Chapter 12
362 MIPS R4000 Microprocessor User's Manual
Release Latency
Release latency is generally defined as the number of cycles the processor
can wait to release the System interface to slave state for an external
request. When no processor requests are in progress, internal activity—
such as refilling the primary cache from the secondary cache—can cause
the processor to wait some number of cycles before releasing the System
interface. Release latency is therefore more specifically defined as the
number of cycles that occur between the assertion of ExtRqst* and the
assertion of Release*.
There are three categories of release latency:
• Category 1: when the external request signal is asserted two
cycles before the last cycle of a processor request, or two cycles
before the last cycle of the last request in a cluster.
• Category 2: when the external request signal is not asserted
during a processor request or cluster, or is asserted during the
last cycle of a processor request or cluster.
• Category 3: when the processor makes an uncompelled change
to slave state.
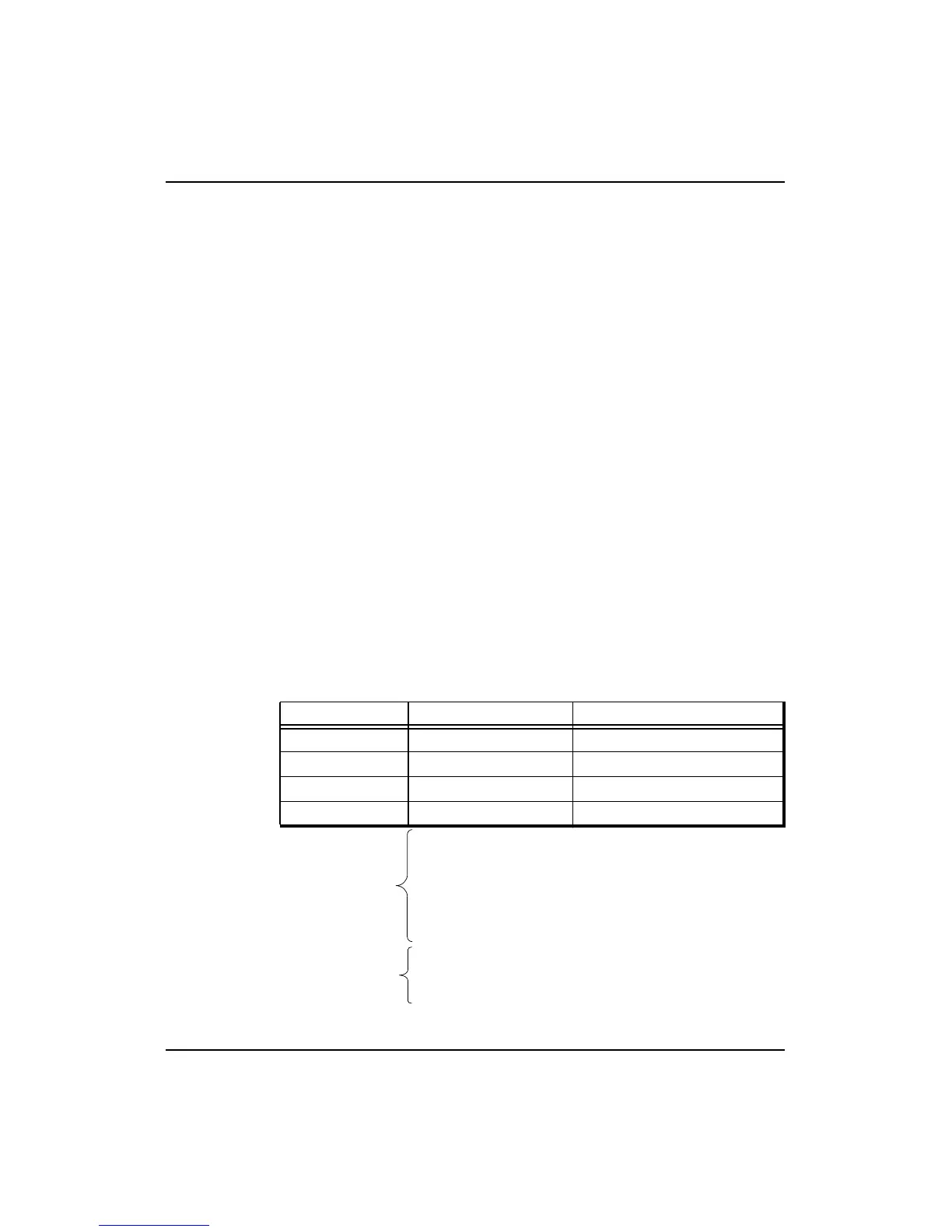
Table 12-9 summarizes the minimum and maximum release latencies for
requests that fall into categories 1, 2, 3a and 3b. Note that the maximum
and minimum cycle count values are subject to change.
Table 12-9 Release Latency for External Requests
Category Minimum PCycles Maximum PCycles
14 6
24 24
3a 0 See (3a), below
3b 0 See (3b), below
(3a) Read =
T
dis
+ 4- or 8-word Secondary cache write cycle time
(depending upon Primary cache size)
+ 4-word Secondary cache write cycle time
+ Secondary cache line size
+ 16 PCycles
(3b) Read
With Write
Forthcoming
4-word Secondary cache Write cycle time
+ 4 PCycles
 Loading...
Loading...