DocID13284 Rev 2 107/564
UM0404 Interrupt and trap functions
serviced. If its level is higher than the current CPU level. Changing the CPU level to a
specific value via software blocks all requests on the same or a lower level. An interrupt
source that is assigned to level 0 will be disabled and never be serviced.
• The ATOMIC and EXTend instructions automatically disable all interrupt requests for
the duration of the following 1...4 instructions. This is useful for semaphore handling
and does not require to re-enable the interrupt system after the inseparable instruction
sequence (see Section 27: System programming on page 545).
5.3.2 Interrupt class management
An interrupt class covers a set of interrupt sources with the same priority from the system’s
viewpoint. Interrupts of the same class must not interrupt each other. The ST10F276
supports this function with two features:
• Classes with up to four members can be established by using the same interrupt
priority (ILVL) and assigning a dedicated group level (GLVL) to each member. This
functionality is built-in and handled automatically by the interrupt controller.
• Classes with more than four members can be established by using a number of
adjacent interrupt priorities (ILVL) and the respective group levels (4 per ILVL). Each
interrupt service routine within this class sets the CPU level to the highest interrupt
priority within the class. All requests from the same or any lower level are blocked now,
and no request of this class will be accepted.
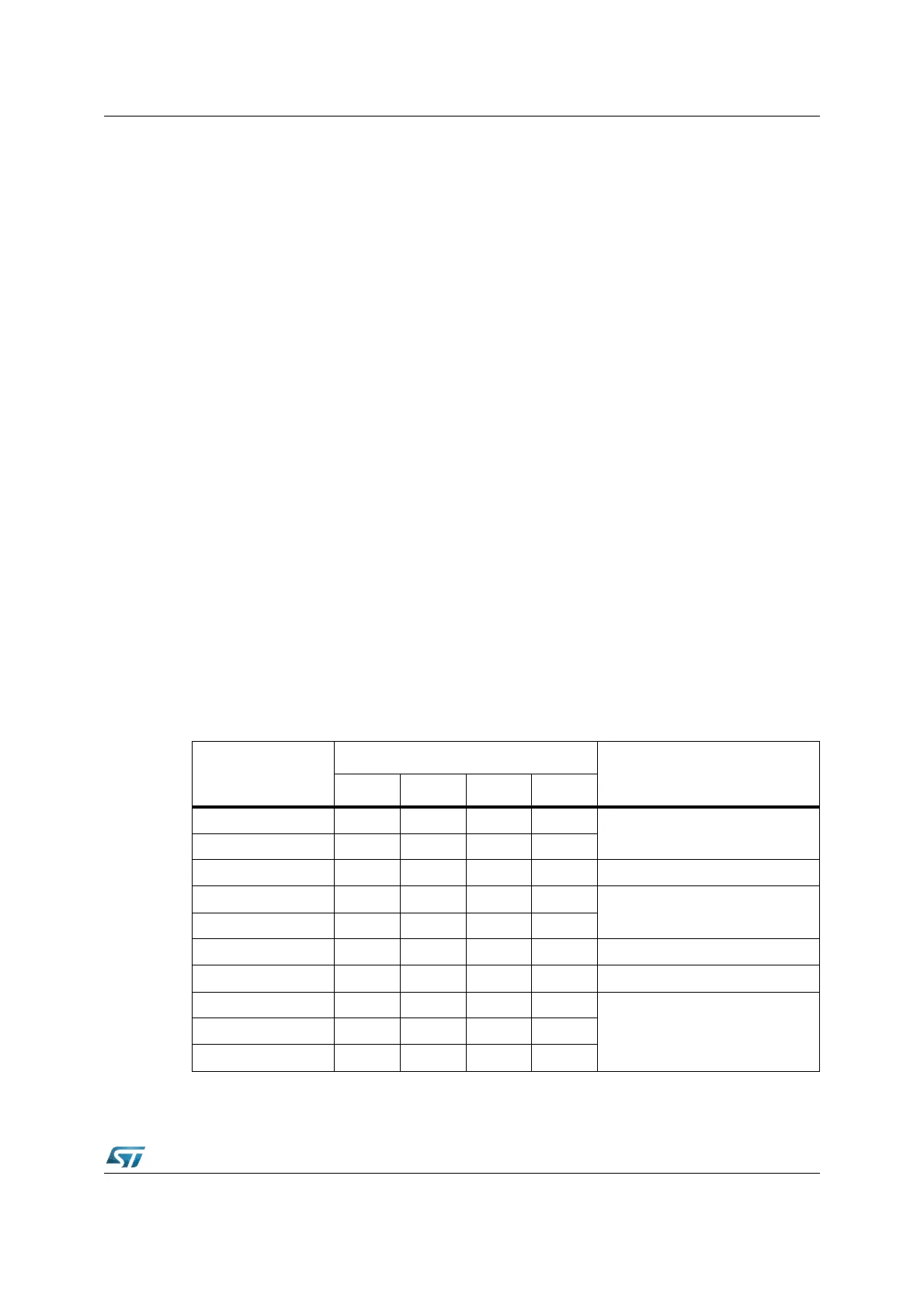
The example below establishes three interrupt classes which cover two or three interrupt
priorities, depending on the number of members in a class.
A level 6 interrupt disables all other sources in class 2 by changing the current CPU level to
8, which is the highest priority (ILVL) in class 2. Class 1 requests or PEC requests are still
serviced in this case.
The 24 interrupt sources (excluding PEC requests) are so assigned to 3 classes of priority
rather than to 7 different levels, as the hardware support would do.
Table 18. Example of software controlled interrupt classes
ILVL (priority)
GLVL
Interpretation
3210
15
PEC service on up to 8 channels
14
13
12 XXXX
Interrupt Class 1: 8 sources on 2
levels
11 XXXX
10
9
8 XXXX
Interrupt Class 2: 10 sources on 3
levels
7 XXXX
6XX

 Loading...
Loading...