Rockwell Automation Publication 2198-UM004D-EN-P - December 2022 327
Chapter 11 Motion Control in PR Mode
These settings are the functions of each bit when a position command is
applied.
Settings:
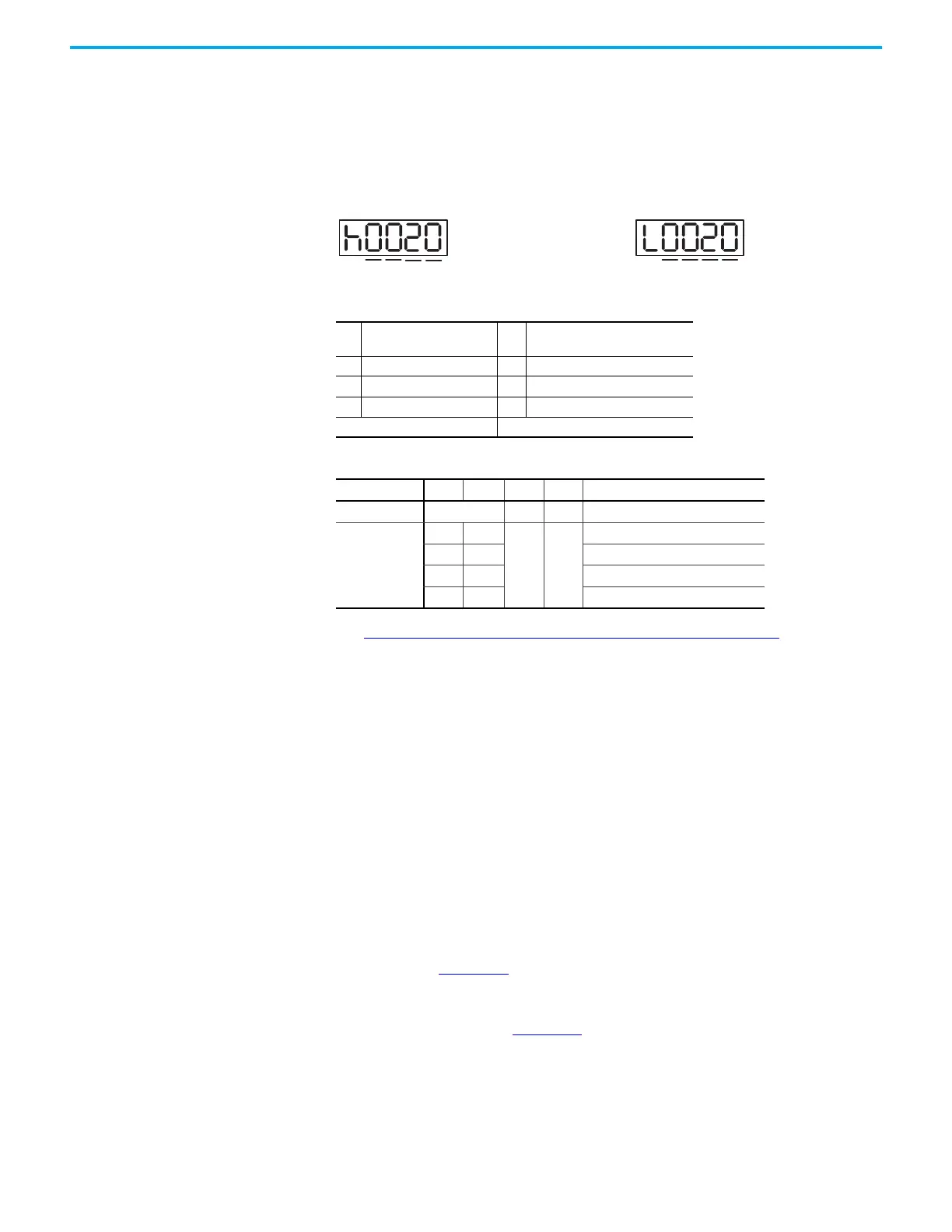
Format of this parameter: (High word h) DCBA: (Low word L) UZYX
• Y OPT: option
See Use the PR Mode Editor in KNX5100C Software
on page 342, where you
can configure the PR Mode for one of two PR Mode position command types:
• Mode 2 = Point-to-Point Command
• Mode 3 = Point-to-Point Command (Proceed to next command when
complete)
Position Command Types
There are four types of position commands for the PR Mode. These same
position commands can be used for IO Mode, although their names are
different. The raC_xxx_K5100_MAM Set_MoveType is shown in brackets. You
can choose the position command according to the application requirements.
The functions of each type are described in the examples below. The condition
in these examples is that a position command is still being executed and
another type of command is inserted. To see how the position commands are
combined, see Figure 135
.
• Absolute position command (ABS, raC_xxx_K5100_MAM Type 0 =
Absolute): when executed, the target position value equals the absolute
command value. In Figure 135
, an ABS command with the value of 60000
PUU is inserted in the previous PR command with setting target position
of 60000 PUU on the coordinate axis.
A SPD, Target speed index X
TYPE, Command type - Set to 2 or
3
B DLY, Delay time index Y OPT, Option
C Reserved Z ACC, Acceleration time index
D Reserved U DEC, Deceleration time index
Data Content Target position [PUU]
BIT 3 2 1 0 Description
Command type CMD OVLP INS -
Data Content
00
--
ABS (absolute positioning)
0 1 REL (relative positioning)
1 0 INC (incremental positioning)
1 1 CAP (high-speed position capturing)
High word Low word
CD
B A
YZU
X

 Loading...
Loading...











