MIPS R4000 Microprocessor User's Manual 63
Memory Management
4.2 Address Spaces
This section describes the virtual and physical address spaces and the
manner in which virtual addresses are converted or “translated” into
physical addresses in the TLB.
Virtual Address Space
The processor virtual address can be either 32 or 64 bits wide,
†
depending
on whether the processor is operating in 32-bit or 64-bit mode.
• In 32-bit mode, addresses are 32 bits wide. The maximum user
process size is 2 gigabytes (2
31
).
• In 64-bit mode, addresses are 64 bits wide. The maximum user
process size is 1 terabyte (2
40
).
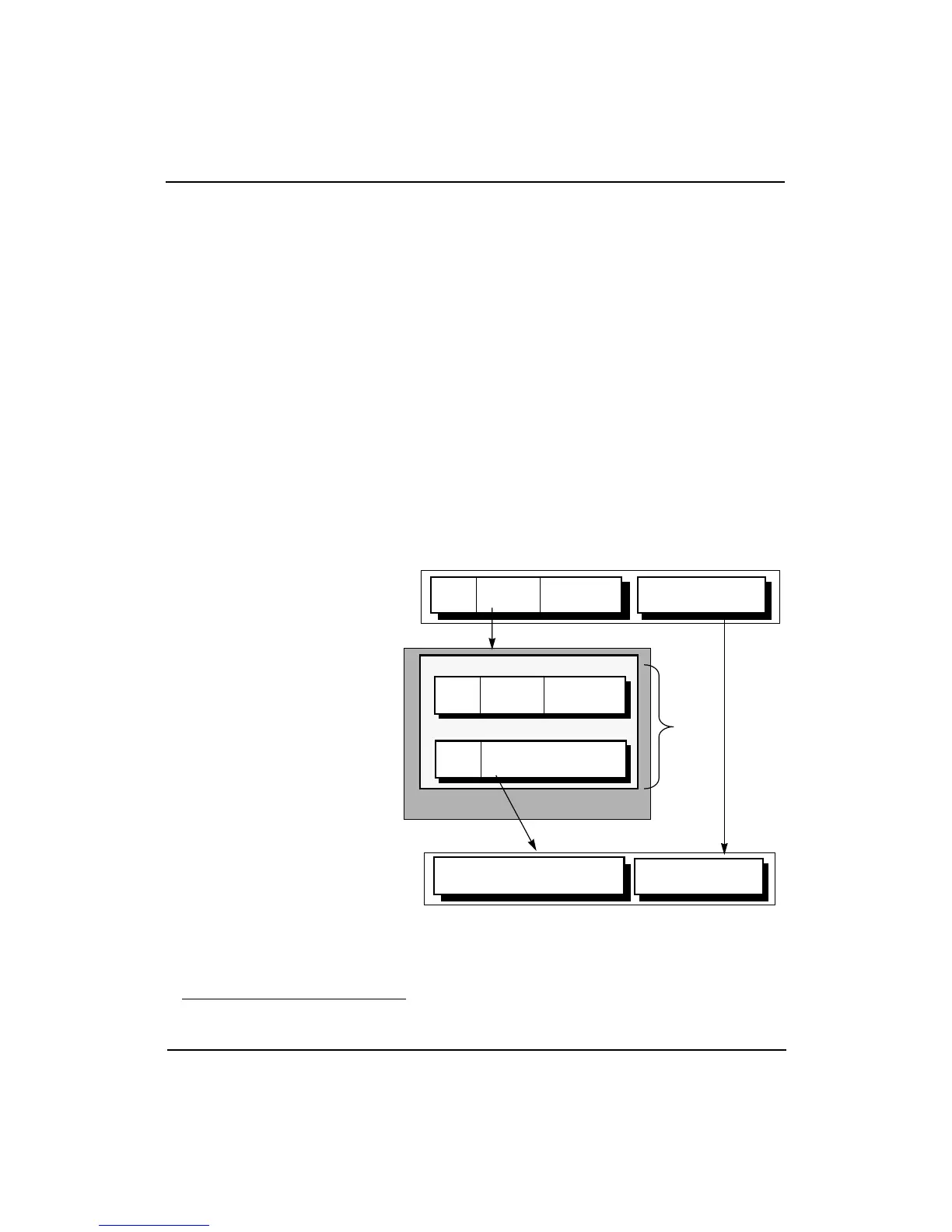
Figure 4-1 shows the translation of a virtual address into a physical
address.
Figure 4-1 Overview of a Virtual-to-Physical Address Translation
† Figure 4-8 shows the 32-bit and 64-bit versions of the processor TLB entry.
1. Virtual address (VA) represented by the
virtual page number (VPN) is compared
with tag in TLB.
Virtual address
2. If there is a match, the page frame
number (PFN) representing the upper
bits of the physical address (PA) is
output from the TLB.
VPN
ASID
G
VPN
ASID
G
PFN
TLB
Physical address
PFN
Offset
Offset
TLB
3. The Offset, which does not pass through
the TLB, is then concatenated to the PFN.
Entry
 Loading...
Loading...