222 Rockwell Automation Publication 2198-UM004D-EN-P - December 2022
Chapter 9 Tuning
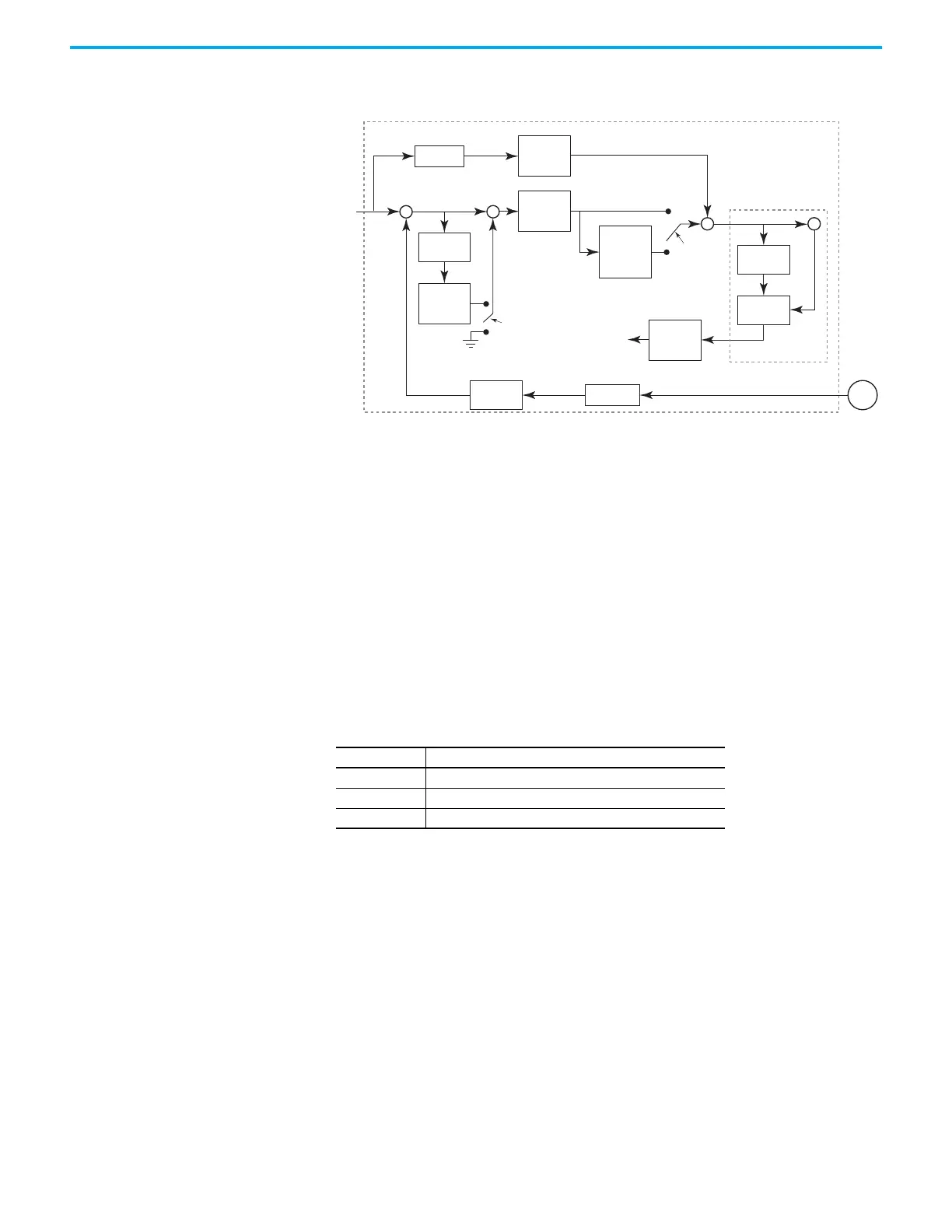
Gain Adjustment of Velocity Loop
Manual Mode
When the Gain Adjustment Mode parameter ID217 (P2.032) is set to 0, Manual
Mode tuning is used and you must set parameters VelocityProportionalGain
ID189 (P2.004), VelocityIntegralGain ID191 (P2.006), and
AccelFeedforwardGain ID192 (P2.007). More detail about adjusting the gains is
as follows:
• Velocity loop gain: The higher the gain, the bigger bandwidth of velocity
loop response is.
• Integral gain: Increasing this gain will increase the low frequency
rigidity and reduce the steady-state error. However, phase margin is
smaller. If this gain is set too high, the system stability will be reduced.
• Feed forward gain: Diminish the deviation of phase delay.
Theoretically, a stepping response can be used to explain proportional gain
(KVP), integral gain (KVI), and feed forward gain (KVF). Speed over time
diagrams are shown below to illustrate the basic principle.
Feed
Forward Gain
ID192 (P2.007)
Speed
Control Gain
ID189 (P2.004)
Torque Constant
Reciprocal
1/KT
Speed Control Unit
Speed Integral
Compensation
ID191 (P2.006)
Integrator
ID235 (P2.053)
Load Initiator
ID144 (P1.037)
System Inertia J
(1 + ID144/P1.037)*JM
Motor Inertia
JM
Low-pass Filter
ID232 (P2.049)
Differentiator
Speed Estimator
Current Command
Torque Command
Encoder
Changing Rate
of Speed
Control Gain
ID190 (P2.005)
Gain switching
condition and
method selection
ID212 (P2.027)
++ +
+
+
+
+
+
–
Gain switching
condition and
method selection
ID212 (P2.027)
Table 84 - Relevant Parameters
Parameter Name
ID189 (P2.004) VelocityProportionalGain (KVP)
ID190 (P2.006) VelocityIntegralGain (KVI)
ID191 (P2.007) AccelFeedForwardGain (KAFF)

 Loading...
Loading...











