Chapter 11
264 MIPS R4000 Microprocessor User's Manual
11.8 Cache Coherency Overview
Systems using more than one R4000MC processor must have a mechanism
to maintain data consistency throughout a multi-cache, multiprocessor
system. This mechanism is called a cache coherency protocol.
Cache Coherency Attributes
Cache coherency attributes are necessary to ensure the consistency of data
throughout the multitude of caches that can be present in the
multiprocessor environment.
Bits in the translation look-aside buffer (TLB) control coherency on a per-
page basis. Specifically, the TLB contains 3 bits per entry that provide five
possible coherency attributes; they are listed below and described more
fully in the following sections.
• uncached (R4000PC, R4000SC, R4000MC)
• noncoherent (R4000PC, R4000SC, R4000MC)
• sharable (R4000MC only, with secondary cache)
• update (R4000MC only, with secondary cache)
• exclusive (R4000MC only, with secondary cache)
Only uncached or noncoherent attributes can be used by an R4000PC or an
R4000SC processor.
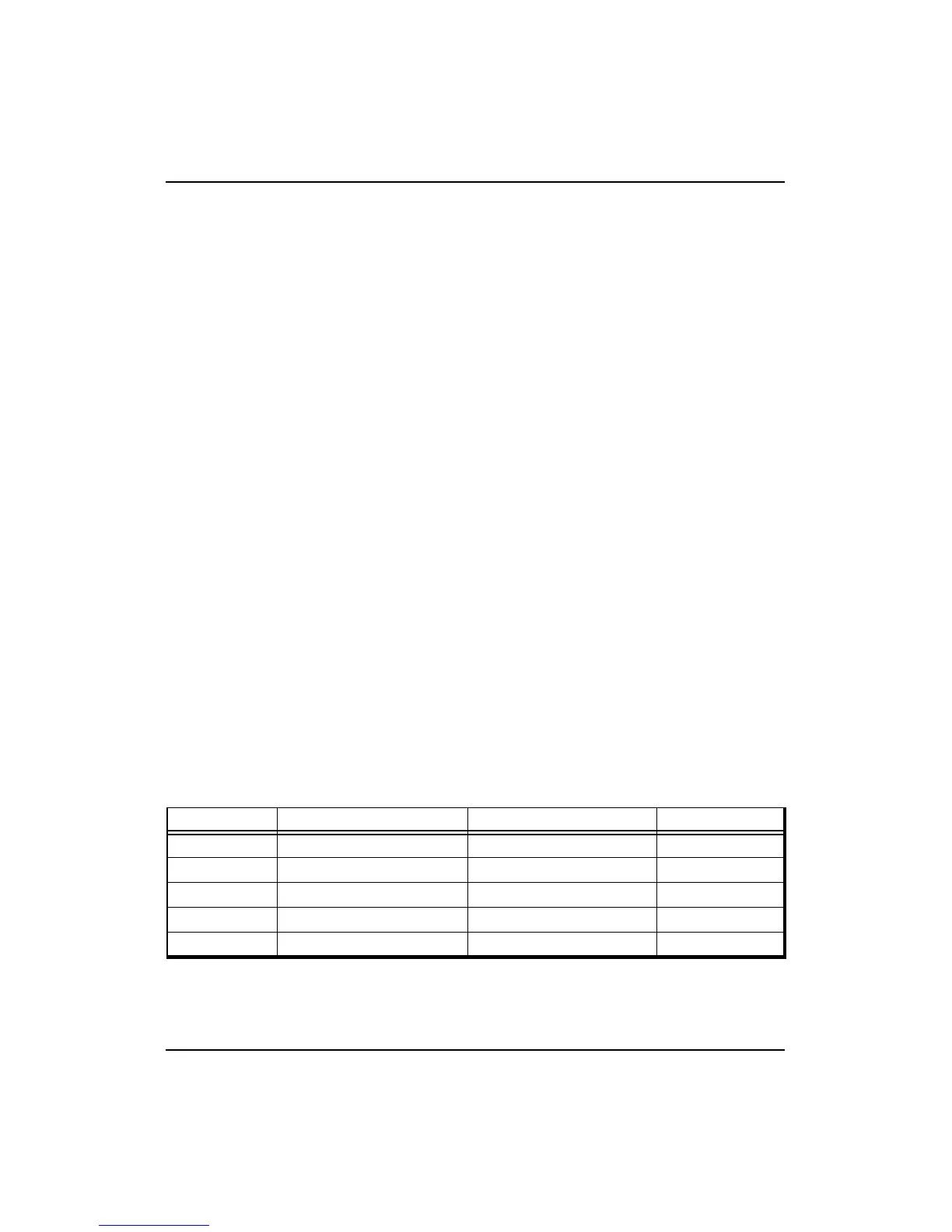
Table 11-4 summarizes the behavior of the processor on load misses, store
misses, and store hits to shared cache lines for each of the five coherency
attributes listed above. The following sections describe in detail the five
coherency attributes.
Table 11-4 Coherency Attributes and Processor Behavior
† These should not occur under normal circumstances.
Attribute Load Miss Store Miss Store Hit Shared
Uncached Main memory read Main memory write NA
Noncoherent Noncoherent read Noncoherent read Invalidate
†
Exclusive Coherent read exclusive Coherent read exclusive Invalidate
†
Sharable Coherent read Coherent read exclusive Invalidate
Update Coherent read Coherent read Update

 Loading...
Loading...