Chapter 12
314 MIPS R4000 Microprocessor User's Manual
Null request requires no action by the processor; it provides a mechanism
for the external agent to either return control of the secondary cache to the
processor, or return the System interface to the master state without
affecting the processor.
Table 12-2 lists the external requests that each type of R4000 can receive
(an X indicates the request is supported on that model).
Table 12-2 Supported External Requests
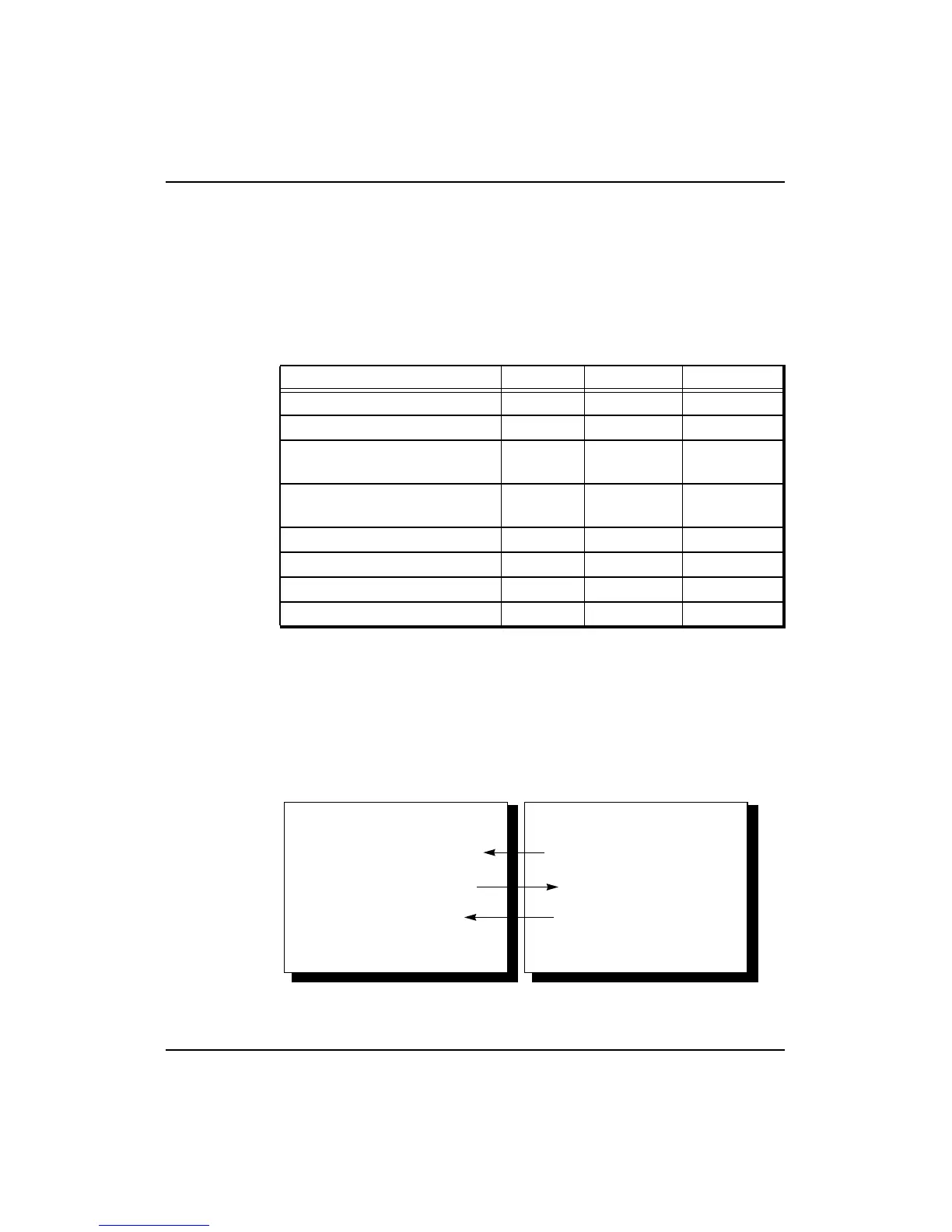
The processor controls the flow of external requests through the
arbitration signals ExtRqst* and Release*, as shown in Figure 12-12. The
external agent must acquire mastership of the System interface before it is
allowed to issue an external request; the external agent arbitrates for
mastership of the System interface by asserting ExtRqst* and then waiting
for the processor to assert Release* for one cycle.
Figure 12-12 External Request
Request Type R4000PC R4000SC R4000MC
External Read X X X
External Write X X X
External Null
(System interface)
XX X
External Null
(Secondary Cache)
XX
External Invalidate X
External Update X
External Snoop X
External Intervention X
R4000
External Agent
1. External system requests bus
mastership by asserting ExtRqst*
2. Processor grants mastership by
asserting Release*
3. External system issues an
External Request
4. Processor regains bus mastership
 Loading...
Loading...