TYPICAL ADAPTIVE MEMORY FUEL CELLS
Open
Throttle
Open
Throttle
Open
Throttle
Open
Throttle
Open
Throttle
Open
Throttle Idle Decel
Vacuum 20 17 13 9 5 0
Above 1,984
rpm
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 Drive 15
Below 1,984
rpm
02 4 6 81012
Neutral
14
MAP volt = 0 1.4 2.0 2.6 3.3 3.9
Fuel Correction Diagnostics
There are two fuel correction diagnostic routines:
• Fuel System Rich
• Fuel System Lean
A DTC is set and the MIL is illuminated if the
PCM detects either of these conditions.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
OPERATION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is a digital
computer containing a microprocessor (Fig. 1). The
PCM receives input signals from various switches
and sensors referred to as Powertrain Control Mod-
ule Inputs. Based on these inputs, the PCM adjusts
various engine and vehicle operations through
devices referred to as Powertrain Control Module
Outputs.
NOTE: PCM Inputs:
• Air Conditioning Pressure Transducer
• ASD Relay
• Battery Voltage
• Brake Switch
• Camshaft Position Sensor
• Crankshaft Position Sensor
• Distance Sensor (from transmission control mod-
ule)
• EGR Position Feedback
• Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
• Heated Oxygen Sensors
• Ignition sense
• Intake Air Temperature Sensor
• Knock Sensor
• Leak Detection Pump Feedback
• Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
• Park/Neutral (from transmission control module)
• PCI Bus
• Power Steering Pressure Switch
• Proportional Purge Sense
• SCI Receive
• Speed Control
• Throttle Position Sensor
• Torque Management Input (From TCM)
• Transaxle Control Module (TCM)
• Transaxle Gear Engagement (From TCM)
• Vehicle Speed (from transmission control mod-
ule)
NOTE: PCM Outputs:
• Air Conditioning Clutch Relay
• Automatic Shut Down (ASD) and Fuel Pump
Relays
• Data Link Connector (PCI and SCI Transmit)
• Double Start Override
• EGR Solenoid
• Fuel Injectors
• Generator Field
• High Speed Fan Relay
• Idle Air Control Motor
• Ignition Coils
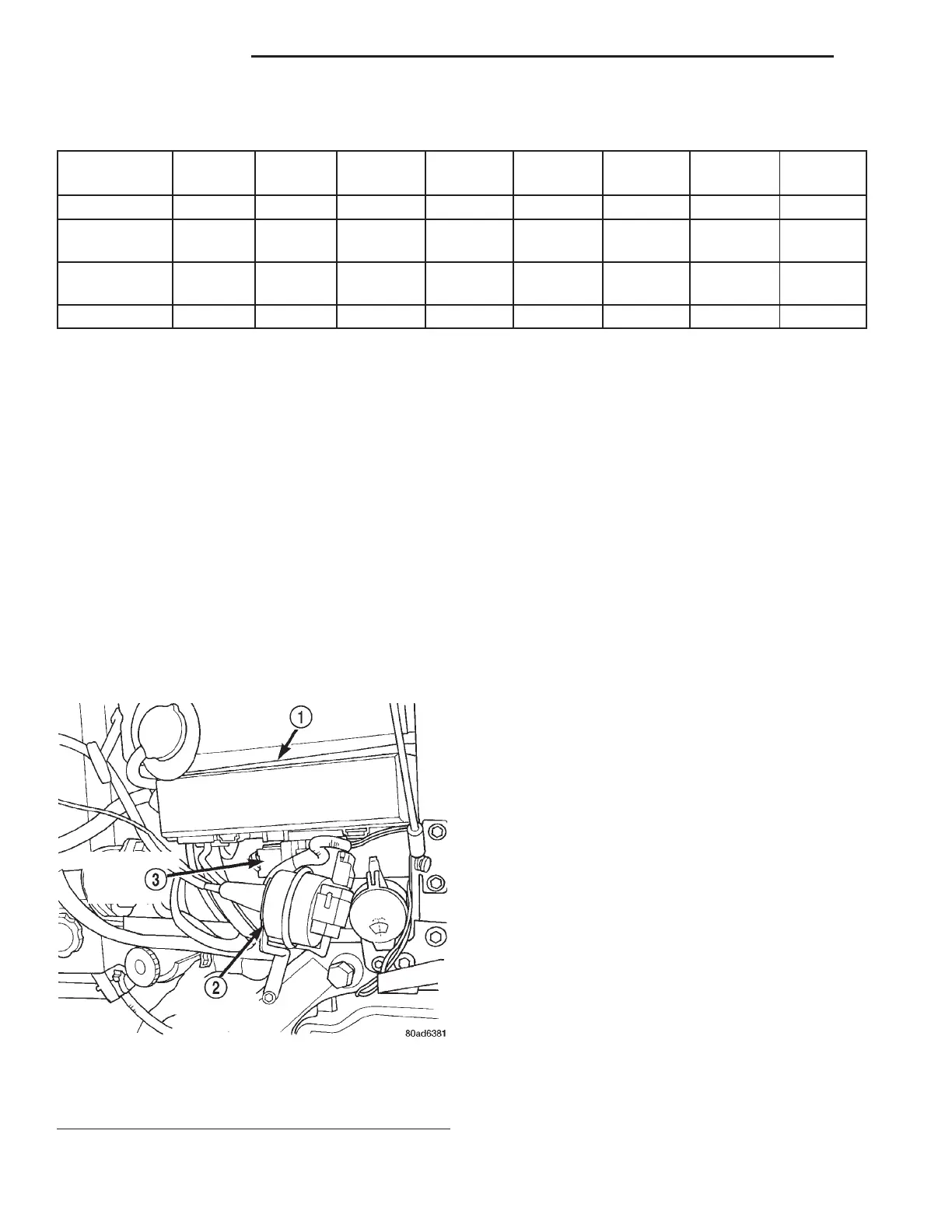
Fig. 1 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
1 – PDC
2 – SPEED CONTROL SERVO
3 – POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
14 - 26 FUEL SYSTEM LH
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
 Loading...
Loading...











