MIPS R4000 Microprocessor User's Manual 75
Memory Management
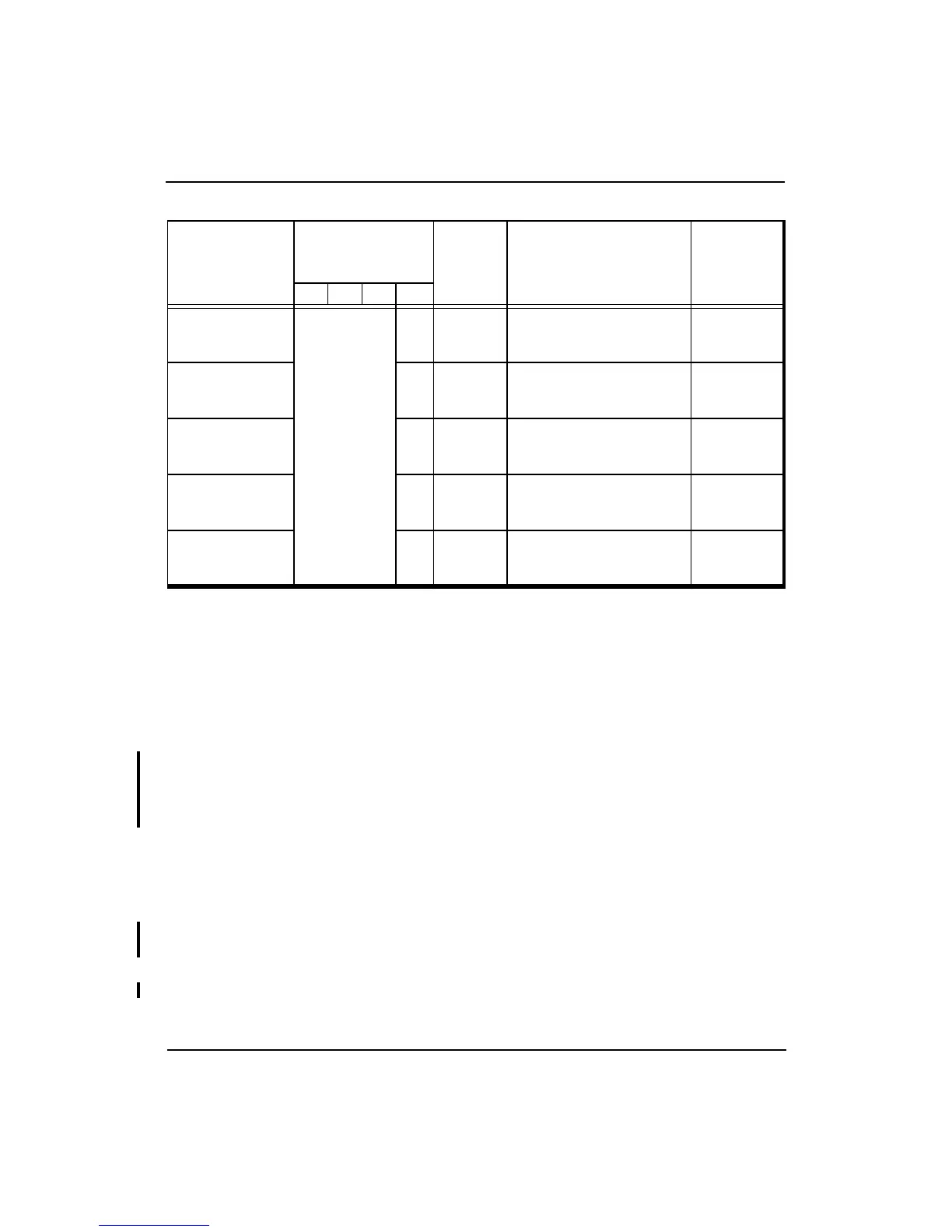
Table 4-3 32-bit Kernel Mode Segments
32-bit Kernel Mode, User Space (kuseg)
In Kernel mode, when KX = 0 in the Status register, and the most-
significant bit of the virtual address, A31, is cleared, the 32-bit kuseg virtual
address space is selected; it covers the full 2
31
bytes (2 Gbytes) of the
current user address space. The virtual address is extended with the
contents of the 8-bit ASID field to form a unique virtual address.
When ERL = 1 in the Status register, the user address region becomes a
2
31
-byte unmapped (that is, mapped directly to physical addresses)
uncached address space. See the Cache Error exception in Chapter 5 for
more information.
32-bit Kernel Mode, Kernel Space 0 (kseg0)
In Kernel mode, when KX = 0 in the Status register and the most-
significant three bits of the virtual address are 100
2
, 32-bit kseg0 virtual
address space is selected; it is the 2
29
-byte (512-Mbyte) kernel physical
space. References to kseg0 are not mapped through the TLB; the physical
address selected is defined by subtracting 0x8000 0000 from the virtual
address. The K0 field of the Config register, described in this chapter,
controls cacheability and coherency.
Address Bit
Values
Status Register
Is One Of These
Values
Segment
Name
Address Range
Segment
Size
KSU EXL ERL KX
A(31) = 0
KSU = 00
2
or
EXL = 1
or
ERL =1
0 kuseg
0x0000 0000
through
0x7FFF FFFF
2 Gbytes
(2
31
bytes)
A(31:29) = 100
2
0 kseg0
0x8000 0000
through
0x9FFF FFFF
512 Mbytes
(2
29
bytes)
A(31:29) = 101
2
0 kseg1
0xA000 0000
through
0xBFFF FFFF
512 Mbytes
(2
29
bytes)
A(31:29) = 110
2
0 ksseg
0xC000 0000
through
0xDFFF FFFF
512 Mbytes
(2
29
bytes)
A(31:29) = 111
2
0 kseg3
0xE000 0000
through
0xFFFF FFFF
512 Mbytes
(2
29
bytes)
 Loading...
Loading...