Rockwell Automation Publication 2198-UM004D-EN-P - December 2022 367
Chapter 11 Motion Control in PR Mode
If one of the PR types uses a delay, the PR queue schedules all subsequent
commands on the basis of the PR type that uses a DLY (Delay Time).
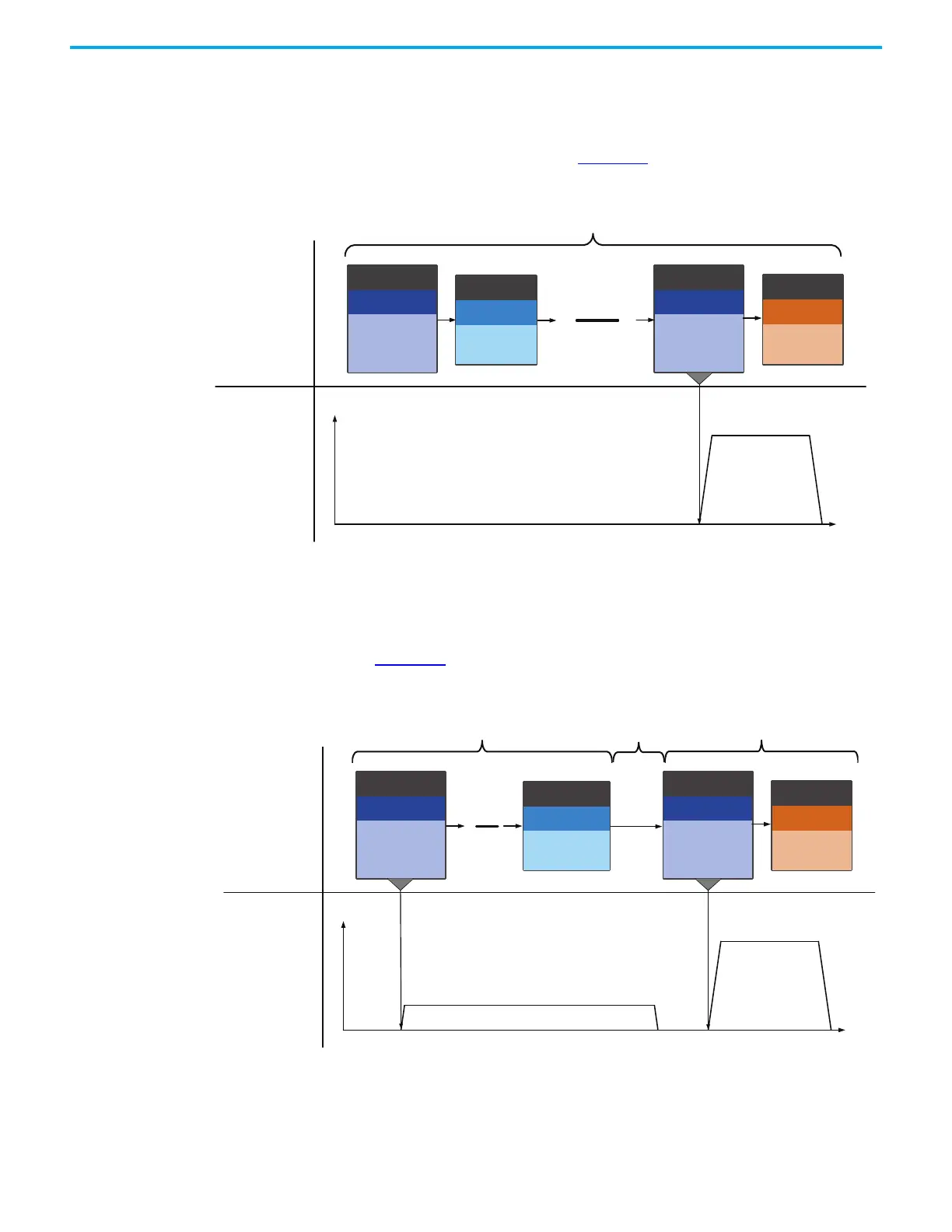
• Example 1 shows multiple commands that are received in the same 1 ms
Command period. You can see that the last PR (PR#07) is the command
that is executed, as shown in Figure 175
.
Figure 175 - Internal Interruption - Multiple Commands without Delay
• Example 2 shows multiple commands that are received in the same 1 ms
update with DLY (Delay Time) used. In this case, the first motion
commanded PR begins executing while the DLY is occurring; the DLY is
grouped with the first 1 ms cycle. Once DLY expires, the next PR (PR#07)
begins executing, which occurs in the second 1 ms cycle, as shown in
Figure 176
.
Figure 176 - Internal Interruption - Multiple Commands with Delay
PR#1 (I)
Position
DLY=[0] 0 ms
1000 PUU
ABS
200 rpm
PR#7 (I)
Position
DLY=[0] 0 ms
10000 PUU
ABS
500 rpm
PR
executor
Motion
command
generator
Time
Speed
PR#2 (I)
Write
DLY=[0] 0 ms
P5.045=100
PR#8 (I)
Jump
DLY=[0] 0 ms
PR#10
Approx. 20 PR Commands
(1 ms Cmd cycle)
Multiple Commands without Delay
Motion
command
generator
Multiple Command without Delay
PR
executor
PR#1 (I)
Position
DLY=[0] 0 ms
1000 PUU
ABS
200 rpm
PR#7 (I)
Position
DLY=[0] 0 ms
10000 PUU
ABS
500 rpm
PR
executor
Motion
command
generator
Time
Speed
PR#6 (I)
Write
DLY=[1] 100 ms
P5.045=100
PR#8 (I)
Jump
DLY=[0] 0 ms
PR#10
Approx. 20 PR Commands
DLY 100 ms
(1 ms Cmd cycle)(1 ms Cmd cycle)
Multiple Commands with Delay
Motion
command
generator
Multiple Command without Delay
PR
executor

 Loading...
Loading...











