Beta Draft Confidential
11-21/19/05 ATM Services Configuration Guide for CBX 3500, CBX 500, GX 550, and B-STDX 9000
Configuring Management Paths
using this method to transfer large amounts of information can have a negative impact
on the local switch. This is because the control processor (CP), switch processor (SP),
or node processor (NP) at the local switch would have to act as the gateway interface
between the host and the remote switches.
You can also configure Subnet Routing for Management VPI/VCI to manage multiple
devices over one VPI/VCI connection. You configure an Autonomous System
External (ASE) mask to connect to an external device, or an IP network of external
devices to enable management VCs to traverse Virtual Network Navigator (VNN)
areas.
Management SPVC (MSPVC) — (CBX and GX only) You can use this type of
connection to connect the switch management port to an SVC terminating address
located on an adjacent switch. This management connection is used as the NMS path,
which enables the NMS to manage the switch.
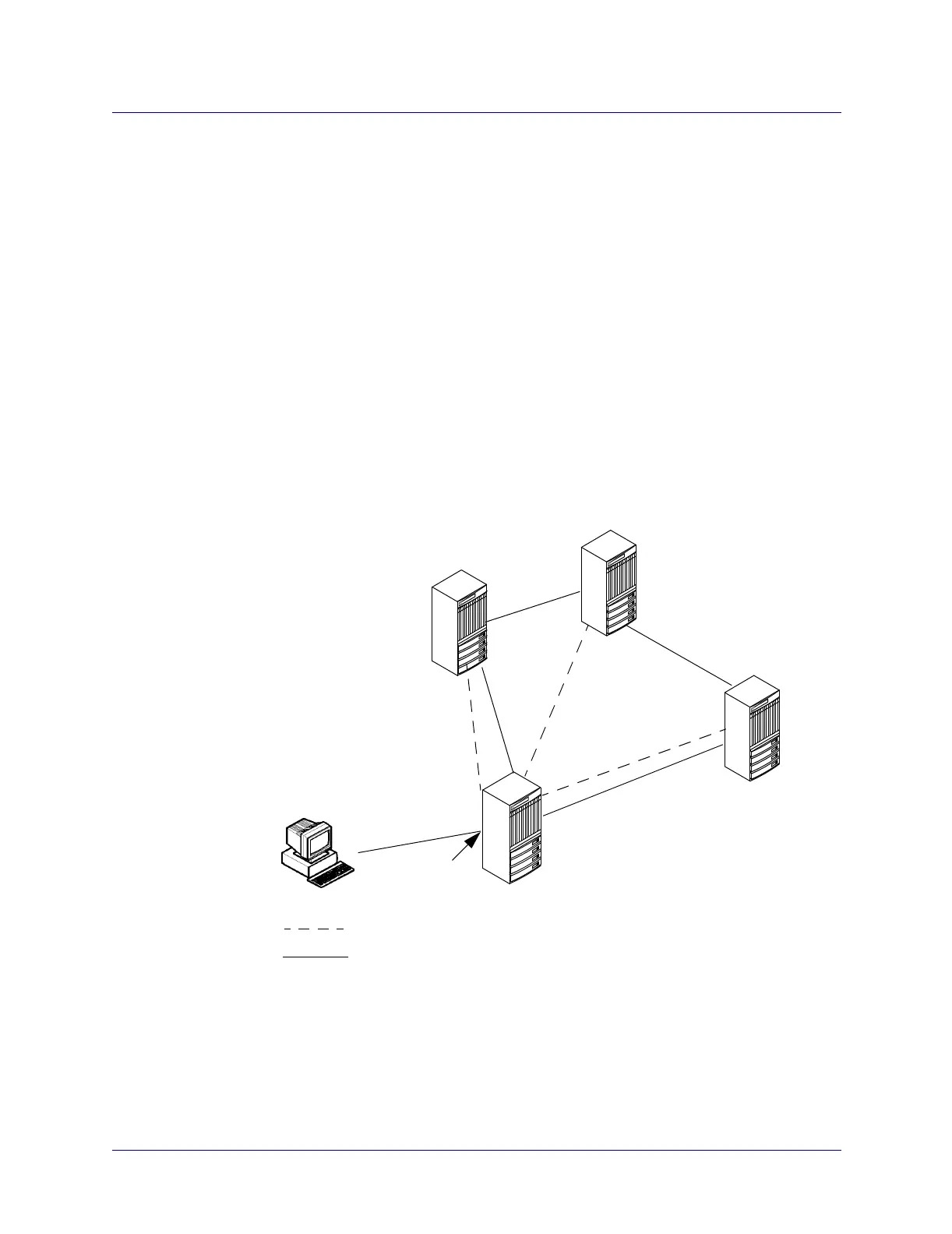
MSPVCs are particularly useful for providing the management connectivity needed in
a PNNI environment as shown in Figure 11-1. See “Using MSPVCs in a PNNI
Environment” on page 11-11 for more information.
Figure 11-1. Connecting a PNNI Network
MPVC
Gateway Switch
NMS
MSPVC connection
PNNI Trunk
 Loading...
Loading...