MIPS R4000 Microprocessor User's Manual 105
CPU Exception Processing
Status Register (12)
The Status register (SR) is a read/write register that contains the operating
mode, interrupt enabling, and the diagnostic states of the processor. The
following list describes the more important Status register fields; Figures
5-5 and 5-6 show the format of the entire register, including descriptions
of the fields. Some of the important fields include:
• The 8-bit Interrupt Mask (IM) field controls the enabling of eight
interrupt conditions. Interrupts must be enabled before they
can be asserted, and the corresponding bits are set in both the
Interrupt Mask field of the Status register and the Interrupt
Pending field of the Cause register. For more information, refer
to the Interrupt Pending (IP) field of the Cause register and
Chapter 15, which describes the interrupts.
• The 4-bit Coprocessor Usability (CU) field controls the usability
of 4 possible coprocessors. Regardless of the CU0 bit setting,
CP0 is always usable in Kernel mode.
• The 9-bit Diagnostic Status (DS) field is used for self-testing,
and checks the cache and virtual memory system.
• The Reverse-Endian (RE) bit, bit 25, reverses the endianness of
the machine. The processor can be configured as either little-
endian or big-endian at system reset; reverse-endian selection
is used in Kernel and Supervisor modes, and in the User mode
when the RE bit is 0. Setting the RE bit to 1 inverts the User
mode endianness.
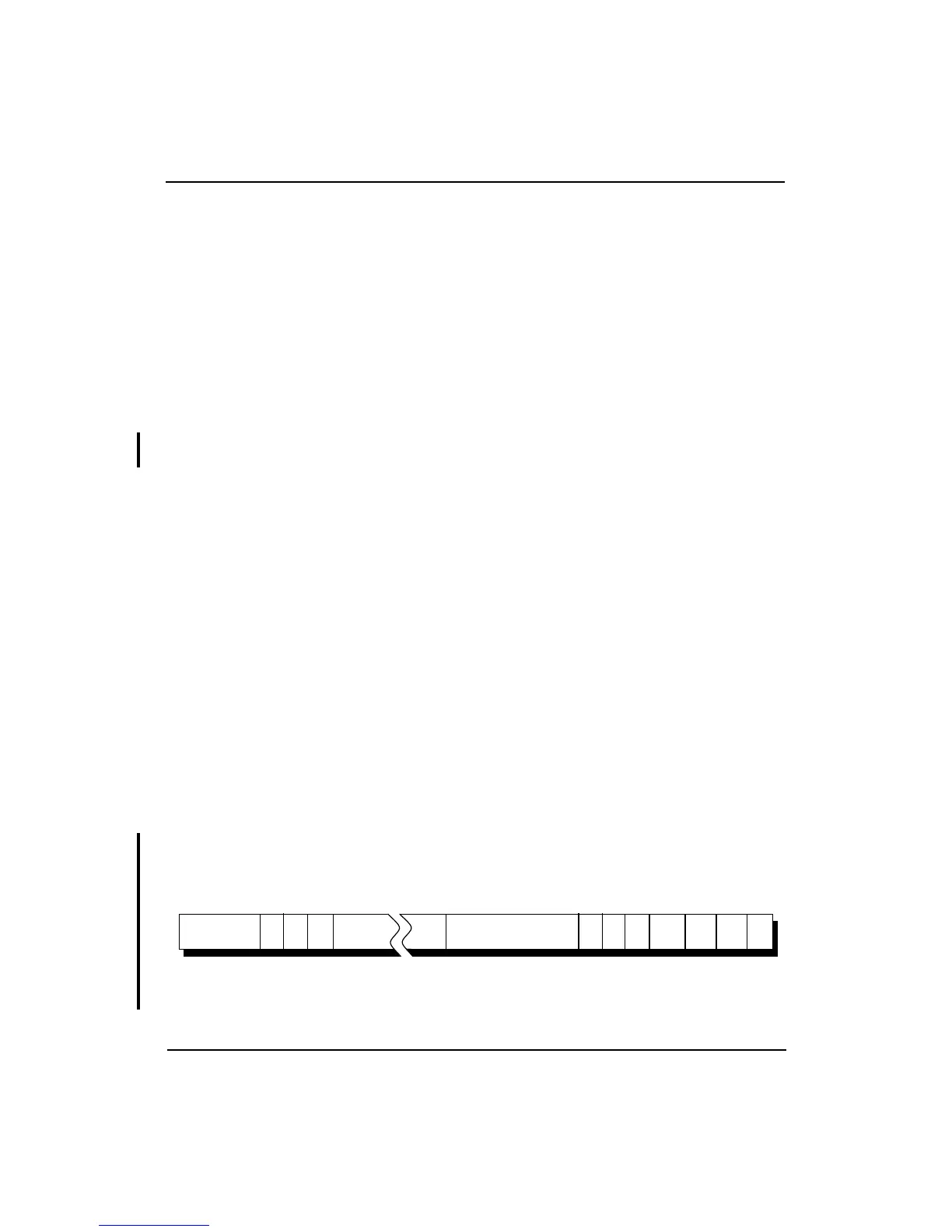
Status Register Format
Figure 5-5 shows the format of the Status register. Table 5-3 describes the
Status register fields. Figure 5-6 and Table 5-4 provide additional
information on the Diagnostic Status (DS) field. All bits in the DS field
except TS are readable and writable.
Figure 5-5 Status Register
Status Register
CU
4
IM7 - IM0
31 1528 27 25 24 16
9
87 54 3 2 1 0
KSU ERL EXL IE
82111
(Cu3:.Cu0)
RE
26
1
DS
KX UX
6
SX
111
11
RP FR
 Loading...
Loading...