220 Rockwell Automation Publication 2198-UM004D-EN-P - December 2022
Chapter 9 Tuning
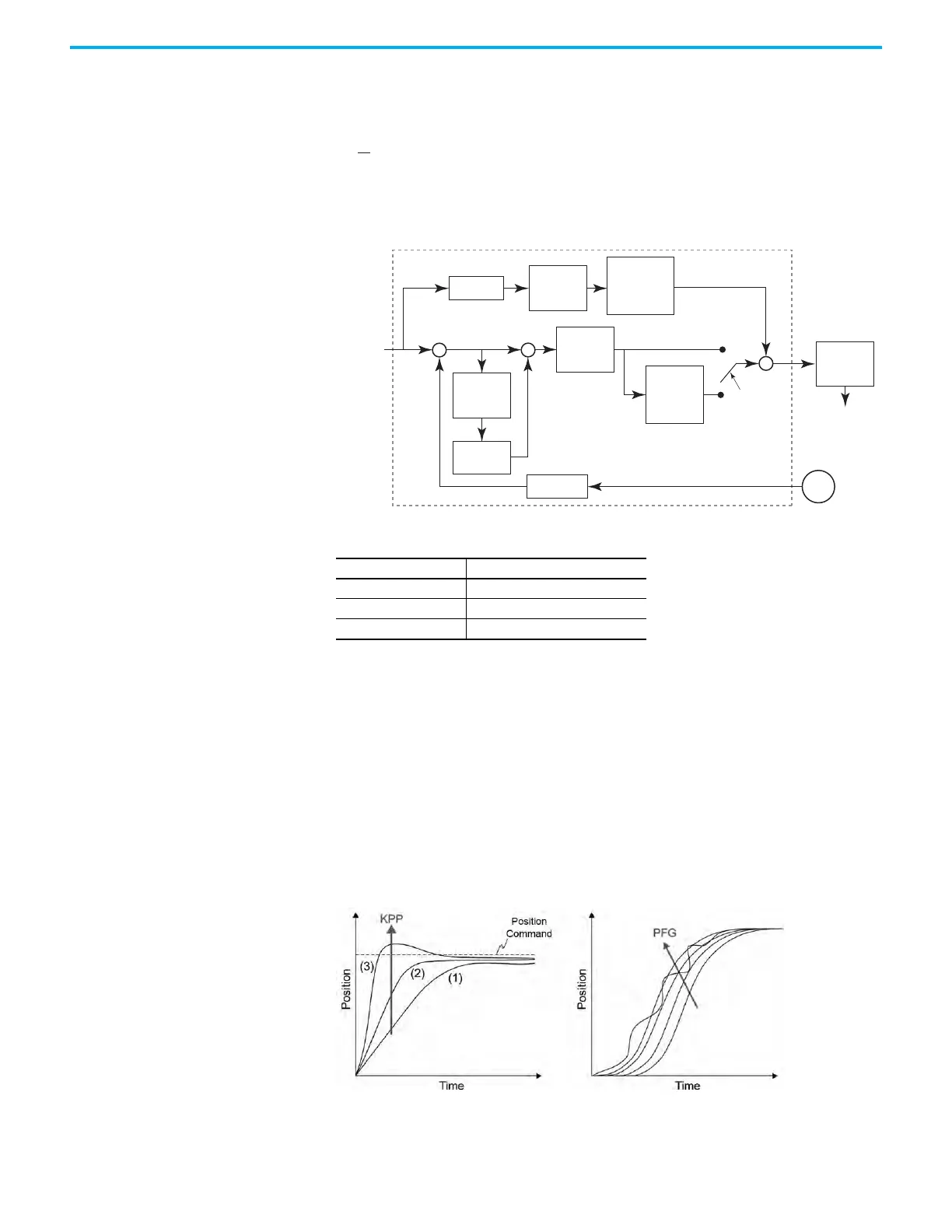
Gain Adjustment of the Position Loop
The position loop gain should not be larger than the velocity loop gain.
There are three types of gain:
1. Proportional gain: a larger gain increases the response of its loop.
2. Integral Gain: a larger gain increases the steady-state performance.
3. Feed forward gain: reduces the deviation of phase delay.
By using inside-out tuning, we tune the inner loop (velocity) first. The
VelocityProportional Gain ID189 (P2.004) and VelocityIntegralGain
ID191 (P2.006) are in the Velocity (Speed) loop and once they are set, you can
manually change the outer loop (position) gains. The
PositionProportionalGain ID185 (P2.000), PositionIntegralGain ID235
(P2.053), and VelocityFeedforwardGain ID187 (P2.002).
The actual position curve changes from (1…3) with the increase in the KPP
value.
Table 83 - Relevant Parameters
Parameter Name
ID185 (P2.000) PositionProportionalGain (KPP)
ID235 (P2.053) PositionIntegralGain (KPI)
ID187 (P2.002) VelocityFeedForwardGain (KVFF)
fv = response bandwidth of speed loop (Hz)
fp = response bandwidth of position loop (Hz)
Example: If the desired position bandwidth is 20 Hz, then
adjust the KPP (ID185, P2.000) to 125 (2 × π × 20 Hz = 125).
fv
Position Feed
Forward Gain
ID187 (P2.002)
Position
Control Gain
ID185 (P2.000)
Max.
Speed Limit
ID160 (P1.055)
Speed Command
Position Control Unit
Command
Position
Loop Izone
ID654 (P2.123)
Integrator
ID235 (P2.053)
Differentiator
Position Counter Encoder
Smooth Constant
of Position Feed
Forward Gain
ID188 (P2.003)
Changing Rate
of Position
Control Gain
ID186 (P2.001)
Gain switching
condition and
method selection
ID212 (P2.027)
++ +
+
+
+
–

 Loading...
Loading...











