MIPS R4000 Microprocessor User's Manual 299
System Interface
12.3 System Interface Protocols
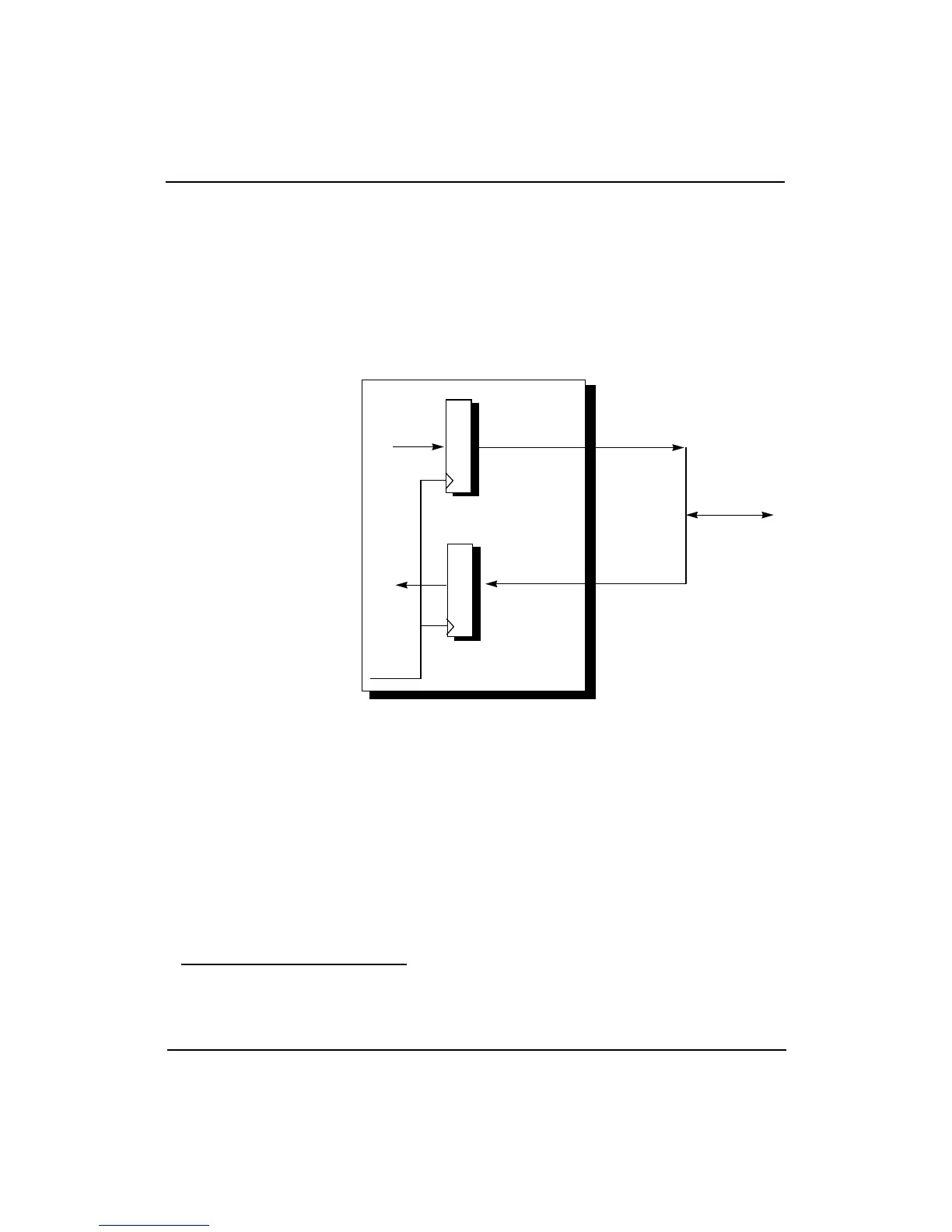
Figure 12-4 shows the System interface operates from register to register.
That is, processor outputs come directly from output registers and begin
to change with the rising edge of SClock.
†
Processor inputs are fed directly to input registers that latch these input
signals with the rising edge of SClock. This allows the System interface to
run at the highest possible clock frequency.
Figure 12-4 System Interface Register-to-Register Operation
Master and Slave States
When the R4000 processor is driving the SysAD and SysCmd buses, the
System interface is in master state. When the external agent is driving the
SysAD and SysCmd buses, the System interface is in slave state.
In master state, the processor asserts the signal ValidOut* whenever the
SysAD and SysCmd buses are valid.
In slave state, the external agent asserts the signal ValidIn* whenever the
SysAD and SysCmd buses are valid.
† SClock is an internal clock used by the processor to sample data at the System interface
and to clock data into the processor System interface output registers; see Chapter 10 for
more details.
R4000
Input data
Output data
SClock

 Loading...
Loading...