MIPS R4000 Microprocessor User's Manual B-7
FPU Instruction Set Details
B.3 Load and Store Instructions
In the R4000 implementation, the instruction immediately following a
load may use the contents of the register being loaded. In such cases, the
hardware interlocks, requiring additional real cycles, so scheduling load
delay slots is still desirable, although not required for functional code.
The behavior of the load store instructions is dependent on the width of
the FGRs.
• When the FR bit in the Status register equals zero, the Floating-
Point General registers (FGRs) are 32-bits wide.
• When the FR bit in the Status register equals one, the Floating-
Point General registers (FGRs) are 64-bits wide.
In the load and store operation descriptions, the functions listed in
Table B-3 are used to summarize the handling of virtual addresses and
physical memory.
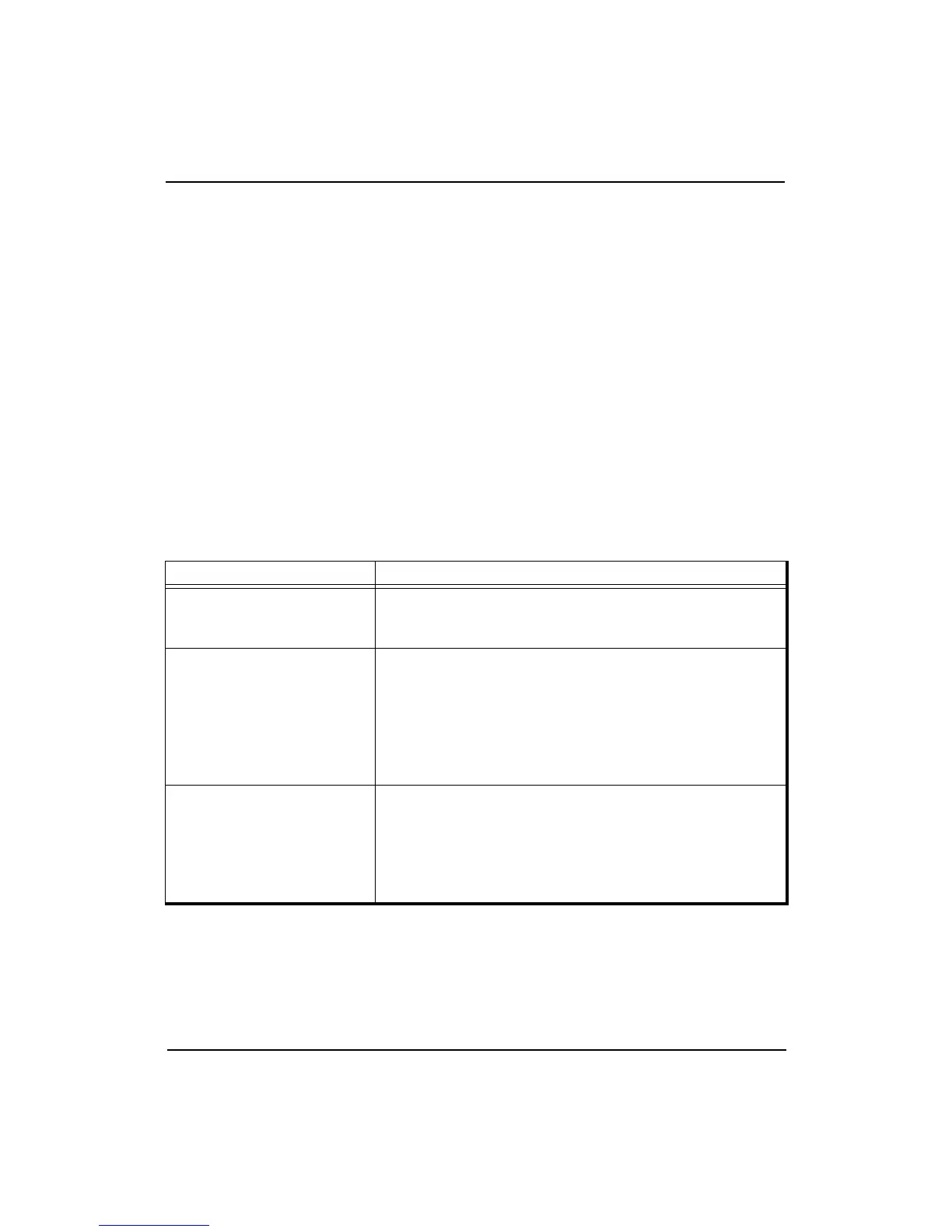
Table B-3 Load and Store Common Functions
Function Meaning
AddressTranslation
Uses the TLB to find the physical address given the virtual
address. The function fails and an exception is taken if the
required translation is not present in the TLB.
LoadMemory
Uses the cache and main memory to find the contents of
the word containing the specified physical address. The
low-order two bits of the address and the Access Type field
indicates which of each of the four bytes within the data
word need to be returned. If the cache is enabled for this
access, the entire word is returned and loaded into the
cache.
StoreMemory
Uses the cache, write buffer, and main memory to store the
word or part of word specified as data in the word
containing the specified physical address. The low-order
two bits of the address and the Access Type field indicates
which of each of the four bytes within the data word
should be stored.
 Loading...
Loading...