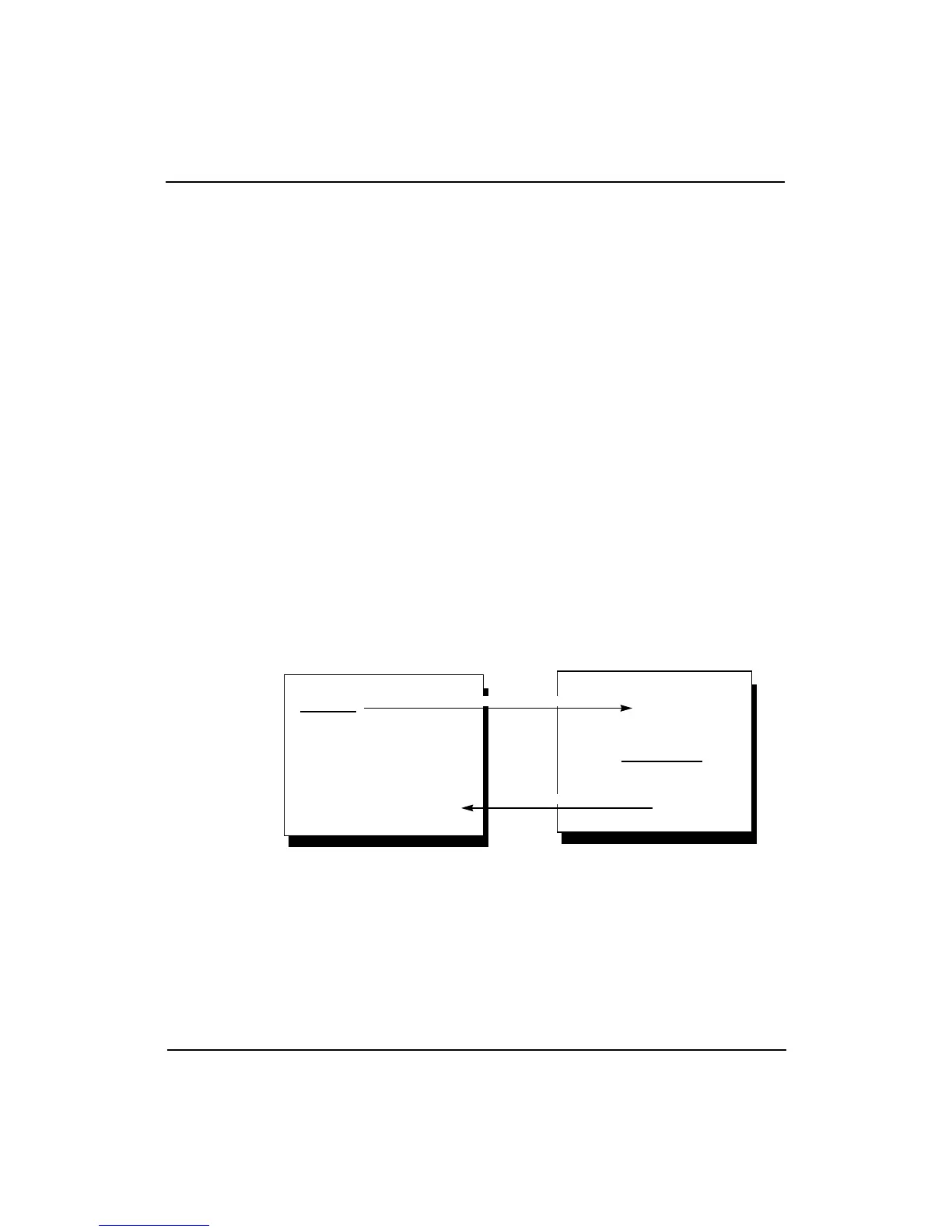
Figure 11-11 shows the R4000MC processor issuing processor coherency
requests and accepting external coherency requests.
Figure 11-11 Coherency Requests: Processor and External
External Agent
• invalidate
• update
• snoop
• intervention
R4000MC
• coherent read
• invalidate
• update
processor coherency request
external coherency request
 Loading...
Loading...