-SCS Parameter Analyzer Reference Manual Appendix D: Using a Model 82 C-
4200A-901-01 Rev. C / February 2017 D-51
Threshold voltage
The threshold voltage, V
TH
, is the point on the C-V curve where the surface potential ψ
S
, equals twice
the bulk potential, φ
B
. This point on the curve corresponds to the onset of strong inversion. For an
enhancement mode MOSFET, V
TH
corresponds to the point where the device begins to conduct.
V
TH
is calculated as follows:
Where:
• V
TH
= threshold voltage (V)
• A = gate area (cm
2
)
• C
OX
= oxide capacitance (pF)
• 10
12
= units multiplier
• ε
S
= permittivity of substrate material
• q = electron charge (1.60219 × 10
-19
coulombs)
• N
BULK
= bulk doping (cm
-3
)
• φ
B
= bulk potential (V)
• V
FB
= flatband voltage (V)
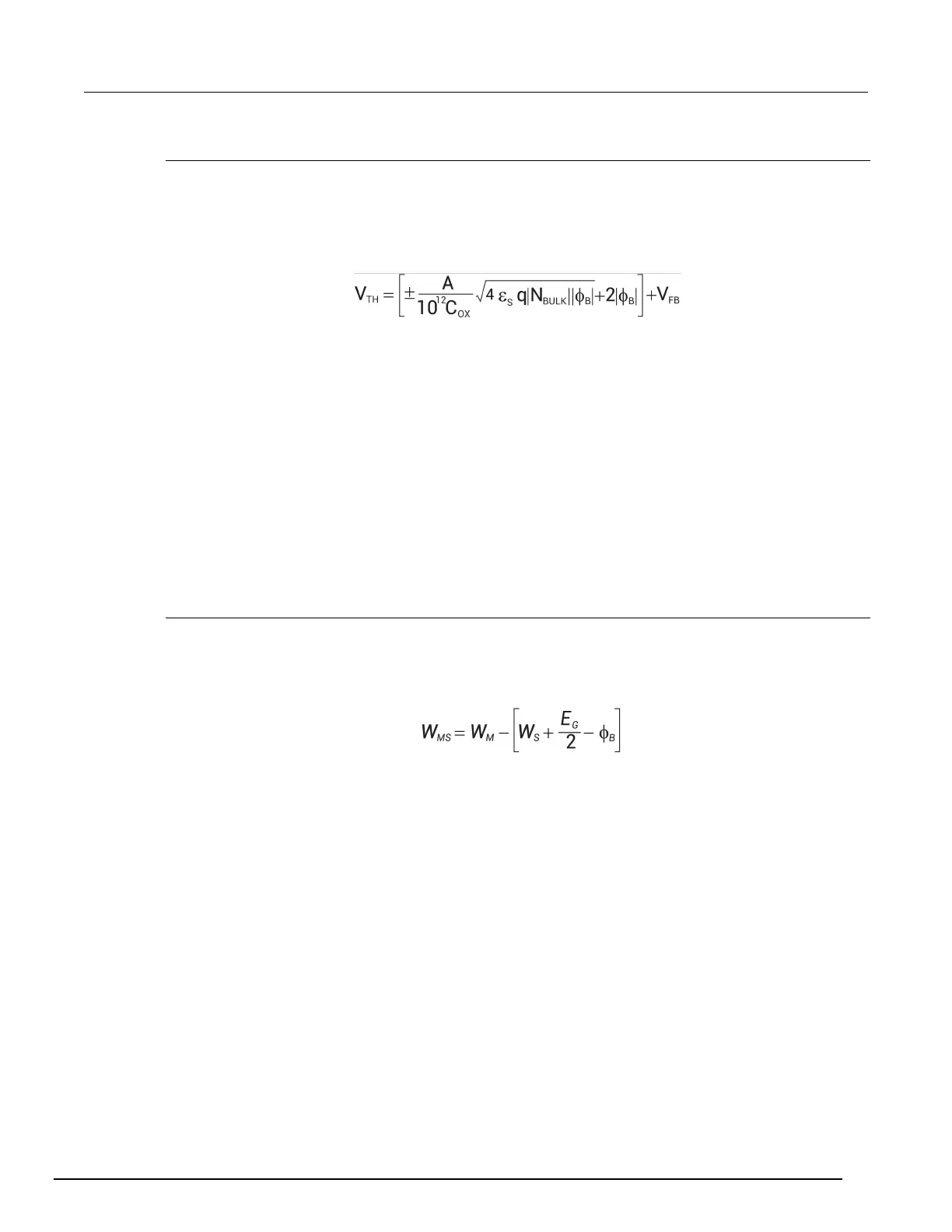
Metal semiconductor work function difference
The metal semiconductor work function difference, W
MS
, is commonly referred to as the work function.
It contributes to the shift in V
FB
from the ideal zero value, along with the effective oxide charge
(Nicollian and Brews 462-477; Sze 395402). The work function represents the difference in work
necessary to remove an electron from the gate and from the substrate, and it is derived as follows:
Where:
• W
M
= metal work function (V)
• W
S
= substrate material work function (electron affinity) (V)
• E
G
= substrate material bandgap (V)
• φ
B
= bulk potential (V)

 Loading...
Loading...