Beta Draft Confidential
About ATM Logical Ports
ATM NNI
ATM Services Configuration Guide for CBX 3500, CBX 500, GX 550, and B-STDX 9000 1/19/052-11
ATM NNI
The CBX 3500, CBX 500, and GX 550 ATM NNI logical port type enables you to
connect ATM-based public networks belonging to two different carriers. This logical
port type implements the B-ICI protocol, which facilitates the multiplexing of services
for inter-carrier (Regional Bell Operating Company [RBOC] and inter-exchange
carrier [IXC]) delivery. You can use an ATM NNI logical port as a feeder port for
Lucent OPTimum trunks and virtual UNIs.
ATM NNI logical ports also support the PNNI routing protocol. To configure PNNI
routing in your Lucent network, see Chapter 21. For a detailed explanation of PNNI
routing, see the ATM Forum Technical Committee Private Network-Network Interface
Specification Version 1.0 (af-pnni-0055.000), available from the ATM Forum’s web
site:
http://www.atmforum.com.
Virtual UNI/NNI
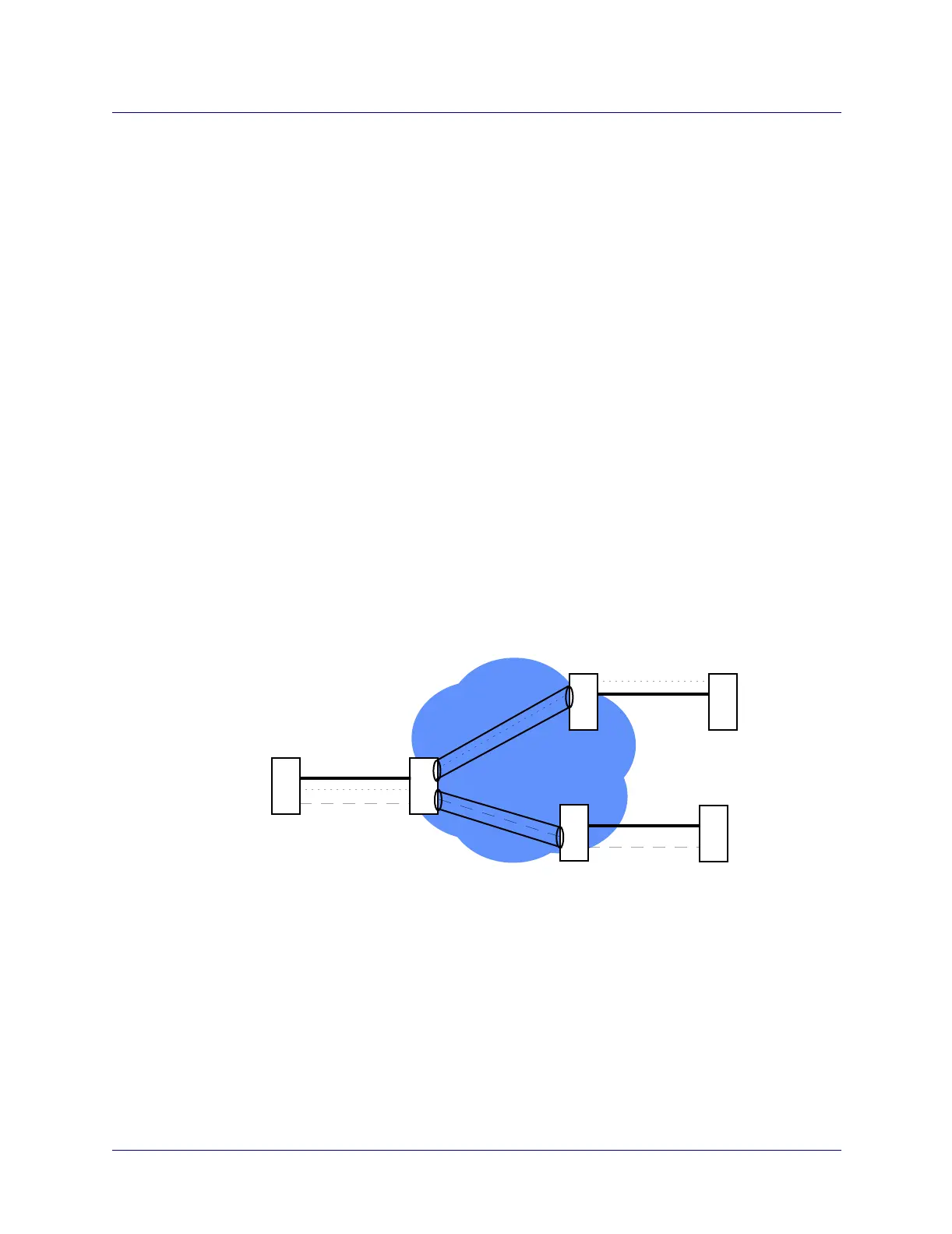
A virtual UNI/NNI forms an extension of the standard “direct” UNI DCE/DTE or NNI
logical port types. In an ATM network, you can use virtual UNI/NNI logical ports to
enable VP tunneling or to connect to a VP multiplexer. VP tunneling allows you to
connect two switches (using signaling) via a virtual path through the ATM network
(network-to-network connection class). See the example in Figure 2-1.
Figure 2-1. Two Virtual UNIs Through Central Network
VP multiplexing enables you to connect a CBX 3500, CBX 500, or GX 550 switch to
a VP multiplexer using a direct UNI (or NNI) logical port on which you have
configured several “virtual” UNI (or NNI) ports. The VPI address range you define for
each virtual UNI/NNI port corresponds to a port on the VP multiplexer. This method
does not use VPCs and the configured logical port bandwidth can be used by any PVC
on any VPI (network-to-endsystem connection class). See the example in Figure 2-2.
ATM
CLOUD
A
B
DTE
DCE
DTE
DCE
VP X
VP Y
C
 Loading...
Loading...