Chapter 12
356 MIPS R4000 Microprocessor User's Manual
12.7 Data Rate Control
The System interface supports a maximum data rate of one doubleword
per cycle. The data rate the processor can support is directly related to the
secondary cache access time; if the access time is too long, the processor
cannot transmit and accept data at the maximum rate.
The rate at which data is delivered to the processor can be determined by
the external agent—for example, the external agent can drive data and
assert ValidIn* every n cycles, instead of every cycle. An external agent
can deliver data at any rate it chooses, but must not deliver data to the
processor any faster than the processor is capable of receiving it.
The processor only accepts cycles as valid when ValidIn* is asserted and
the SysCmd bus contains a data identifier; thereafter, the processor
continues to accept data until it receives the data word tagged as the last
one.
Data Transfer Patterns
A data pattern is a sequence of letters indicating the data and unused cycles
that repeat to provide the appropriate data rate. For example, the data
pattern DDxx specifies a repeatable data rate of two doublewords every
four cycles, with the last two cycles unused. Table 12-6 lists the maximum
processor data rate for each of the possible secondary cache write cycle
times, and the most efficient data pattern for each data rate.
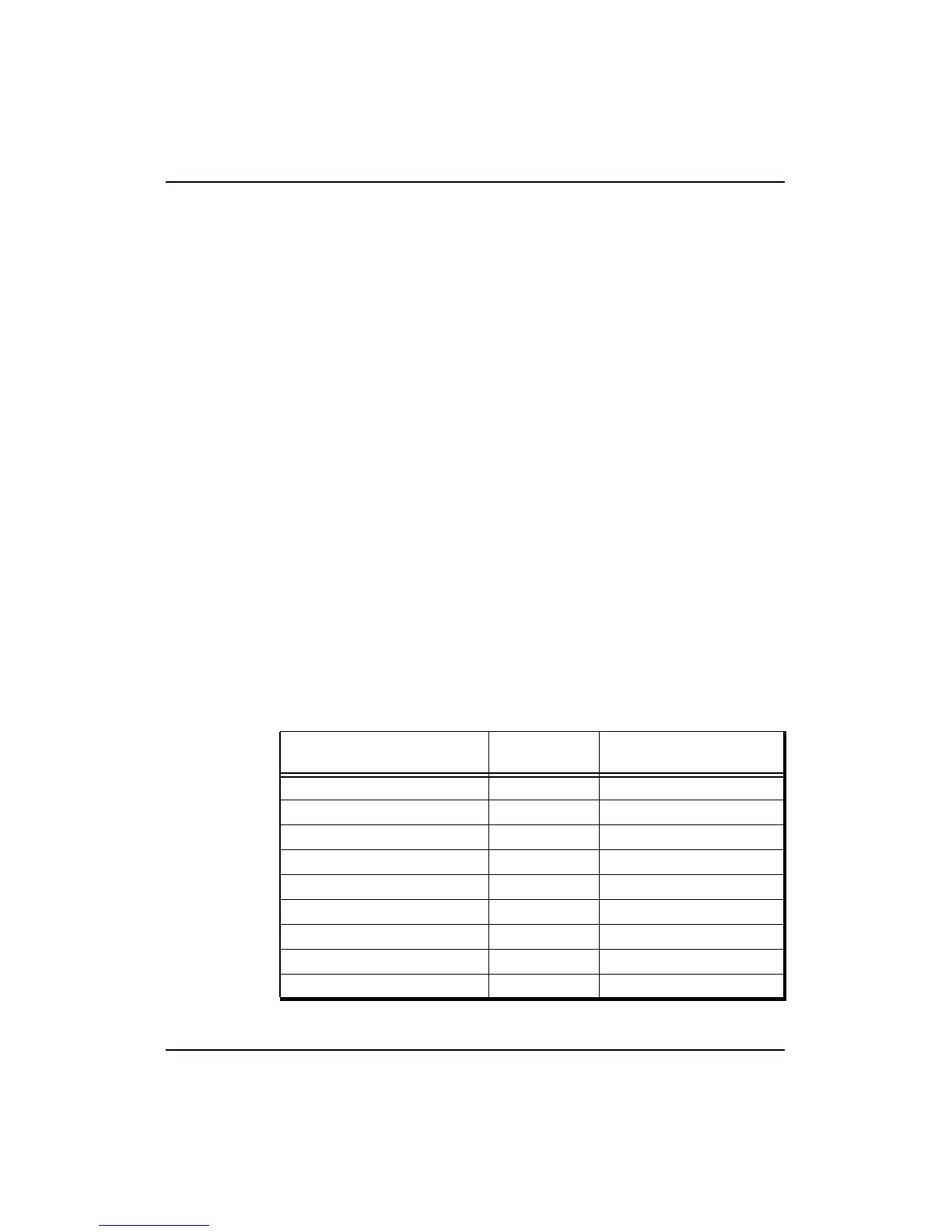
Table 12-6 Transmit Data Rates and Patterns
Maximum Data Rate Data Pattern
Maximum Secondary
Cache Access
1 Double/1 SClock Cycle D 4 PCycles
2 Doubles/3 SClock Cycles DDx 6 PCycles
1 Double/2 SClock Cycles DDxx 8 PCycles
1 Double/2 SClock Cycles DxDx 8 PCycles
2 Doubles/5 SClock Cycles DDxxx 10 PCycles
1 Double/3 SClock Cycles DDxxxx 12 PCycles
1 Double/3 SClock Cycles DxxDxx 12 PCycles
1 Double/4 SClock Cycles DDxxxxxx 16 PCycles
1 Double/4 SClock Cycles DxxxDxxx 16 PCycles
 Loading...
Loading...