Memory organization UM0404
46/564 DocID13284 Rev 2
The upper 256 bytes of the IRAM (00’FD00h through 00’FDFFh) and the GPRs of the
current bank are provided for single bit storage, and therefore, they are bit addressable (see
Figure 1 on page 23).
2.3.1 System stack
The system stack may be defined within the IRAM. The size of the system stack is
controlled by bit-field STKSZ in the SYSCON register (see Table 5).
For all system stack operations the IRAM is accessed via the Stack Pointer (SP) register.
The stack grows downward from higher towards lower IRAM address locations.
Only word accesses are supported by the system stack. A stack overflow (STKOV) and a
stack underflow (STKUN) register are provided to control the lower and upper limits of the
selected stack area.
These two stack boundary registers can be used, not only for protection against data
destruction, but also allow to implement a circular stack with hardware supported system
stack flushing and filling (except for the 2 Kbyte stack option).
The technique of implementing this circular stack is described in Section 27.1: Stack
operations on page 547.
2.3.2 General purpose registers
The general purpose registers (GPRs) use a block of 16 consecutive words within the
IRAM. The Context Pointer (CP) register determines the base address of the currently
active register bank. This register bank may consist of up to 16 word GPRs (R0, R1, ... ,
R15) and/or of up to 16 byte GPRs (RL0, RH0, ... , RL7, RH7) and 8 word registers R8-R15.
The 16 byte GPRs are mapped onto the first eight word GPRs (see Table 6).
In contrast to the system stack, a register bank grows from lower towards higher address
locations and occupies a maximum space of 32 bytes.
The GPRs are accessed via short 2-, 4- or 8-bit addressing modes using the context pointer
(CP) register as base address (independent of the current DPP register contents).
Additionally, each bit in the currently active register bank can be accessed individually.
The ST10F276 supports fast register bank (context) switching. Multiple register banks can
physically exist within the IRAM at the same time. Only the register bank selected by the
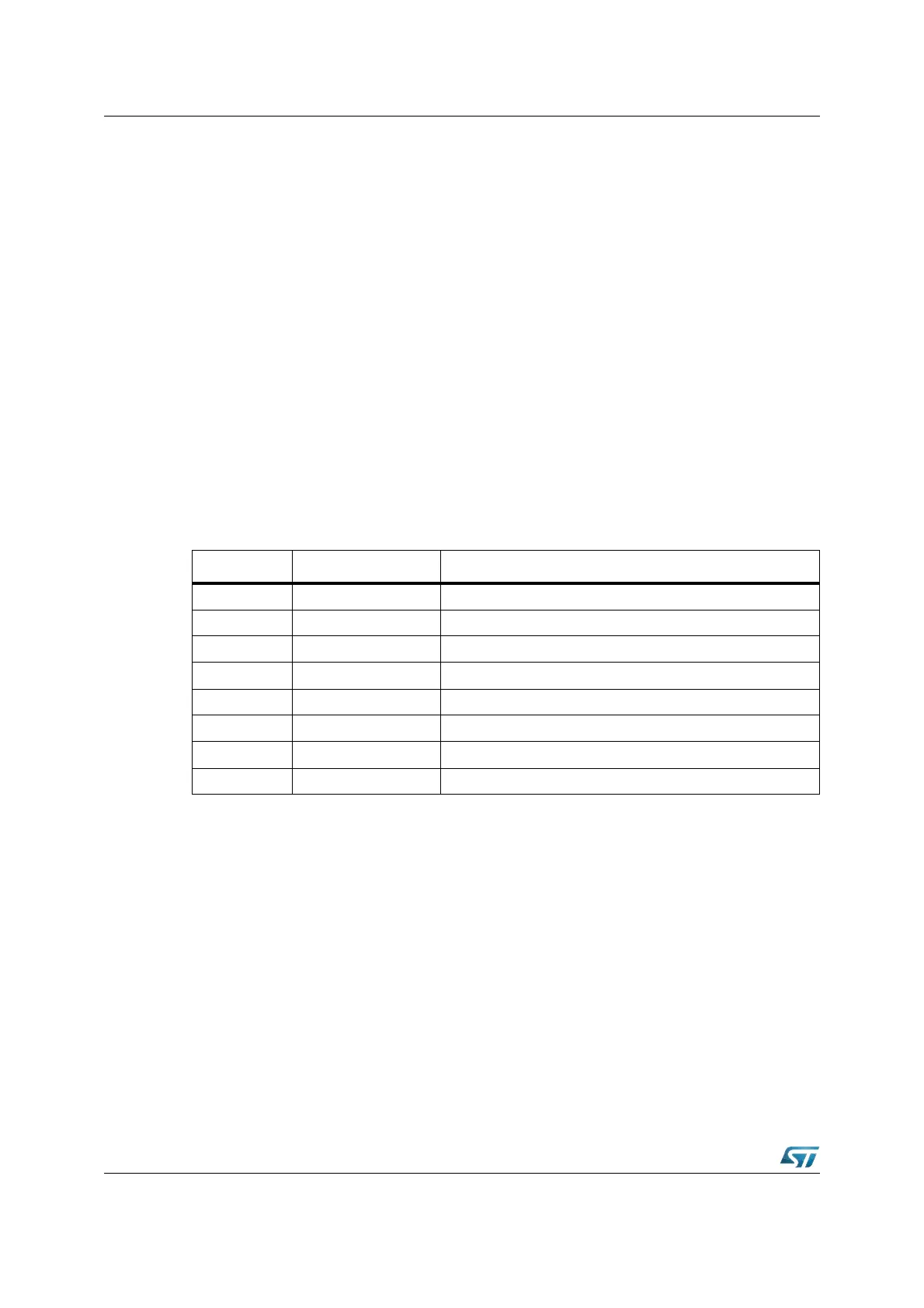
Table 5. Stack size
(STKSZ) Stack size (words) IRAM addresses (words)
0 0 0b 256 00’FBFEh...00’FA00h (Default after Reset)
0 0 1b 128 00’FBFEh...00’FB00h
0 1 0b 64 00’FBFEh...00’FB80h
0 1 1b 32 00’FBFEh...00’FBC0h
1 0 0b 512 00’FBFEh...00’F800h
1 0 1b --- Reserved. Do not use this combination.
1 1 0b --- Reserved. Do not use this combination.
1 1 1b 1024 00’FDFEh...00’F600h (Note: No circular stack)

 Loading...
Loading...