xl1/19/05 ATM Services Configuration Guide for CBX 3500, CBX 500, GX 550, and B-STDX 9000
About This Guide
Beta Draft Confidential
How to Use This Guide
This guide contains the following information:
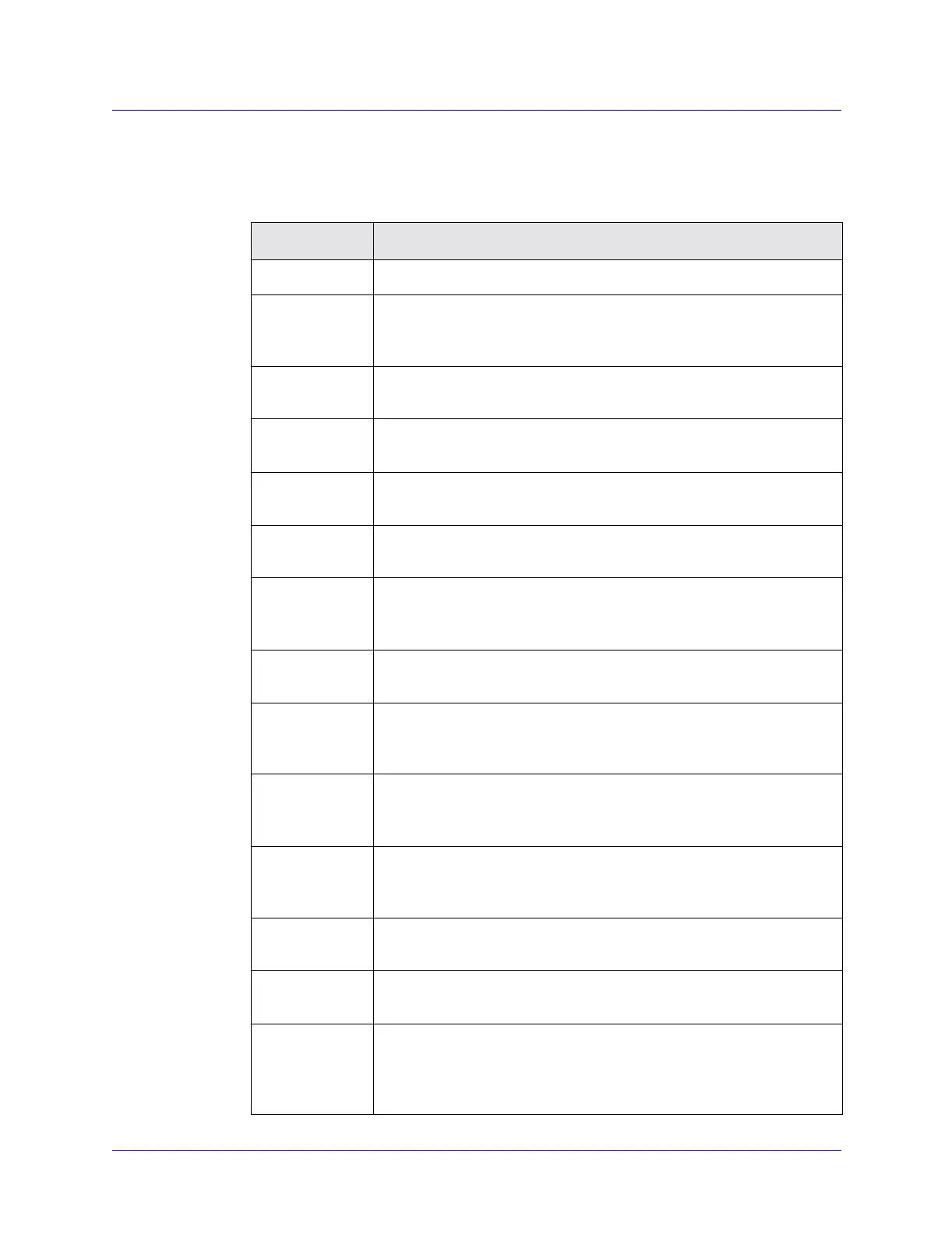
Read To Learn About
Chapter 1 How the information in this guide is organized.
Chapter 2 Concepts you need to understand before you configure ATM logical
ports. These concepts include: virtual paths and channels, signaling, and
Interim Link Management Interface (ILMI).
Chapter 3 Configuring ATM logical ports on a CBX 3500, CBX 500, or GX 550
Multiservice switch.
Chapter 4 Configuring ATM logical ports on Frame Relay modules in a
B-STDX 9000 or CBX 500 switch.
Chapter 5 The operation of the ATM Flow Control Processor (FCP) for supported
CBX 500 input/output modules (IOMs).
Chapter 6 Working with the ATM FCP and answers to frequently asked questions
(FAQ).
Chapter 7 Configuring ATM trunks, Automatic Protection Switching (APS) trunk
backup, and external trunks. This chapter also describes adding external
objects to the Navis EMS-CBGX map.
Chapter 8 Configuring ATM over MPLS trunks via Juniper T-series routers and
JUNOS.
Chapter 9 Configuring end-to-end solutions over an IP/MPLS core network. This
chapter describes the use of Layer 2 tunnels and Pseudo Wire
Edge-to-Edge Encapsulation (PWE3).
Chapter 10 Configuring point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, and redirect PVCs. This
chapter also describes how to configure Frame Relay-to-ATM
interworking circuits.
Chapter 11 Configuring NMS paths using a management PVC, management virtual
path identifier/virtual channel identifier (VPI/VCI), or management soft
permanent virtual circuit (MSPVC) connection.
Chapter 12 Configuring traffic descriptors to manage Quality of Service (QoS)
throughout your ATM network.
Chapter 13 Configuring your ATM services to provide Layer2 Virtual Private
Networks (VPNs).
Chapter 14 Configuring fault tolerant (resilient User-to-Network Interface (UNI)
and Network-to-Network (NNI)) PVC services to provide backup
services should a logical port endpoint fail. This chapter also describes
APS Resilient UNI.
 Loading...
Loading...