10-5
Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual, R8.5
78-18343-02
Chapter 10 Network Reference
10.2.1 Ring Networks
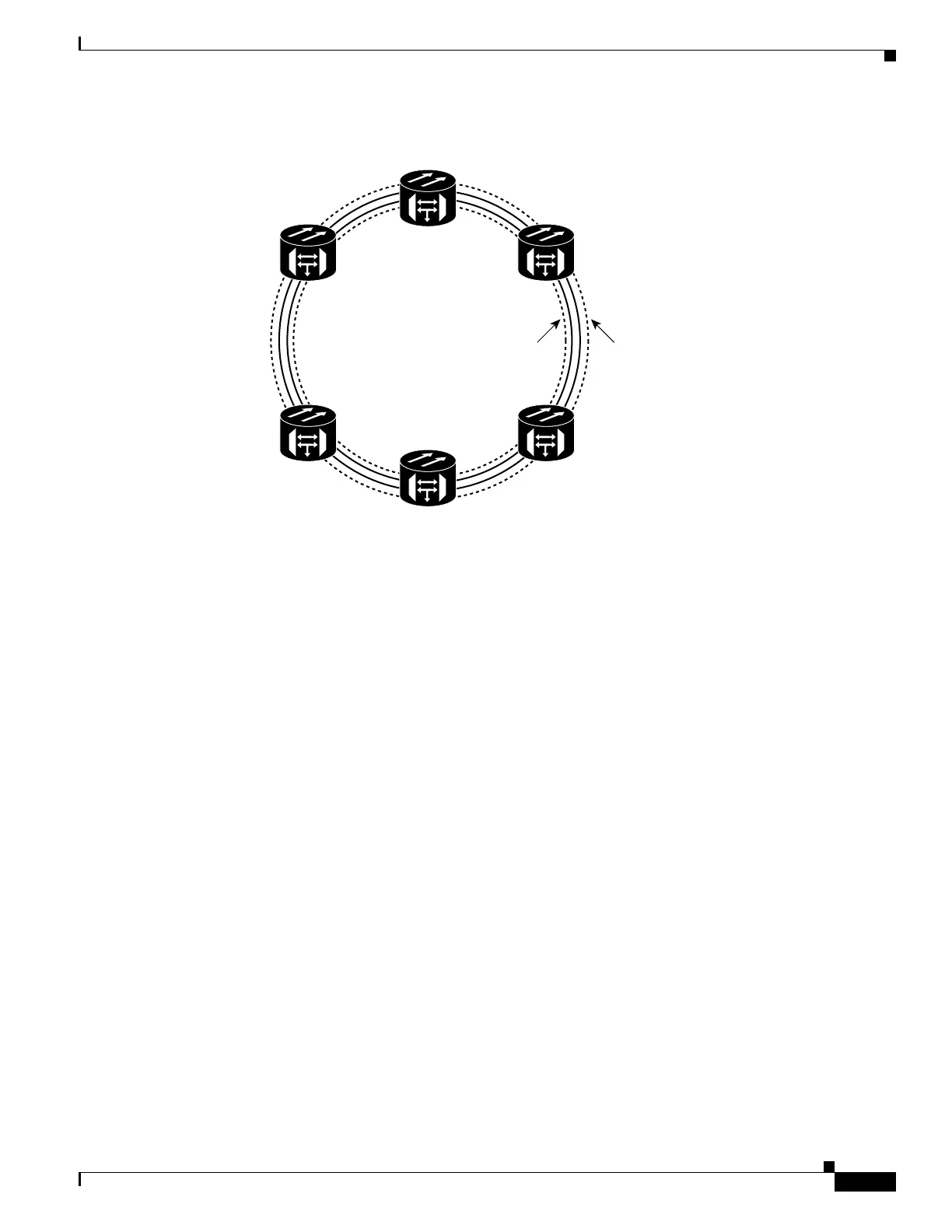
Figure 10-3 Any-to-Any Traffic Topology
10.2.1.4 Meshed Traffic Topology
The meshed traffic topology (Figure 10-4) does not use hubbed nodes; only amplified and passive
OADM nodes are present. Protected traffic can be provisioned between any two nodes; however, the
selected channel cannot be reused in the ring. Unprotected multihop traffic can be provisioned in the
ring. A meshed ring must be designed to prevent amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) lasing. This is
done by configuring a particular node as an anti-ASE node. An anti-ASE node can be created in two
ways:
• Equip an OADM node with 32MUX-O cards and 32DMX-O cards. This solution is adopted when
the total number of wavelengths deployed in the ring is higher than ten. OADM nodes equipped with
32MUX-O cards and 32DMX-O cards are called full OADM nodes.
• When the total number of wavelengths deployed in the ring is lower than ten, the anti-ASE node is
configured by using an OADM node where all the channels that are not terminated in the node are
configured as “optical pass-through.” In other words, no channels in the anti-ASE node can travel
through the express path of the OADM node.
For more information about OADM nodes, see the “9.1.3 OADM Node” section on page 9-8. For more
information about anti-ASE nodes, see the “9.1.5 Anti-ASE Node” section on page 9-15.
ROADM
ROADM
ROADM
115730
ROADM ROADM
ROADM
OSC
OSC

 Loading...
Loading...