MIPS R4000 Microprocessor User's Manual 363
System Interface
External Request Response Latency
The number of cycles the processor takes to respond to an external
intervention request, read request, or snoop request, are referred to as the
intervention response latency, external read response latency, or snoop response
latency, respectively.
The number of latency cycles is the number of unused cycles between the
address cycle of the request and the first data cycle of the response.
Intervention response latency and snoop response latency are a function
of processor internal activity and secondary cache access time. Table 12-
10 summarizes the minimum and maximum intervention response
latency and snoop response latency. Note that the latency values are
subject to change.
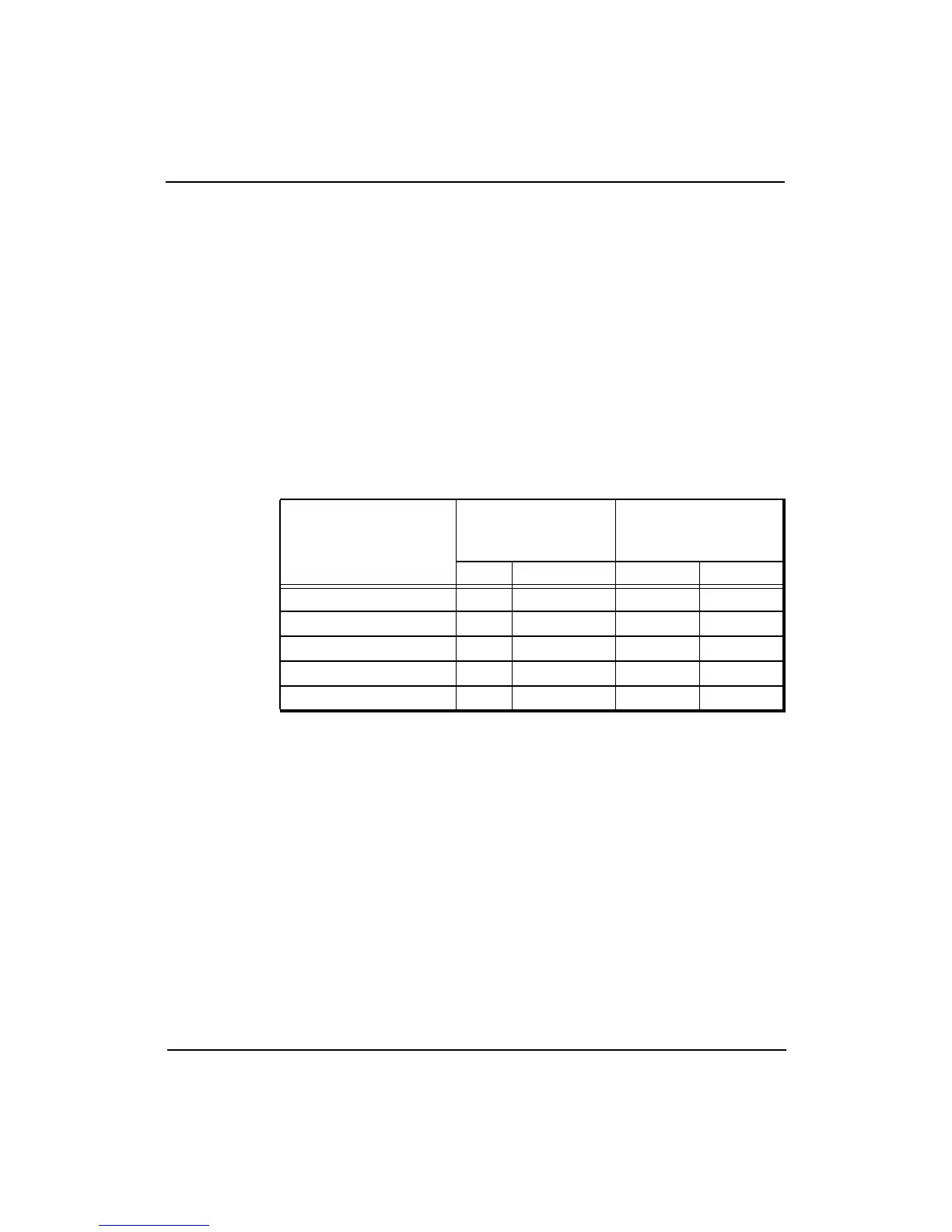
Table 12-10 Intervention Response and Snoop Response Latencies
External read response latency is a function of processor internal activity.
Minimum and maximum external read response latency is 4 PCycles.
Maximum Secondary
Cache
Access
Intervention
Response
Latency
Snoop Response
Latency
Min Max Min Max
1-4 PCycles 6 26 6 26
5-6 PCycles 8 28 8 28
7-8 PCycles 10 30 10 30
9-10 PCycles 12 32 12 32
11-12 PCycles 14 34 14 34
 Loading...
Loading...